|
Central Research Institute Of Electric Power Industry
The Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI; 電力中央研究所) is a Japanese non-profit foundation that conducts research and development of technologies in a variety of scientific and technical fields related to the electric power industry. Also, CRIEPI researches many aspects of social matters through subordinate laboratories. CRIEPI not only engages in research and education in Japan, but also provides education, training and technology transfer worldwide. It is similar to the U.S. EPRI, though its energy research extends into areas that could be considered to be in the domain of the USDOE's national laboratories in the United States, such as research and design of fission reactor concepts. In 2004, CRIEPI developed a U.S. presence due to the proposed Galena Nuclear Power Plant in Galena, Alaska, that is proposed to use an advanced reactor design – the Toshiba 4S – developed by Toshiba Corporation and CRIEPI. References External li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation (nonprofit Organization)
A foundation (also a charitable foundation) is a category of nonprofit organization or charitable trust that typically provides funding and support for other charitable organizations through grants, but may also engage directly in charitable activities. Foundations include public charitable foundations, such as community foundations, and private foundations, which are typically endowed by an individual or family. However, the term "foundation" may also be used by such organizations that are not involved in public grantmaking. Description Legal entities existing under the status of "foundations" have a wide diversity of structures and purposes. Nevertheless, there are some common structural elements. * Legal requirements followed for establishment * Purpose of the foundation * Economic activity * Supervision and management provisions * Accountability and auditing provisions * Provisions for the amendment of the statutes or articles of incorporation * Provisions for the dissol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Transfer
Technology transfer (TT), also called transfer of technology (TOT), is the process of transferring (disseminating) technology from the person or organization that owns or holds it to another person or organization, in an attempt to transform inventions and scientific outcomes into new products and services that benefit society. Technology transfer is closely related to (and may arguably be considered a subset of) knowledge transfer. A comprehensive definition of technology transfer today includes the notion of collaborative process as it became clear that global challenges could be resolved only through the development of global solutions. Knowledge and technology transfer plays a crucial role in connecting innovation stakeholders and moving inventions from creators to public and private users. Intellectual property (IP) is an important instrument of technology transfer, as it establishes an environment conducive to sharing research results and technologies. Analysis in 2003 showe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EPRI
EPRI, is an American independent, nonprofit organization that conducts research and development related to the generation, delivery, and use of electricity to help address challenges in the energy industry, including reliability, efficiency, affordability, health, safety, and the environment. EPRI's principal offices and laboratories are located in Palo Alto, California; Charlotte, North Carolina; Knoxville, Tennessee; Washington, DC; and Lenox, Massachusetts. History In November 1965, the Great Northeastern Blackout left 30 million people in the United States without electricity. Historic in scale and impact, it demonstrated the nation's growing dependence upon electricity and its vulnerability to power loss. The event marked a watershed moment for the U.S. electricity sector and triggered the creation of the Electric Power Research Institute. Following the blackout, leaders in Congress held hearings in the early 1970s about the lack of research supporting the power indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USDOE
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States. The DOE oversees the U.S. nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and domestic energy production and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the Secretary of Energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current Secretary of Energy is Jennifer Granholm, who has served in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
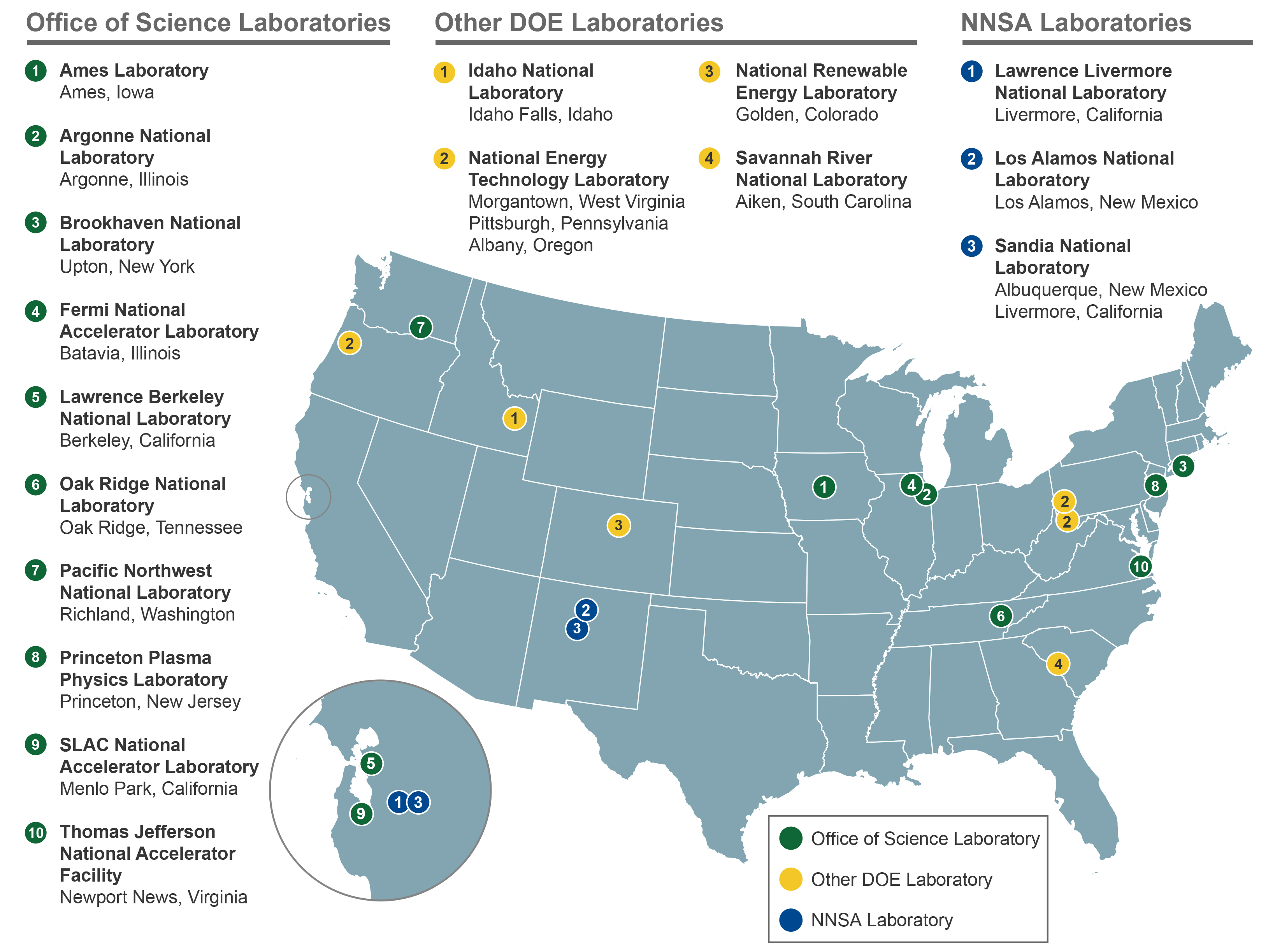
United States Department Of Energy National Laboratories
The United States Department of Energy National Laboratories and Technology Centers is a system of facilities and laboratories overseen by the United States Department of Energy (DOE) for scientific and technological research. Sixteen of the seventeen DOE national laboratories are federally funded research and development centers administered, managed, operated and staffed by private-sector organizations under management and operating (M&O) contract with DOE (with the National Energy Technology Laboratory being the exception). History The system of centralized national laboratories grew out of the massive scientific endeavors of World War II, in which new technologies such as radar, the computer, the proximity fuse, and the atomic bomb proved decisive for the Allied victory. Though the United States government had begun seriously investing in scientific research for national security in World War I, it was only in late 1930s and 1940s that monumental amounts of resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galena Nuclear Power Plant
The Galena Nuclear Power Plant was a proposed nuclear power plant to be constructed in the Yukon River village of Galena, Alaska. If it had been built in the projected timeframe, it would have been the first non-military nuclear power plant built in Alaska to be utilized for public utility generation. In April 2008, Marvin Yoder, a consultant on the project, said that Toshiba was planning to make the application to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in 2009, and that if approval had been given in 2010 or 2011, the reactor could have been operational by 2012 or 2013. The company was also developing a 50 megawatt (electric) version of the reactor. The plan had been to build a 10-megawatt Toshiba 4S reactor that would have been buried underground, and fuel would have powered the reactor for 30 years. According to Dennis Witmer, an energy consultant with the Center for Energy and Power at the University of Alaska Fairbanks The University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF or Alaska) is a pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toshiba 4S
The Toshiba 4S (Ultra super safe, Small and Simple) is a micro sodium reactor design. General description The plant design is developed by a partnership that includes Toshiba and the Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) of Japan. The technical specifications of the 4S reactor are unique in the nuclear industry. The actual reactor would be located in a sealed, cylindrical vault 30 m (98 ft) underground, while the building above ground would be 22×16×11 m (72×52.5×36 ft) in size. This power plant is designed to provide 10 megawatts of electrical power with a 50 MW version available in the future. The 4S is a fast neutron sodium reactor. It uses neutron reflector panels around the perimeter to maintain neutron density. These reflector panels replace complicated control rods, yet keep the ability to shut down the nuclear reaction in case of an emergency. Additionally, the Toshiba 4S utilizes liquid sodium as a coolant, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Atmospheric Research
The US National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR ) is a US federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) managed by the nonprofit University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) and funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF). NCAR has multiple facilities, including the I. M. Pei-designed Mesa Laboratory headquarters in Boulder, Colorado. Studies include meteorology, climate science, atmospheric chemistry, solar-terrestrial interactions, environmental and societal impacts. Tools and technologies NCAR was instrumental in developing lidar, light radar, now a key archaeological tool, as well as providing a broad array of tools and technologies to the scientific community for studying Earth’s atmosphere, including, * Specialized instruments to measure atmospheric processes * Research aircraft * High-performance computing and cyberinfrastructure, including supercomputers * Mauna Loa Solar Observatory * Cooperative field campaigns * Atmosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Think Tanks Based In Japan
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, and deliberation. But other mental processes, like considering an idea, memory, or imagination, are also often included. These processes can happen internally independent of the sensory organs, unlike perception. But when understood in the widest sense, any mental event may be understood as a form of thinking, including perception and unconscious mental processes. In a slightly different sense, the term ''thought'' refers not to the mental processes themselves but to mental states or systems of ideas brought about by these processes. Various theories of thinking have been proposed, some of which aim to capture the characteristic features of thought. ''Platonists'' hold that thinking consists in discerning and inspecting Platonic forms and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Power In Japan
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
