|
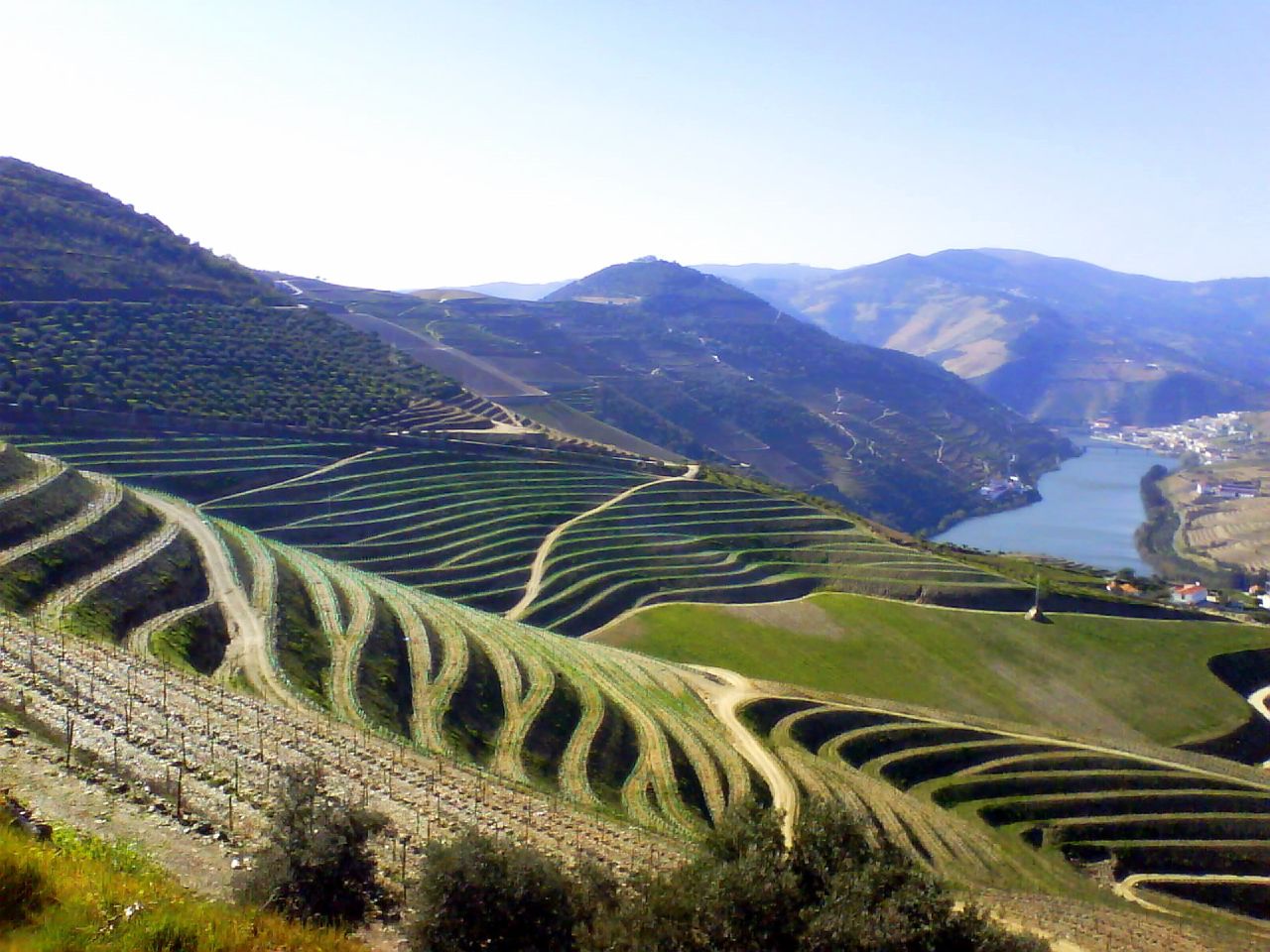
Central Otago Wines
The Central Otago wine region is a geographical indication in New Zealand's South Island, and the world's southernmost commercial wine growing region. While Central Otago is best known for Pinot Noir, many white wine varieties are also popular. History of the wine region Significant European occupation in this region started with the Otago gold rush in the 1860s. French immigrant gold miner Jean Desire Feraud soon started planting vines and embarking upon small-scale commercial wine production, even winning medals in Australian wine competitions. Late in the nineteenth century, the New Zealand government hired Romeo Bragato to survey the country. While this early experimentation showed the wine-growing potential of the region, the wine industry did not survive for long on a commercial basis. From the 1950s through to the late 1970s, there were many small-scale trial plantings of vines by private individuals and under the auspices of the New Zealand Department of Agriculture. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Indication
A geographical indication (GI) is a name or sign used on products which corresponds to a specific geographical location or origin (e.g., a town or region). The use of a geographical indication, as an indication of the product's source, is intended as a certification that the product possesses certain qualities, is made according to traditional methods, or enjoys a good reputation due to its geographical origin. Article 22.1 of the TRIPS Agreement defines geographical indications as ''"...indications which identify a good as originating in the territory of a Member World_Trade_Organization.html" ;"title="f the World Trade Organization">f the World Trade Organization or a region or locality in that territory, where a given quality, reputation or other characteristic of the good is essentially attributable to its geographical origin."'' ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' ('Appellation of origin') is a sub-type of geographical indication where quality, method, and reputation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winery
A winery is a building or property that produces wine, or a business involved in the cultivation and production of wine, such as a wine company. Some wine companies own many wineries. Besides wine making equipment, larger wineries may also feature warehouses, bottling lines, laboratories, and large expanses of tanks known as tank farms. Wineries may have existed as long as 8,000 years ago. Ancient history The earliest known evidence of winemaking at a relatively large scale, if not evidence of actual wineries, has been found in the Middle East. In 2011 a team of archaeologists discovered a 6000 year old wine press in a cave in the Areni region of Armenia, and identified the site as a small winery. Previously, in the northern Zagros Mountains in Iran, jars over 7000 years old were discovered to contain tartaric acid crystals (a chemical marker of wine), providing evidence of winemaking in that region. Archaeological excavations in the southern Georgian region of Kvemo Kartli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinot Noir
Pinot noir (), also known as Pinot nero, is a red-wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. The name also refers to wines created predominantly from Pinot noir grapes. The name is derived from the French language, French words for ''pine'' and ''black.'' The word ''pine'' alludes to the grape variety having tightly clustered, pinecone—shaped bunches of fruit. Pinot noir is grown around the world, mostly in cooler climates, and the variety is chiefly associated with the Burgundy (wine), Burgundy region of France (wine), France. Pinot noir is now used to make red wines around the world, as well as champagne, Sparkling wine, sparkling white wines such as the Italian wine, Italian Franciacorta, and Wine from the United Kingdom, English sparkling wines. Regions that have gained a reputation for red Pinot noir wines include the Willamette Valley (wine), Willamette Valley of Oregon (wine), Oregon; the Carneros (AVA), Carneros, Central Coast (AVA), Central Coast, Sonoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinton Central Otago Pinot
__NOTOC__ Hinton may refer to: Places Australia *Hinton, New South Wales Canada *Hinton, Alberta ** Hinton/Entrance Airport ** Hinton/Jasper-Hinton Airport **Hinton CN railway station England *Hinton, Dorset, a civil parish **Hinton Martell, Dorset **Hinton Parva, Dorset *Hinton, South Gloucestershire, Gloucestershire *Hinton, Stroud, Gloucestershire, a village near Berkeley *Hinton, Hampshire * Hinton, Herefordshire *Hinton, Northamptonshire * Hinton, Shropshire * Hinton, Somerset * Hinton, Suffolk *Hinton Admiral, Hampshire **Hinton Admiral railway station *Hinton Ampner, Hampshire *Hinton Blewett, Somerset *Hinton Charterhouse, Somerset *Hinton Daubney, Hampshire *Hinton Parva, Wiltshire, also known as Little Hinton *Hinton St George, Somerset *Hinton St Mary, Dorset *Hinton Waldrist, Oxfordshire *Hinton-in-the-Hedges, Northamptonshire *Hinton on the Green, Worcestershire *Broad Hinton, Wiltshire *Cherry Hinton, Cambridgeshire *Great Hinton, Wiltshire *Tarrant Hinton, Dorset U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrigation (wine)
Irrigation in viticulture is the process of applying extra water in the cultivation of grapevines. It is considered both controversial and essential to wine production. In the physiology of the grapevine, the amount of available water affects photosynthesis and hence growth, as well as the development of grape berries. While climate and humidity play important roles, a typical grape vine needs 25-35 inches (635-890 millimeters) of water a year, occurring during the spring and summer months of the growing season (vine), growing season, to avoid stress.T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' p. 15 Dorling Kindersley 2005 A vine that does not receive the necessary amount of water will have its growth altered in a number of ways; some effects of water stress (particularly, smaller berry size and somewhat higher sugar content) are considered desirable by wine grape growers. In many Old World wine regions, natural rainfall is considered the only source for water that wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Island
The North Island ( , 'the fish of Māui', historically New Ulster) is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but less populous South Island by Cook Strait. With an area of , it is the List of islands by area, world's 14th-largest island, constituting 43% of New Zealand's land area. It has a population of which is % of New Zealand's residents, making it the most populous island in Polynesia and the List of islands by population, 28th-most-populous island in the world. Twelve main urban areas (half of them officially cities) are in the North Island. From north to south, they are Whangārei, Auckland, Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton, Tauranga, Rotorua, Gisborne, New Zealand, Gisborne, New Plymouth, Napier, New Zealand, Napier, Hastings, New Zealand, Hastings, Whanganui, Palmerston North, and New Zealand's capital city Wellington, which is located at the south-west tip of the island. Naming and usage The island has been known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
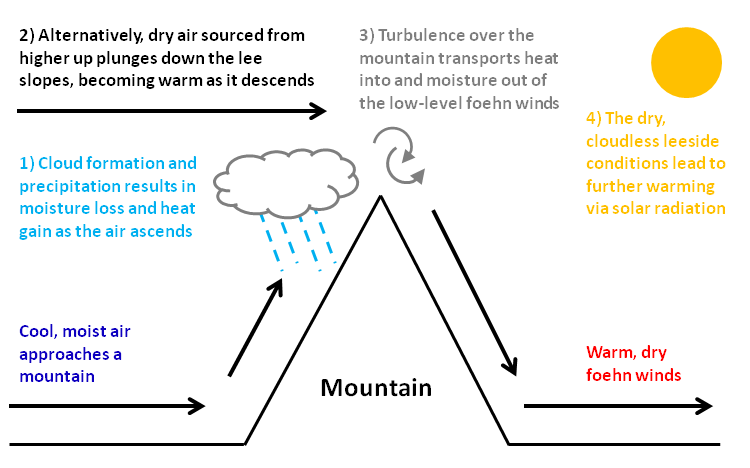
Foehn Wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany, and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin , a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by or just , the term was adopted as . In the Southern Alps, the phenomenon is known as but also and in Serbo-Croatian and Slovene. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nor'west Arch
The nor'west arch is a band of high white lenticular cloud that forms on the eastern side of New Zealand's South Island and which looks like an arch in an otherwise clear blue sky over the Southern Alps. It is accompanied by a strong hot northwesterly or northerly wind known as a "nor'wester". In Canterbury, where it is a well known feature, it is also called the Canterbury arch. It also occurs in Otago and Marlborough and east of mountain ranges along the east coast of the North Island. Closer to the Canterbury coast, some distance from the mountains of the Southern Alps, it appears as a clear area of blue above the mountains, with white cloud streaming to the east from it. The phenomenon is similar to the Chinook arch seen in the Pacific regions of the United States and Canada. Formation The nor'west arch is a föhn cloud or a lenticular cloud. The northwesterly wind drives warm moist air from over the Tasman Sea, and it is pushed up by the presence of the Southern Alps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainfall
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward side of mountains, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Climate (wine)
In viticulture, the climates of wine regions are categorised based on the overall characteristics of the area's climate during the growing season. While variations in macroclimate are acknowledged, the climates of most wine regions are categorised (somewhat loosely based on the Köppen climate classification) as being part of a Mediterranean (for example Tuscany), maritime (ex: Bordeaux) or continental climate (ex: Columbia ValleyA. Mumma 'The Washington wine difference: it's in the vineyard'' Wines & Vines, November 2005). The majority of the world's premium wine production takes place in one of these three climate categories in locations between the 30th parallel and 50th parallel in both the northern and southern hemisphere.T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' pg 14-15 Dorling Kindersley 2005 While viticulture does exist in some tropical climates, most notably Brazil, the amount of quality wine production in those areas is so small that the climate effect h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location (geography), ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational equipotential surface, surface (see Geodetic datum#Vertical datum, Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and ''three-dimensional space, depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo (volcano), Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest ECEF, geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation, the term ''elevation'' or ''aerodrome elevation'' is defined by the IC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |