|
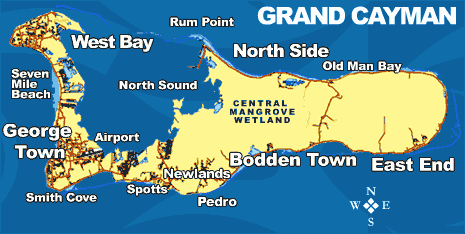
Central Mangrove Wetland
The Central Manrove Wetland is a large area of mangrove dominated wetland on Grand Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs). Description The 3553 ha IBA covers about 30% of the island area. It lies to the east of North Sound and includes Meagre Bay Pond, Pease Bay Pond and the islet of Booby Cay. The vegetation consists mainly of red, white and black mangroves, and buttonwood. It varies compositionally from stands of dwarf red mangrove on the border with North Sound to a forest of black mangrove on the outer southern boundary. There are also areas of seasonally open water as well as scattered islets carrying native dry forest vegetation. The IBA includes the saline lake of Malportas Pond which is separated from the mangrove area and a major site for both resident and wintering waterbirds. Birds The IBA was identified as such by BirdLife International because it supports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Grand Kayman
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conocarpus Erectus
''Conocarpus erectus'', commonly called buttonwood or button mangrove, is a mangrove shrub in the family Combretaceae. This species grows on shorelines in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. Range Locations it is known from include Florida, Bermuda, the Bahamas, the Caribbean, Central and South America from Mexico to Brazil on the Atlantic Coast and Mexico to Ecuador on the Pacific Coast, western Africa and in Melanesia and Polynesia. It was introduced in Kuwait because it can thrive in high temperatures and absorbs brackish water. Description ''Conocarpus erectus'' is usually a dense multiple-trunked shrub, tall, but can grow into a tree up to or more tall, with a trunk up to in diameter. The United States National Champion green buttonwood is tall, has a spread of , and a circumference of . The bark is thick and has broad plates of thin scales which are gray to brown. The twigs are brittle, and angled or narrowly winged in cross-section. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Areas Of The Cayman Islands
Importance is a property of entities that matter or make a difference. For example, World War II was an important event and Albert Einstein was an important person because of how they affected the world. There are disagreements in the academic literature about what type of difference is required. According to the causal impact view, something is important if it has a big causal impact on the world. This view is rejected by various theorists, who insist that an additional aspect is required: that the impact in question makes a value difference. This is often understood in terms of how the important thing affects the well-being of people. So on this view, World War II was important, not just because it brought about many wide-ranging changes but because these changes had severe negative impacts on the well-being of the people involved. The difference in question is usually understood counterfactually as the contrast between how the world actually is and how the world would have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-crowned Pigeon
The white-crowned pigeon (''Patagioenas leucocephala'') is a fruit and seed-eating species of bird in the dove and pigeon family Columbidae. It is found primarily in the Caribbean. John James Audubon painted these pigeons, including the watercolour painting in his work, '' Birds of America'', published in the early 19th century. Taxonomy In the first half of the 18th century the white-crowned pigeon was described and illustrated by several naturalists including John Ray in 1713, Hans Sloane in 1725 and Mark Catesby in 1731. When in 1758 the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus updated his ''Systema Naturae'' for the tenth edition, he placed the white-crowned pigeon with all the other pigeons in the genus ''Columba''. Linnaeus included a brief description, coined the binomial name ''Columba leucocephala'' and cited the earlier authors. The specific epithet combines the Ancient Greek ''leukos'' meaning "white" and ''-kephalos'' meaning "-headed". Although Linnaeus gave the location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
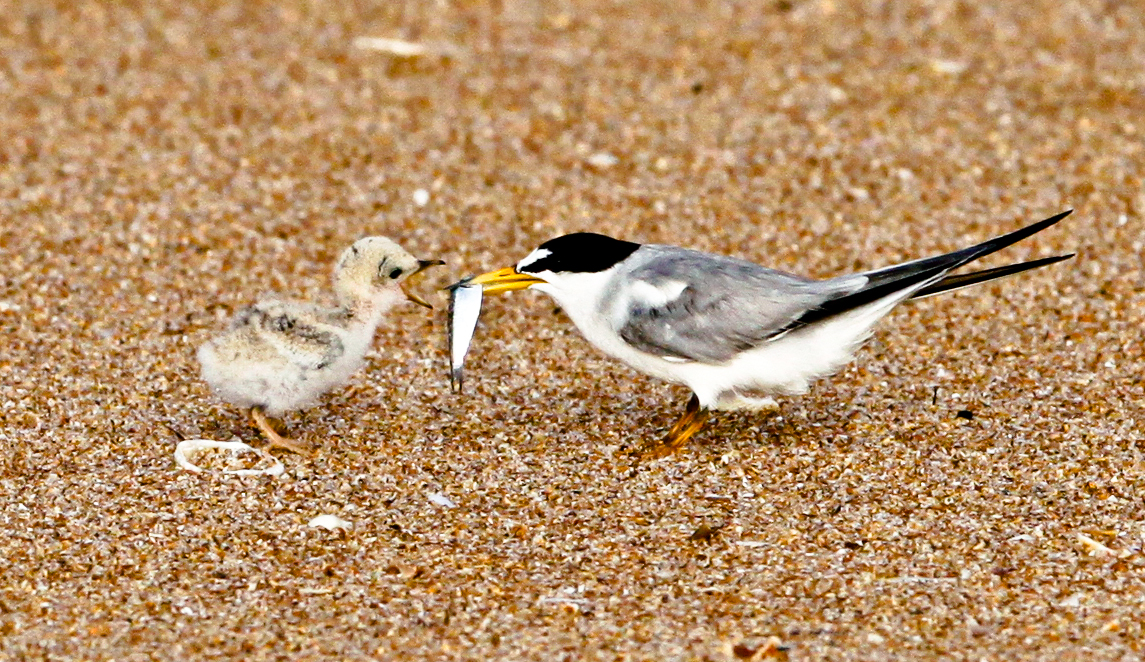
Least Tern
The least tern (''Sternula antillarum'') is a species of tern that breeds in North America and locally in northern South America. It is closely related to, and was formerly often considered conspecific with, the little tern of the Old World. Other close relatives include the yellow-billed tern and Peruvian tern, both from South America. It is a small tern, long, with a wingspan of , and weighing . The upper parts are a fairly uniform pale gray, and the underparts white. The head is white, with a black cap and line through the eye to the base of the bill, and a small white forehead patch above the bill; in winter, the white forehead is more extensive, with a smaller and less sharply defined black cap. The bill is yellow with a small black tip in summer, all blackish in winter. The legs are yellowish. The wings are mostly pale gray, but with conspicuous black markings on their outermost primaries. It flies over water with fast, jerky wingbeats and a distinctive hunchback appeara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indian Whistling Duck
The West Indian whistling duck (''Dendrocygna arborea'') is a whistling duck that breeds in the Caribbean. Alternative names are black-billed whistling duck and Cuban whistling duck. Distribution The West Indian whistling duck is widely scattered throughout the West Indies, including a large breeding population in the Bahamas, and smaller numbers in Cuba, the Cayman Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, Jamaica, Hispaniola (both the Dominican Republic and Haiti), and Puerto Rico. It is largely sedentary, apart from local movements, which can be 100 km or more. Description The West Indian whistling duck is the largest and darkest of the whistling ducks. With a length of and female weighs from and male weights from , this species is about the size of a mallard.Carboneras, C. and G. M. Kirwan (2020). ''West Indian Whistling-Duck (Dendrocygna arborea)'', version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding important sites for birds, maintaining and restoring key bird habitats, and empowering conservationists worldwide. It has a membership of more than 2.5 million people across 116 country partner organizations, including the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, the Wild Bird Society of Japan, the National Audubon Society and American Bird Conservancy. BirdLife International has identified 13,000 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas and is the official International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List authority for birds. As of 2015, BirdLife International has established that 1,375 bird species (13% of the total) are threatened with extinction ( critically endangered, endangered or vulnerable). BirdLife Internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterbird
A water bird, alternatively waterbird or aquatic bird, is a bird that lives on or around water. In some definitions, the term ''water bird'' is especially applied to birds in freshwater ecosystems, although others make no distinction from seabirds that inhabit marine environments. Some water birds (e.g. wading birds) are more terrestrial while others (e.g. waterfowls) are more aquatic, and their adaptations will vary depending on their environment. These adaptations include webbed feet, beaks, and legs adapted to feed in the water, and the ability to dive from the surface or the air to catch prey in water. The term ''aquatic bird'' is sometimes also used in this context. A related term that has a narrower meaning is waterfowl. Some piscivorous birds of prey, such as ospreys and sea eagles, hunt aquatic prey but do not stay in water for long and lives predominantly over dry land, and are not considered water birds. The term waterbird is also used in the context of conservat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malportas Pond
Malportas Pond is a salt-water pond on the north coast of Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands, near North Side village. It has an area of or , and like the nearby Rock and Point ponds, it is an important area for breeding waterfowl. Local farmer Willie Ebanks introduced West Indian whistling-ducks on the pond in 1990, and it also has populations of heron, egrets, moorhens, and coots. It forms part of the Central Mangrove Wetland Important Bird Area, identified as such by BirdLife International because it supports populations of waterbird A water bird, alternatively waterbird or aquatic bird, is a bird that lives on or around water. In some definitions, the term ''water bird'' is especially applied to birds in freshwater ecosystems, although others make no distinction from seab ...s. References Landforms of the Cayman Islands Important Bird Areas of the Cayman Islands Grand Cayman {{CaymanIslands-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical And Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forests
The tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest is a habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature and is located at tropical and subtropical latitudes. Though these forests occur in climates that are warm year-round, and may receive several hundred centimeters of rain per year, they have long dry seasons that last several months and vary with geographic location. These seasonal droughts have great impact on all living things in the forest. Deciduous trees predominate in most of these forests, and during the drought a leafless period occurs, which varies with species type. Because trees lose moisture through their leaves, the shedding of leaves allows trees such as teak and mountain ebony to conserve water during dry periods. The newly bare trees open up the canopy layer, enabling sunlight to reach ground level and facilitate the growth of thick underbrush. Trees on moister sites and those with access to ground water tend to be evergreen. Infertile sites also te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicennia Germinans
''Avicennia germinans'', the black mangrove, is a shrub or small tree growing up to 12 meters (39 feet) in the acanthus family, Acanthaceae. It grows in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, on both the Atlantic and Pacific Coasts, and on the Atlantic Coast of tropical Africa, where it thrives on the sandy and muddy shores where seawater reaches. It is common throughout coastal areas of Texas and Florida, and ranges as far north as southern Louisiana and coastal Georgia in the United States. Like many other mangrove species, it reproduces by vivipary. Seeds are encased in a fruit, which reveals the germinated seedling when it falls into the water. Unlike other mangrove species, it does not grow on prop roots, but possesses pneumatophores that allow its roots to breathe even when submerged. It is a hardy species and expels absorbed salt mainly from its leathery leaves. The name "black mangrove" refers to the color of the trunk and heartwood. The leaves often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |