|
Central Atlantic Magmatic Province
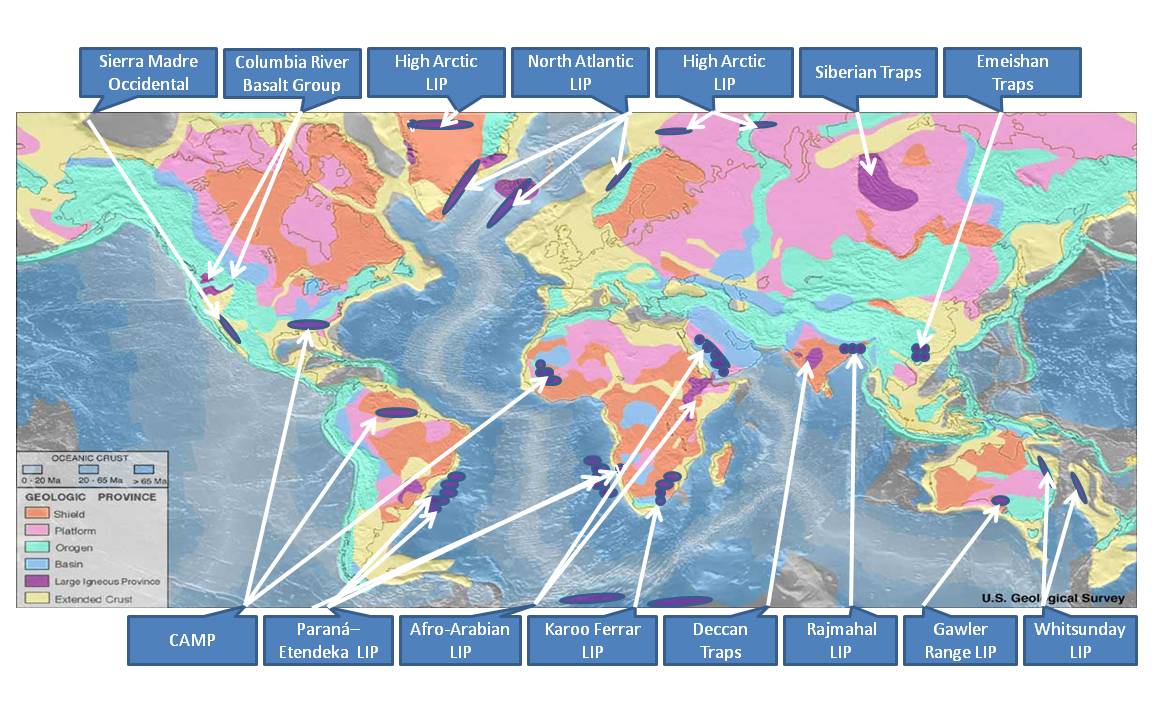
The Central Atlantic magmatic province (CAMP) is the Earth's largest continental large igneous province, covering an area of roughly 11 million km2. It is composed mainly of basalt that formed before Pangaea broke up in the Mesozoic Era, near the end of the Triassic and the beginning of the Jurassic periods. The subsequent breakup of Pangaea created the Atlantic Ocean, but the massive igneous upwelling provided a legacy of basaltic dikes, sills, and lavas now spread over a vast area around the present central North Atlantic Ocean, including large deposits in northwest Africa, southwest Europe, as well as northeast South America and southeast North America (found as continental tholeiitic basalts in subaerial flows and intrusive bodies). The name and CAMP acronym were proposed by Andrea Marzoli (Marzoli et al. 1999) and adopted at a symposium held at the 1999 Spring Meeting of the American Geophysical Union. The CAMP volcanic eruptions occurred about 201 million years ago and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Igneous Province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive ( sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Overview Definition In 1992, Coffin and Eldholm initially defined the term "large igneous province" as representing a variety of mafic igneous provinces with areal extent greater than 100,000 km2 that represented "massive crustal emplacements of predominantly mafic (magnesium- and iron-rich) extrusive and intrusive rock, and origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fracture in the Crust (geology), crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is often also called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. Etymology The word ''lava'' comes from Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rift (geology)
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems. Major rifts occur along the central axis of most mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust and lithosphere is created along a divergent boundary between two tectonic plates. ''Failed rifts'' are the result of continental rifting that failed to continue to the point of break-up. Typically the transition from rifting to spreading develops at a triple junction where three converging rifts meet over a hotspot. Two of these evolve to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopolith
A lopolith is a large igneous intrusion which is lenticular in shape with a depressed central region. Lopoliths are generally concordant with the intruded strata with dike or funnel-shaped feeder bodies below the body. The term was first defined and used by Frank Fitch Grout during the early 1900s in describing the Duluth gabbro complex in northern Minnesota and adjacent Ontario. Lopoliths typically consist of large layered intrusions that range in age from Archean to Eocene. Examples include the Duluth gabbro, the Sudbury igneous complex of Ontario, the Bushveld igneous complex of South Africa, the Great Dyke in Zimbabwe, the Skaergaard complex of Greenland and the Humboldt lopolith of Nevada. The Sudbury occurrence has been attributed to an impact event and associated crustal melting. See also * Laccolith * Phacolith *Batholith A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
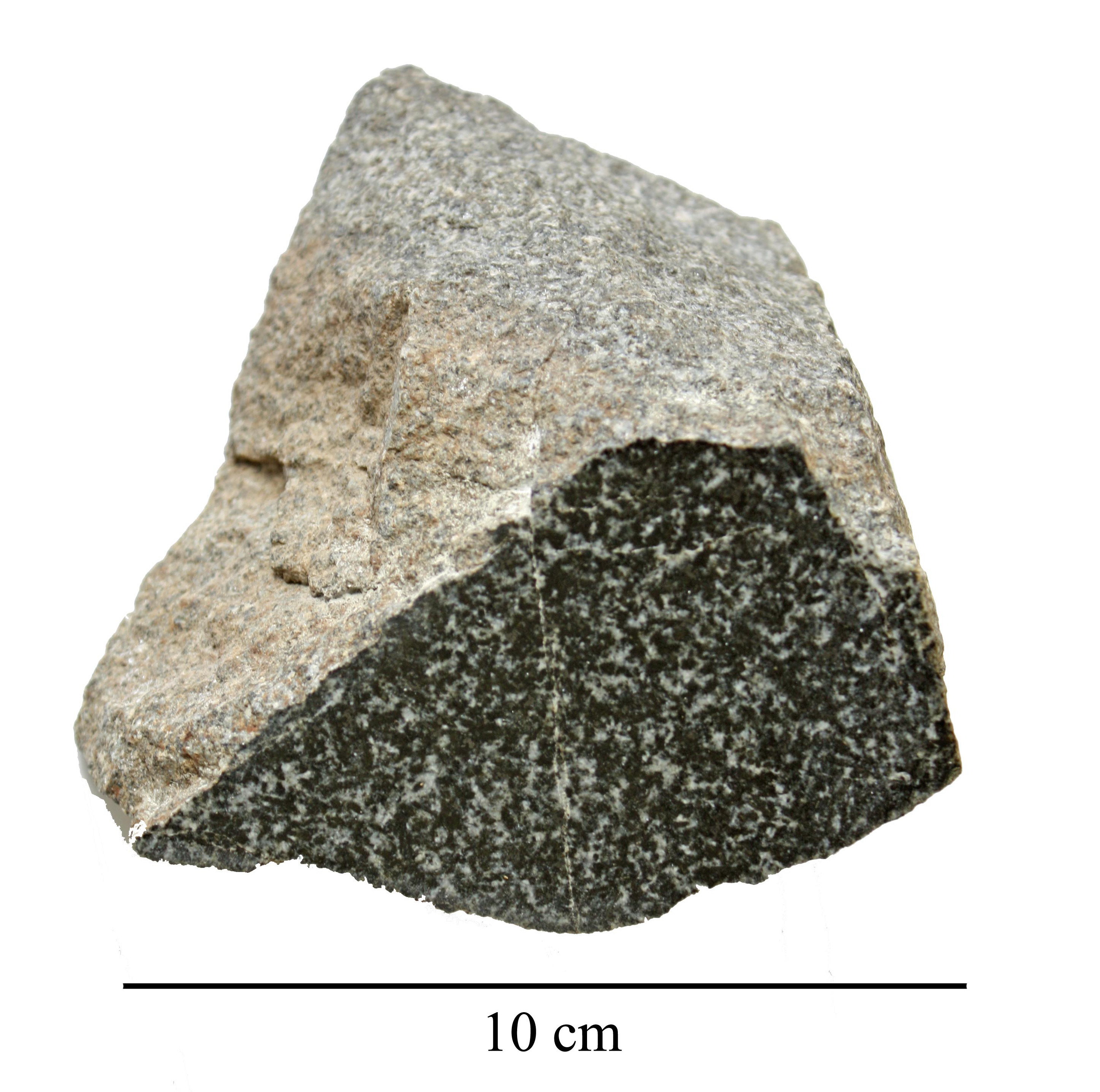
Diabase
Diabase (), also called dolerite () or microgabbro, is a mafic, holocrystalline, subvolcanic rock equivalent to volcanic basalt or plutonic gabbro. Diabase dikes and sills are typically shallow intrusive bodies and often exhibit fine-grained to aphanitic chilled margins which may contain tachylite (dark mafic glass). ''Diabase'' is the preferred name in North America, while ''dolerite'' is the preferred name in the rest of the English-speaking world, where sometimes the name ''diabase'' refers to altered dolerites and basalts. Some geologists prefer to avoid confusion by using the name ''microgabbro''. The name ''diabase'' comes from the French , and ultimately from the Greek 'act of crossing over, transition', whereas the name ''dolerite'' comes from the French , from the Greek 'deceitful, deceptive', because it was easily confused with diorite. Petrography Diabase normally has a fine but visible texture of euhedral lath-shaped plagioclase crystals (62%) set i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholeiite
The tholeiitic magma series () is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the Calc-alkaline magma series, calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma into a more evolved, silica rich end member. Rock types of the tholeiitic magma series include tholeiitic basalt, ferro-basalt, Basaltic andesite, tholeiitic basaltic andesite, Andesite, tholeiitic andesite, dacite and rhyolite. The variety of basalt in the series was originally called ''tholeiite'' but the International Union of Geological Sciences recommends that ''tholeiitic basalt'' be used in preference to that term.Le Maitre ''et al.'' 2002 Tholeiitic rock types tend to be more enriched in iron and less enriched in magnesium and aluminium than calc-alkaline rock types. They are thought to form in a less oxidized environment than calc-alkaline rocks. Tholeiitic basalt is formed at mid-ocean ridges and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprising most of the region, as well as the tiny adjuncts of Andorra, Gibraltar, and, pursuant to the traditional definition of the Pyrenees as the peninsula's northeastern boundary, a small part of France. With an area of approximately , and a population of roughly 53 million, it is the second-largest European peninsula by area, after the Scandinavian Peninsula. Etymology The Iberian Peninsula has always been associated with the River Ebro (Ibēros in ancient Greek and Ibērus or Hibērus in Latin). The association was so well known it was hardly necessary to state; for example, Ibēria was the country "this side of the Ibērus" in Strabo. Pliny the Elder, Pliny goes so far as to assert that the Greeks had called "the whole of the peninsula" Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh-largest by population, with over 212 million people. The country is a federation composed of 26 Federative units of Brazil, states and a Federal District (Brazil), Federal District, which hosts the capital, Brasília. List of cities in Brazil by population, Its most populous city is São Paulo, followed by Rio de Janeiro. Brazil has the most Portuguese-speaking countries, Portuguese speakers in the world and is the only country in the Americas where Portuguese language, Portuguese is an Portuguese-speaking world, official language. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazil, coastline of . Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it Borders of Brazil, borders all other countries and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot (geology), hotspot reaching the surface of the Earth via a mantle plume. List of flood basalt provinces, Flood basalt provinces such as the Deccan Traps of India are often called ''Trap rock, traps'', after the Swedish word ''trappa'' (meaning "staircase"), due to the characteristic stairstep geomorphology of many associated landscapes. Michael R. Rampino and Richard Stothers (1988) cited eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurring in the past 250 million years, creating large igneous provinces, lava plateaus, and mountain ranges. However, more have been recognized such as the large Ontong Java Plateau, and the Chilcotin Group, though the latter may be linked to the Columbia River Basalt Group. Large igneous provinces have been connected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic–Jurassic Extinction Event
The Triassic–Jurassic (Tr-J) extinction event (TJME), often called the end-Triassic extinction, marks the boundary between the Triassic and Jurassic periods, . It represents one of five major extinction events during the Phanerozoic, profoundly affecting life on land and in the oceans. In the seas, about 23–34% of marine genus, genera disappeared; Coral, corals, Bivalvia, bivalves, Brachiopod, brachiopods, Bryozoa, bryozoans, and Radiolaria, radiolarians suffered severe losses of diversity and Conodont, conodonts were completely wiped out, while marine vertebrates, Gastropoda, gastropods, and benthic foraminifera were relatively unaffected. On land, all Archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptiles other than Crocodylomorpha, crocodylomorphs, dinosaurs, and pterosaurs became extinct. Crocodylomorphs, dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and mammals were left largely untouched, allowing them to become the dominant land animals for the next 135 million years. Plants were likewise significantly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |