|
Cave-in-Rock State Park
Cave-In-Rock State Park is an Illinois state park, on , in the town of Cave-in-Rock, Hardin County, Illinois, in the United States. The state park contains the historic Cave-In-Rock, a landmark of the Ohio River. It is maintained by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources (IDNR).Joe McFarland, "The Hole in the River", ''Outdoor Illinois'' XVIII:11 (November 2010), pages 2-5. Geology The park's primary feature is a -wide riverside cave formed by wind and water erosion and cataclysmic effects of the 1811–12 New Madrid earthquakes. The Cave-in-Rock was worn into the limestone bluffs of the Ohio River by floods, especially those caused by glacial meltwater following the Wisconsin ice age. Unlike Mammoth Cave in nearby Kentucky, it was not formed by typical karst processes; it is a tunnel eroded into the bluff. History Cave-in-Rock was known and used for thousands of years by the Native Americans. The first European to discover the Cave was M. de Lery of France, who in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its south. Of the fifty U.S. states, Illinois has the List of U.S. states and territories by GDP, fifth-largest gross domestic product (GDP), the List of U.S. states and territories by population, sixth-largest population, and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 25th-most land area. Its capital city is Springfield, Illinois, Springfield in the center of the state, and the state's largest city is Chicago in the northeast. Present-day Illinois was inhabited by Indigenous peoples of the Americas#History, Indigenous cultures for thousands of years. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi and Illinois River, Illinois rivers in the 17th century Illinois Country, as part of their sprawling colony of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
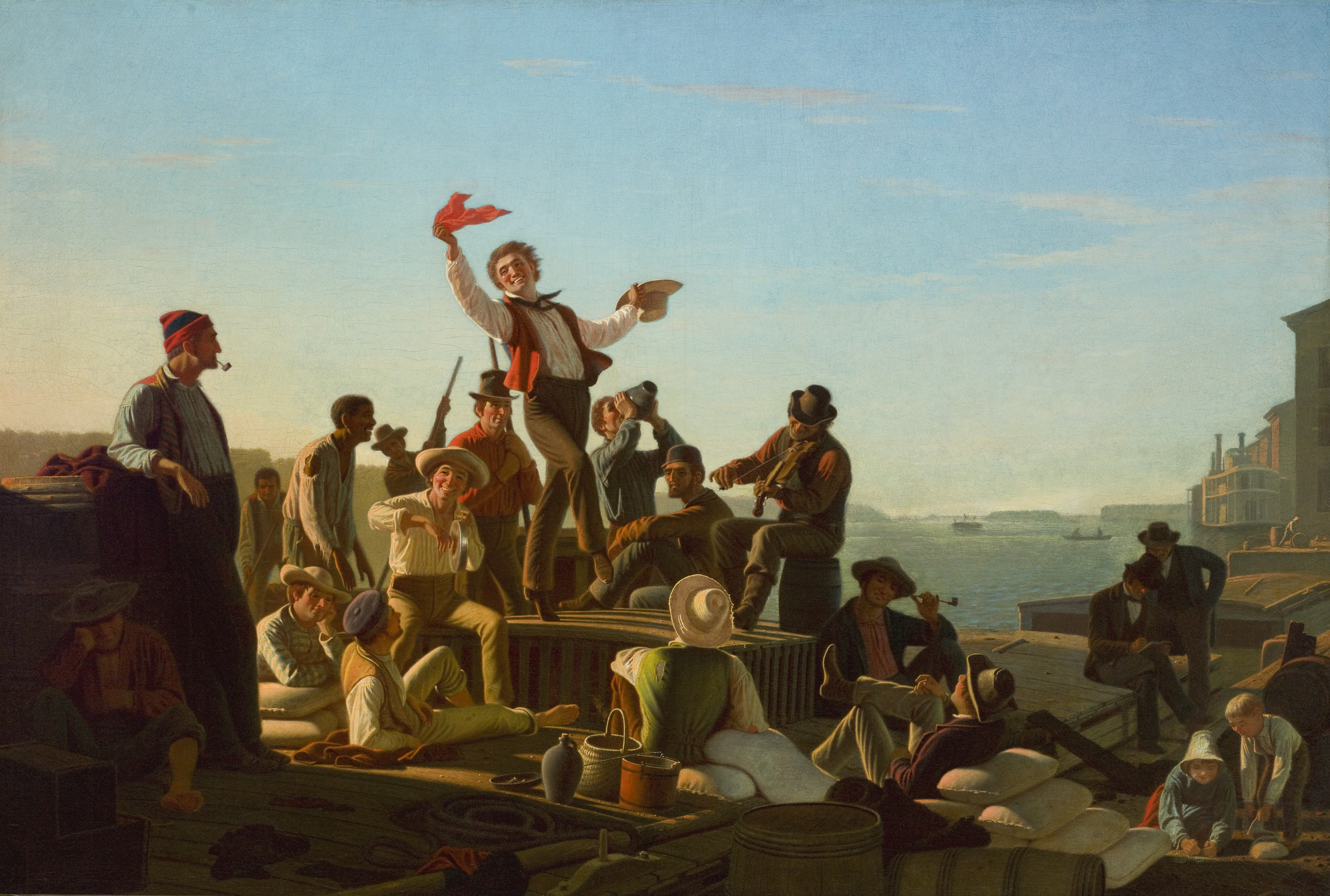
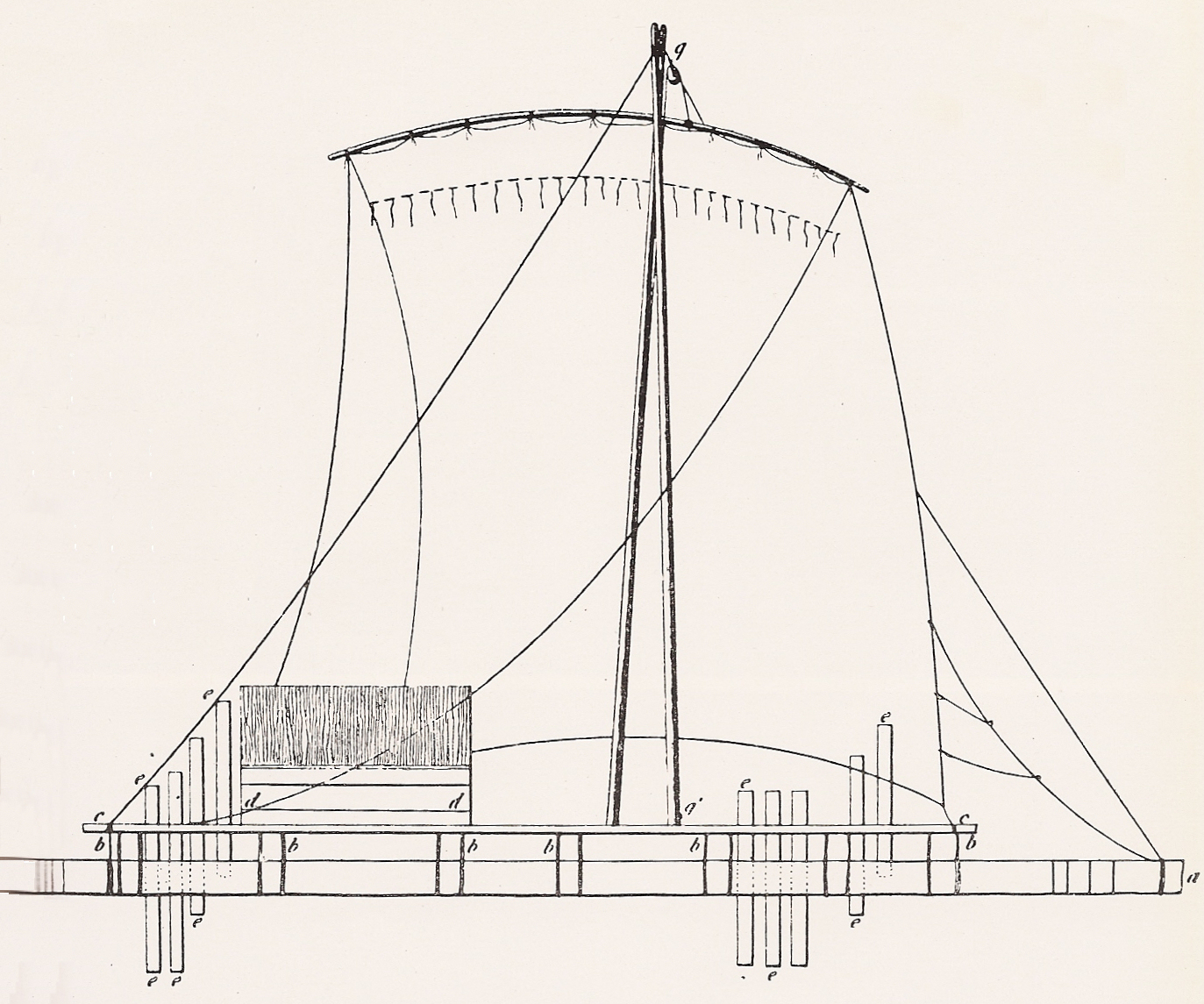
Flatboats
A flatboat (or broadhorn) was a rectangular flat-bottomed boat with square ends used to transport freight and passengers on inland waterways in the United States. The flatboat could be any size, but essentially it was a large, sturdy tub with a hull. A flatboat was almost always a one-way (downstream) vessel, and was usually dismantled for lumber when it reached its destination. Early History The flatboat trade first began in 1781, with Pennsylvania farmer Jacob Yoder building the first flatboat at Old Redstone Fort on the Monongahela River. Yoder's ancestors immigrated from Switzerland, where small barges called weidlings are still common today, having been used for hundreds of years to transport goods downriver. Yoder shipped flour down the Ohio River and Mississippi River to the port of New Orleans. Other flatboats would follow this model, using the current of the river to propel them to New Orleans where their final product could be shipped overseas. Through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, by tying them together into rafts and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keelboat
A keelboat is a riverine cargo-capable working boat, or a small- to mid-sized recreational sailing yacht. The boats in the first category have shallow structural keels, and are nearly flat-bottomed and often used leeboards if forced in open water, while modern recreational keelboats have prominent fixed fin keels, and considerable draft. The two terms may draw from cognate words with different final meaning. A keel boat, keelboat, or keel-boat is a type of usually long, narrow cigar-shaped riverboat, or unsheltered water barge A barge is typically a flat-bottomed boat, flat-bottomed vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. Original use was on inland waterways, while modern use is on both inland and ocean, marine water environments. The firs ... which is sometimes also called a poleboat—that is built about a slight keel and is designed as a boat built for the navigation of rivers, shallow lakes, and sometimes canals that were commonly used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatboat
A flatboat (or broadhorn) was a rectangular flat-bottomed boat with square ends used to transport freight and passengers on inland waterways in the United States. The flatboat could be any size, but essentially it was a large, sturdy tub with a hull. A flatboat was almost always a one-way (downstream) vessel, and was usually dismantled for lumber when it reached its destination. Early History The flatboat trade first began in 1781, with Pennsylvania farmer Jacob Yoder building the first flatboat at Old Redstone Fort on the Monongahela River. Yoder's ancestors immigrated from Switzerland, where small barges called weidlings are still common today, having been used for hundreds of years to transport goods downriver. Yoder shipped flour down the Ohio River and Mississippi River to the port of New Orleans. Other flatboats would follow this model, using the current of the river to propel them to New Orleans where their final product could be shipped overseas. Through th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky Route 91
Kentucky Route 91 (KY 91) is a state highway that traverses three counties in western Kentucky. It begins in Hopkinsville, Kentucky and ends at the Ohio River, the Kentucky–Illinois state line in northern Crittenden County. Route description Hopkinsville to Princeton It begins at a junction with U.S. Route 68 and Kentucky Route 80 in Hopkinsville, Kentucky, the Christian County seat. It crosses KY-1682, the Hopkinsville By-Pass before leaving town. It goes on a northwesterly path, and its junction with Kentucky Route 398 is KY 91's access point to Pennyrile Forest State Resort Park. KY 91 enters Caldwell County, and then it would meet Kentucky Routes 139 and 293, along with US 62 in downtown Princeton. It then traverses Interstate 69 on the northwest outskirts of Princeton.DeLorme. ''Kentucky Atlas & Gazetteer''. (2010) (Map, Fourth Edition) pp. 60-61 Princeton to Cave-in-Rock KY 91 meets Kentucky Route 70 and then U.S. Route 641 at Fredonia, a community northwest of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Route 1
Illinois Route 1 (IL 1) is a state highway (US), state highway in the U.S. state of Illinois. Running parallel to the Indiana border, the highway starts at the Cave-In-Rock Ferry, free ferry crossing to Kentucky at Cave-In-Rock, Illinois, Cave-in-Rock on the Ohio River and runs north to the south side of Chicago as Halsted Street at an intersection with Interstate 57, Interstate 57. This is a distance of . Route description Cave-in-Rock to Birds IL 1 begins at the ferry dock for the Cave-in-Rock Ferry in the eponymous village of Cave-in-Rock, Illinois, Cave-in-Rock along the Ohio River. A continuation of Kentucky Route 91 (KY 91), IL 1 begins its journey in the Shawnee National Forest, leaving the village of Cave-in-Rock for the hamlet of Loves Crossing, where it meets the eastern terminus of Illinois Route 146, IL 146. For the next , IL 1 winds north through the forest, reaching a junction with Illinois Route 13, IL 13, which connects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave-In-Rock Ferry
The Cave-In-Rock Ferry is one of four passenger ferry services that cross the Ohio River into the U.S. state of Kentucky. It connects Illinois Route 1 in Cave-In-Rock, Illinois, Cave-In-Rock, Hardin County, Illinois, to Kentucky Route 91, 10.6 miles north of Marion, Kentucky. It is the only public river crossing available between the Brookport Bridge at Paducah, Kentucky, and the Shawneetown Bridge at Old Shawneetown, Illinois. History In October 1829, the county court of Livingston County, Kentucky granted James Ford a franchise to operate a ferry. Since 1994, Lonnie Lewis of Lonnie Lewis Inc., doing business as Cave in Rock Ferry Company, has operated the ferry. Operation is jointly funded by the Kentucky Transportation Cabinet (KYTC) and the Illinois Department of Transportation (IDOT). The Loni Jo is the current vessel that traverses the river. As of July 2022, 500 vehicles cross daily. The ferry operates 16 hours from 6 a.m. to 10 p.m. daily. Commuters use the ferry to avo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James–Younger Gang
The James–Younger Gang was a notable 19th-century gang of American outlaws that revolved around Jesse James and his brother Frank James. The gang was based in the state of Missouri, the home of most of the members. Membership fluctuated from robbery to robbery, as the outlaws' raids were usually separated by many months. As well as the notorious James brothers, at various times it included the Younger brothers (Cole Younger, Cole, Jim Younger, Jim, John Younger, John, and Bob Younger, Bob), John Jarrett (married to the Youngers' sister Josie), Arthur McCoy, George Shepherd, Oliver Shepherd, William McDaniel, Tom McDaniel, Clell Miller, Charlie Pitts, William Chadwell (alias Bill Stiles), and Matthew "Ace" Nelson. The James–Younger Gang had its origins in a group of Confederate States of America, Confederate bushwhackers that participated in the bitter partisan fighting that wracked Missouri in the American Civil War, Missouri during the American Civil War. After the war, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesse James
Jesse Woodson James (September 5, 1847April 3, 1882) was an American outlaw, Bank robbery, bank and Train robbery, train robber, guerrilla and leader of the James–Younger Gang. Raised in the "Little Dixie (Missouri), Little Dixie" area of Missouri, James and his family maintained strong Southern United States, Southern sympathies. He and his brother Frank James joined pro-Confederate States of America, Confederate guerrillas known as "bushwhackers" operating in Missouri in the American Civil War, Missouri and Kansas in the American Civil War, Kansas during the American Civil War. As followers of William Quantrill and William T. Anderson, "Bloody Bill" Anderson, they were accused of committing atrocities against Union soldiers and civilian abolitionists, including the Centralia Massacre (Missouri), Centralia Massacre in 1864. After the war, as members of various List of Old West gangs, gangs of outlaws, Jesse and Frank robbed banks, stagecoaches, and trains across the Midwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank James
Alexander Franklin James (January 10, 1843 – February 18, 1915) was a Confederate States Army, Confederate American Civil War, soldier and Guerrilla warfare in the American Civil War, guerrilla; in the Reconstruction era, post-Civil War period, he was an outlaw. The older brother of outlaw Jesse James, Frank was also part of the James–Younger Gang. Childhood James was born in Kearney, Missouri, to Baptism, Baptist minister of religion, minister Reverend Robert S. James, Robert Sallee James and his wife Zerelda James, Zerelda (Cole) James. The couple came from Kentucky. He was of English people, English, Welsh people, Welsh and Scottish people, Scottish descent. Frank was the oldest of three children. His father died in 1850 and his mother remarried Benjamin Simms in 1852. After his death, she married a third time to Dr. Reuben Samuel in 1855, when Frank was 13 years old. As a child, James showed interest in his late father's sizable library, especially the works of Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Pirate
A river pirate is a pirate who operates along a river. The term has been used to describe many different kinds of pirate groups who carry out riverine attacks in Asia, Africa, Europe, North America, and South America. They are usually prosecuted under national, not international law. Asia China In Asia, river piracy is a major threat even today. The "Yangtze Patrol", from 1854 to 1949, was a prolonged naval operation, protecting American treaty ports and U.S. citizens along the Yangtze River from river pirates and Chinese insurgents. During the 1860s and 1870s, American merchant ships were prominent on the lower Yangtze, operating inland up to the deepwater port of Hankou . In 1874, the U.S. gunboat reached as far as Ichang, at the foot of the Yangtze gorges, from the sea. In this period, most US personnel found a tour in the Yangtze to be uneventful, as a major American shipping company had sold its interests to a Chinese firm, leaving the patrol with little to protect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |