|
Cavanal Hill
Cavanal Hill (officially Cavanal Mountain), located near Poteau, Oklahoma, is described by a sign at its base as the "'World's Highest Hill' – Elevation: 1,999 feet". The actual summit elevation is above sea level; the difference in elevation between the summit and the Poteau River to the north is . Hill / mountain The billing is based on a delineation between a hill and a mountain, that being if the geographical feature were 2,000 feet or higher than its base, then it would be classified as a mountain instead of a hill. However, the United States Geographic Names Information System The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and location information about more than two million physical and cultural features, encompassing the United States and its territories; the Compact of Free Association, asso ... contains thousands of summits with "hill" in their names which are higher than 2,000 feet. Etymology One source claims that the name is derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Flore County, Oklahoma
LeFlore County is a county along the eastern border of the U.S state of Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, its population was 48,129. Its county seat is Poteau. The county is part of the Fort Smith metropolitan area and the name honors a Choctaw family named LeFlore. The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Oklahoma is the federal district court with jurisdiction in LeFlore County. History The Choctaw Nation signed the Treaty of Doak's Stand in 1820, ceding part of their ancestral home in the Southeastern U.S. and receiving a large tract in Indian Territory. They signed the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek in 1830, which ceded the remainder of their original homeland. Most of the remainder of the Choctaw were removed to Indian Territory, escorted by federal military troops, in several waves. In 1832, the federal government constructed the Choctaw Agency in Indian Territory about west of Fort Smith, Arkansas. The town of Skullyville developed around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
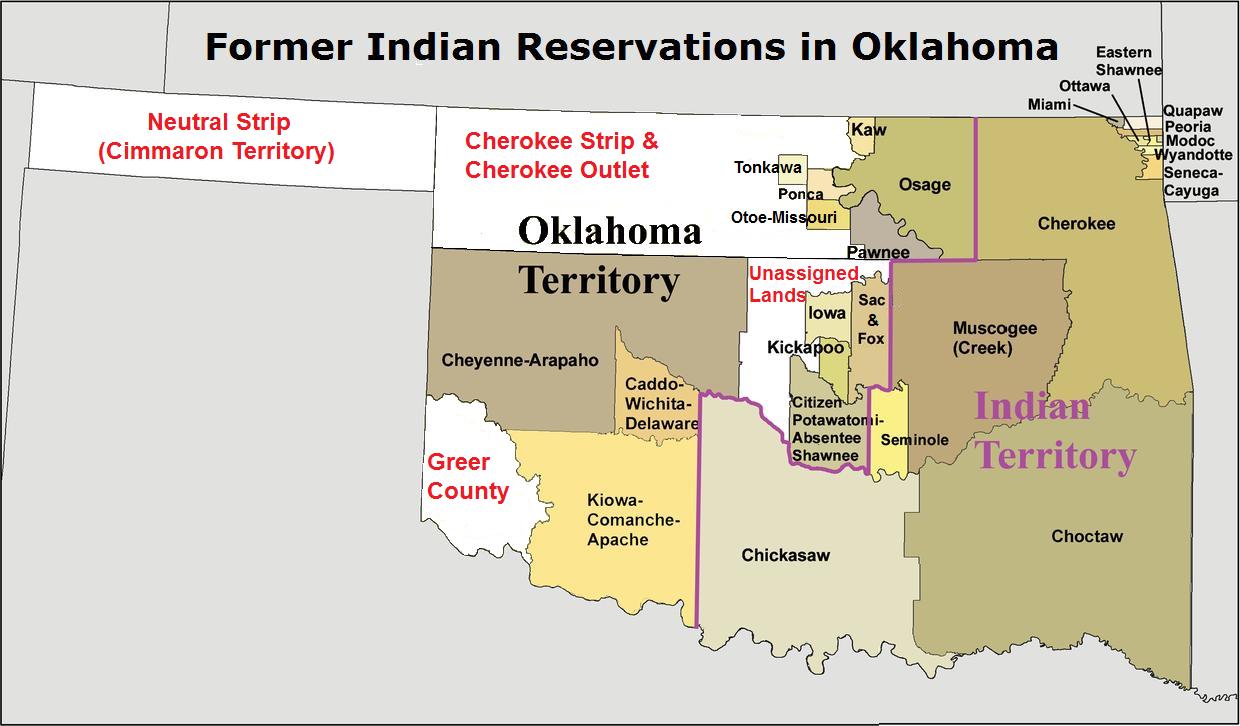
Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northeast, Arkansas to the east, New Mexico to the west, and Colorado to the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "The Sooner State", in reference to the Sooners, American pioneer, American settlers who staked their claims in formerly American Indian-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thrust Belt, one of the important Orogeny, orogenic belts of North America. The Ouachitas continue in the subsurface to the northeast, where they make a poorly understood connection with the Appalachian Mountains, Appalachians and to the southwest, where they join with the Marathon Uplift, Marathon uplift area of West Texas. Together with the Ozark Plateaus, the Ouachitas form the U.S. Interior Highlands. The highest natural point is Mount Magazine at . The Ouachita Mountains is a List of ecoregions in the United States (EPA), Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The region has been subdivided into six List of ecoregions in the United States (EPA), Level IV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poteau, Oklahoma
Poteau ( ) is a city in, and county seat of, LeFlore County, Oklahoma, United States. Its population was 8,520 as of the 2010 census. History In 1719, Bernard de la Harpe led a group of French explorers through this area, and gave the river its present name. The present-day city was founded in 1885, its name derived from the nearby Poteau River. During the late 1700s, a large French outpost was at Belle Point (Ft. Smith). Further up the Poteau River was a secondary post at the base of Cavanal Mountain. Because of this, the river was named the "Post River", or Poteau River, and the outpost was simply called the post, or "Poteau". ''Poteau'' is a French word meaning post.Harold Crain, "Poteau," ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. Accessed March 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poteau River
The Poteau River is a river located in the U.S. states of Arkansas and Oklahoma extending 141 miles (227 kilometers).U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed June 3, 2011 It is the only river in Oklahoma that flows north and is the seventh-largest river in the state. The Poteau River is a tributary of the Arkansas River, which is a tributary of the Mississippi River. Prior to Oklahoma's statehood, during the Indian Territory period (1838-1906), the stream served as the boundary between Skullyville County and Sugar Loaf County, two of the counties making up the Moshulatubbee District of the Choctaw Nation. The Poteau River also serves as the border between the states of Arkansas and Oklahoma for one mile to the south of Fort Smith. This border gives an additional 57 acres of land to Arkansas that would have instead been an exclave of the Choctaw Nation before 1905 when it was handed over to Arkansas. Etymology '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are inselberg, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. mountain formation, Mountains are formed through tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosystems of mountains: different elevations hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Names Information System
The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and location information about more than two million physical and cultural features, encompassing the United States and its territories; the Compact of Free Association, associated states of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Palau; and Antarctica. It is a type of gazetteer. It was developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in cooperation with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of feature names. Data were collected in two phases. Although a third phase was considered, which would have handled name changes where local usages differed from maps, it was never begun. The database is part of a system that includes topographic map names and bibliographic references. The names of books and historic maps that confirm the feature or place name are cited. Variant names, alternatives to official federal names for a feature, are also recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Nuttall
Thomas Nuttall (5 January 1786 – 10 September 1859) was an English botanist and zoologist who lived and worked in America from 1808 until 1841. Nuttall was born in the village of Long Preston, near Settle in the West Riding of Yorkshire and spent some years as an apprentice printer in England. Soon after going to the United States he met professor Benjamin Smith Barton in Philadelphia. Barton encouraged his strong interest in natural history. Early explorations in the United States In 1810 he travelled to the Great Lakes and in 1811 travelled on the Astor Expedition led by William Price Hunt on behalf of John Jacob Astor up the Missouri River. Nuttall was accompanied by the English botanist John Bradbury, who was collecting plants on behalf of Liverpool botanical gardens. Nuttall and Bradbury left the party at the trading post with the Arikara Indians in South Dakota, and continued farther upriver with Ramsay Crooks. In August they returned to the Arikara post and jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
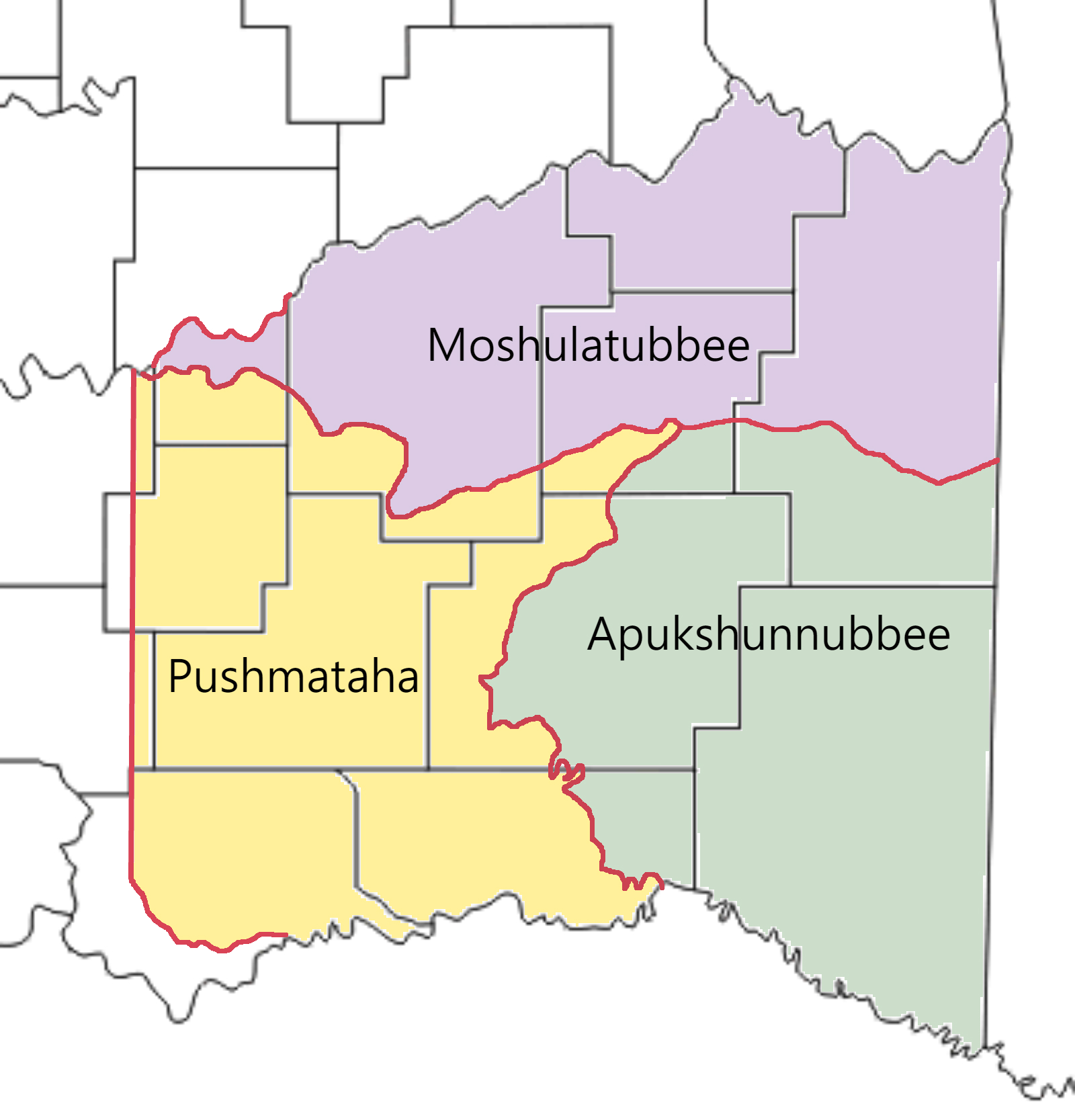
Skullyville County, Choctaw Nation
Skullyville County was a political subdivision of the Choctaw Nation of Indian Territory, prior to Oklahoma being admitted as a state. The county formed part of the Nation's Moshulatubbee District, or First District, one of three administrative super-regions. History The county was also called ''Iskvlli Kaunti'', from the Choctaw word , which means a 'small piece of money or coin.' (The apparent lower-case letter "v" is the Greek letter upsilon, which makes a short "u" sound, for a pronunciation akin to "iskulli.") Skullyville County was home, from 1832, of the United States agency for the Choctaws in the Indian Territory. The agency was located about fifteen miles west of Fort Smith. The village which grew up around the agency came to be known as Skullyville, that word being a corruption of with the suffix, -''ville'', suggesting a literal translation of ''money town''. The agency itself, however, was called {{Lang, cho, Iskvlli ai Ilhpita, or 'the place where money is don ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Loaf County, Choctaw Nation
Sugar Loaf County was a political subdivision of the Choctaw Nation of Indian Territory, prior to Oklahoma being admitted as a state. The county formed part of the Nation's Moshulatubbee District, or First District, one of three administrative super-regions. History The county was also called ''Nvnih Chufvk Kaunti''. The Choctaw word ''nvnih'' means “a mountain or high hill” and ''chufvk'' means “a pointed object.” (The apparent lower-case letter “v” is the Greek letter upsilon, which makes a short “u” sound, for a pronunciation akin to ''“nunih chufuk.''”) This description referred to Sugar Loaf Mountain, which anchored the county's eastern border with Arkansas southeast of Poteau, east of the community of Gilmore. Sugar Loaf Mountain, whose summit is very conical, is locally prominent, rising from the valley floor to an elevation of 2,560 feet. Sugar Loaf County was one of the original 19 counties created by the General Council of the Choctaw Nation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshulatubbee District
Moshulatubbee District was one of three provinces, or districts, comprising the former Choctaw Nation in the Indian Territory. Also called the First District, it encompassed the northern one-third of the nation. In some historic records it is spelled Mushulatubbe. The Moshulatubbee District was named in honor of Chief Moshulatubbee, a Choctaw Indian warrior and statesman. Moshulatubbee was chief of the ''Okla Tannap'' ("Lower Towns") District in the original Choctaw Nation of the Southeast. Many Choctaw from that period referred to the Moshulatubbee District as the Okla Tannap District. The other two districts were known as Apukshunnubbee and Pushmataha, also named after important leaders. History The districts were established when the Choctaw Nation removed to the Indian Territory. These districts were intended as areas for members of the three major clans, or groupings of Choctaw who comprised the nation. In time, the clan affiliations and allegiances were reduced after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |