|
Cathorops Nuchalis
''Cathorops nuchalis'', the Orinoco sea catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1864. It is a tropical, fresh and saltwater catfish which occurs between Venezuela and Guyana. It reaches a standard length Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of fish anatomy, their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is ... of . References Ariidae Fish described in 1864 Taxa named by Albert Günther {{Ariidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Günther
Albert Karl Ludwig Gotthilf Günther , also Albert Charles Lewis Gotthilf Günther (3October 18301February 1914), was a German-born British zoologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. Günther is ranked the second-most productive reptile taxonomist (after George Albert Boulenger) with more than 340 reptile species described. Early life and career Günther was born in Esslingen in Swabia ( Württemberg). His father was a ''Stiftungs-Commissar'' in Esslingen and his mother was Eleonora Nagel. He initially schooled at the Stuttgart Gymnasium. His family wished him to train for the ministry of the Lutheran Church for which he moved to the University of Tübingen. A brother shifted from theology to medicine, and he, too, turned to science and medicine at Tübingen in 1852. His first work was "''Ueber den Puppenzustand eines Distoma''" (On the pupal state of ''Distoma''). He graduated in medicine with an M.D. from Tübingen in 1858, the same year in which he published a handbook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers", with some seemingly not having them. Siluriformes as a whole are Fish scale, scale-less, with neither the Armoured catfish, armour-plated nor the naked species having scales. This order of fish are Autapomorphy, defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish range in size and behavior from the three List of largest fish, largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivorous and scavenging bottom feeders, down to tiny ectoparasitic species known as the Candiru (fish), candirus. In the Southern United States, catfish species may be known by a variety of slang names, such as "mud cat", " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariidae
The Ariidae or ariid catfish are a family (taxonomy), family of catfish that mainly live in Marine (ocean), marine waters with many freshwater and brackish water species. They are found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate zones. The family includes about 143 species. Fossilized pectoral spines and skull bone fragments of ariid catfish are known from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian and Maastrichtian) of Argentina, which are among the oldest known remains of Siluroidea, siluroid catfish. Taxonomy The relationships of this family are not yet clear. Two of the genus, genera, ''Gogo (fish), Gogo'' and ''Ancharius (fish), Ancharius'', have been moved to a separate family called Anchariidae. The Ariidae are divided into three subfamilies: ''Galeichthys'' is the only genus classified in the subfamily Galeichthyinae and similarly ''Bagre (fish), Bagre'' is the only genus in the subfamily Bagreinae, while the rest of the genera are classified in the subfamily Ariinae. Previously, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's axial tilt; the width of the tropics (in latitude) is twice the tilt. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). Due to the overhead sun, the tropics receive the most solar energy over the course of the year, and consequently have the highest temperatures on the planet. Even when not directly overhead, the sun is still close to overhead throughout the year, therefore the tropics also have the lowest seasonal variation on the planet; "winter" and "summer" lose their temperature contrast. Instead, seasons are more commonly divided by precipitation variations than by temperature variations. The tropics maintain wide diversity of local climates, such as rain forests, monsoons, sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mineral-rich waters, such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranean rivers and lakes. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of vascular plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to survive. Fresh water is the water resource that is of the most and immediate use to humans. Fresh water is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltwater
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish water, but less salty than brine. The salt concentration is usually expressed in parts per thousand (permille, ‰) and parts per million (ppm). The USGS salinity scale defines three levels of saline water. The salt concentration in slightly saline water is 1,000 to 3,000 ppm (0.1–0.3%); in moderately saline water is 3,000 to 10,000 ppm (0.3–1%); and in highly saline water is 10,000 to 35,000 ppm (1–3.5%). Seawater has a salinity of roughly 35,000 ppm, equivalent to 35 grams of salt per one liter (or kilogram) of water. The saturation level is only nominally dependent on the temperature of the water. At one liter of water can dissolve about 357 grams of salt, a concentration of 26.3 percent by weight (% w/w). At (the boiling temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an area of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. Venezuela is a presidential republic consisting of States of Venezuela, 23 states, the Venezuelan Capital District, Capital District and Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital. The territory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the country's largest city. Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. With a land area of , Guyana is the third-smallest sovereign state by area in mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname, and is the List of South American countries by population, second-least populous sovereign state in South America after Suriname; it is also List of countries and dependencies by population density, one of the least densely populated countries on Earth. The official language of the country is English language, English, although a large part of the population is bilingual in English and the indigenous languages. It has a wide variety of natural habitats and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
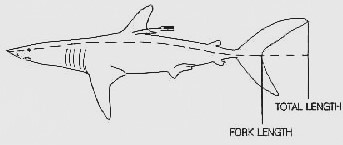
Standard Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of fish anatomy, their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the Glossary of ichthyology#H, hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal fin, caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most Actinopterygii, bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1864
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |