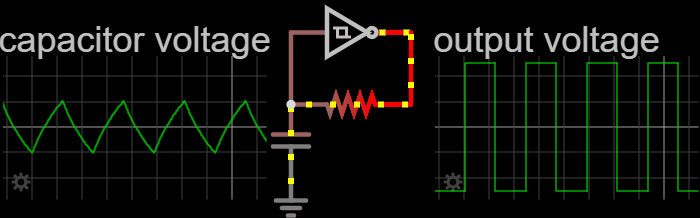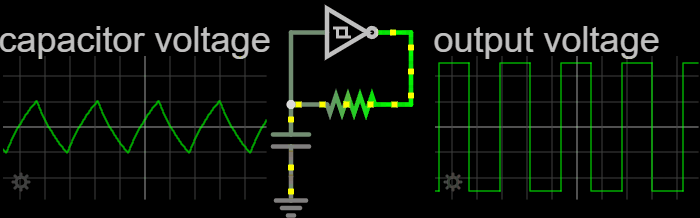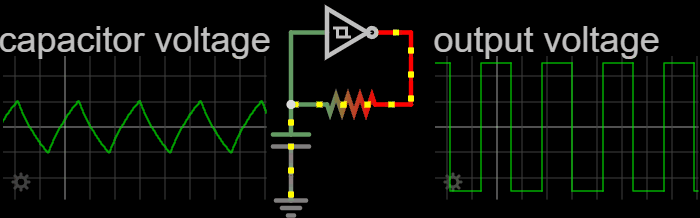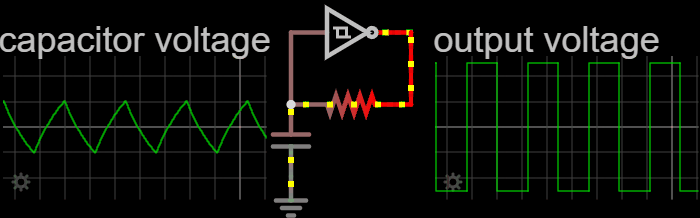
|
Cathode Follower Oscillator
The Cathode follower oscillator (or differential amplifier oscillator, emitter follower oscillator, source-coupled oscillator or Peltz oscillator) is an electronic oscillator electronic circuit, circuit in which the oscillation frequency is determined by a tuned circuit consisting of capacitors and inductors, that is, an LC oscillator. This oscillator uses one connection to get a signal from the LC-circuit and feeds an amplified signal back. The amplifier is a long-tail pair of two triodes, two p-channel bipolar transistors or two JFET, junction FETs. Operation Triode In the Cathode follower oscillator schematic, the long tail amplifier is connected to a tap of the LC-circuit inductance for a light load on the LC-circuit. A grid-leak couples the grid of the left triode to the LC-circuit. The left triode uses common anode circuit which has high input impedance, low output impedance and no voltage amplification. The long-tail resistor couples the two triodes. The right triode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peltz Oscillator Pnp
Peltz may refer to: * Dietrich Peltz (1914–2001), German Luftwaffe bomber pilot and general of the Wehrmacht * John Peltz (1861–1906), American professional baseball player * Mary Ellis Peltz (1890-1981) American opera critic, and founding editor of Opera News * Nelson Peltz (born 1942), American businessman * Nicola Peltz (born 1995), American actress * Perri Peltz (born 1961), American television journalist * Peter Peltz (1915–2001), American artist * Will Peltz William Peltz (born May 30, 1986) is an American actor, known for his roles in the supernatural horror film ''Unfriended'' (2014), the comedy-drama film '' Men, Women & Children'' (2014), and the supernatural drama television series ''Manifest'' ... (born 1986), American actor See also * Pelts {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found in many electronic devices, such as radio receivers, television sets, radio and television broadcast transmitters, computers, computer peripherals, cellphones, radar, and many other devices. Oscillators are often characterized by the frequency of their output signal: *A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an oscillator that generates a frequency below approximately 20 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesizers, to distinguish it from an audio frequency oscillator. *An audio oscillator produces frequencies in the audio range, 20 Hz to 20 kHz. *A radio frequency (RF) oscillator produces signals above the audio range, more generally in the range of 100 kHz to 100 GHz. There are two ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or Conductive trace, traces through which electric current can flow. It is a type of electrical circuit. For a circuit to be referred to as ''electronic'', rather than ''electrical'', generally at least one active component must be present. The combination of components and wires allows various simple and complex operations to be performed: signals can be amplified, computations can be performed, and data can be moved from one place to another. Circuits can be constructed of discrete components connected by individual pieces of wire, but today it is much more common to create interconnections by photolithographic techniques on a laminated Substrate (semiconductor), substrate (a printed circuit board or PCB) and solder the components to these interconnections to create a finished circuit. In an integrated circuit or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuned Circuit
An LC circuit, also called a resonant circuit, tank circuit, or tuned circuit, is an electric circuit consisting of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C, connected together. The circuit can act as an electrical resonator, an electrical analogue of a tuning fork, storing energy oscillating at the circuit's resonant frequency. LC circuits are used either for generating signals at a particular frequency, or picking out a signal at a particular frequency from a more complex signal; this function is called a bandpass filter. They are key components in many electronic devices, particularly radio equipment, used in circuits such as oscillators, filters, tuners and frequency mixers. An LC circuit is an idealized model since it assumes there is no dissipation of energy due to resistance. Any practical implementation of an LC circuit will always include loss resulting from small but non-zero resistance within the components and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the '' condenser microphone''. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The utility of a capacitor depends on its capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed specifically to add capacitance to some part of the circuit. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors, often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconductin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a Electromagnetic coil, coil. When the current flowing through the coil changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces an electromotive force (''emf'') (voltage) in the conductor, described by Faraday's law of induction. According to Lenz's law, the induced voltage has a polarity (direction) which opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors oppose any changes in current through them. An inductor is characterized by its inductance, which is the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of inductance is the Henry (unit), henry (H) named for 19th century American scientist Joseph Henry. In the measurement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LC Oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found in many electronic devices, such as radio receivers, television sets, radio and television broadcast transmitters, computers, computer peripherals, cellphones, radar, and many other devices. Oscillators are often characterized by the frequency of their output signal: *A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an oscillator that generates a frequency below approximately 20 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesizers, to distinguish it from an audio frequency oscillator. *An audio oscillator produces frequencies in the audio range, 20 Hz to 20 kHz. *A radio frequency (RF) oscillator produces signals above the audio range, more generally in the range of 100 kHz to 100 GHz. There are two general types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-tail Pair
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs V_\text^- and V_\text^+ and one output V_\text, in which the output is ideally proportional to the difference between the two voltages: : V_\text = A(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where A is the gain of the amplifier. Single amplifiers are usually implemented by either adding the appropriate feedback resistors to a standard op-amp, or with a dedicated integrated circuit containing internal feedback resistors. It is also a common sub-component of larger integrated circuits handling analog signals. Mathematics of the amplifier : V_\text = A_\text(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where V_\text^+ and V_\text^- are the input voltages, and A_\text is the differential gain. In practice, however, the gain is not quite equal for the two inputs. This means, for instance, that if V_\text^+ an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triodes
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''thermionic valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode (Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention helped make amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony possible. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophiles who p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Transistors
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small Electric current, current injected at one of its Terminal (electronics), terminals to control a much larger current between the remaining two terminals, making the device capable of Amplifier, amplification or Electronic switch, switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the Doping (semiconductor), doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |