|
Catherine Descartes
Catherine Descartes (1637–1706) was a French poet and philosopher, and the niece of French philosopher René Descartes. A prominent figure in the French salon movement, her best known works included "Shade of Descartes" (''"L'Ombre de Descartes"'') and ''Report on the Death of M. Descartes, the Philosopher''. She was also interviewed by her uncle's biographer Adrien Baillet following his death, due to her close relationship with him. Regarded as one of the influential ''cartésiennes'', a sub-movement of women who discussed the works of René Descartes, she became more critical of the masculine aspects of his philosophy later in life. Early life Born in 1637, her father was Pierre de la Bretailliere, the older brother of René Descartes and a councillor in the Parlemant of Brittany. Catherine Descartes was the youngest of four sisters and had at least two brothers. Admired for her intellect, there was a popular saying that her famous uncle's "mantle" had "fallen on the distaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Descartes I Samtal Med Sveriges Drottning, Kristina
René (''born again'' or ''reborn'' in French) is a common first name in French-speaking, Spanish-speaking, and German-speaking countries. It derives from the Latin name Renatus. René is the masculine form of the name (Renée being the feminine form). In some non-Francophone countries, however, there exists the habit of giving the name René (sometimes spelled without an accent) to girls as well as boys. In addition, both forms are used as surnames (family names). René as a first name given to boys in the United States reached its peaks in popularity in 1969 and 1983 when it ranked 256th. Since 1983 its popularity has steadily declined and it ranked 881st in 2016. René as a first name given to girls in the United States reached its peak in popularity in 1962 when it ranked 306th. The last year for which René was ranked in the top 1000 names given to girls in the United States was 1988. Persons with the given name * René, Duke of Anjou (1409–1480), titular king of Naple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathematics was central to his method of inquiry, and he connected the previously separate fields of geometry and algebra into analytic geometry. Descartes spent much of his working life in the Dutch Republic, initially serving the Dutch States Army, later becoming a central intellectual of the Dutch Golden Age. Although he served a Protestant state and was later counted as a deist by critics, Descartes considered himself a devout Catholic. Many elements of Descartes' philosophy have precedents in late Aristotelianism, the revived Stoicism of the 16th century, or in earlier philosophers like Augustine. In his natural philosophy, he differed from the schools on two major points: first, he rejected the splitting of corporeal substance i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salon (France)
The salons of Early Modern Revolutionary France played an integral role in the cultural and intellectual development of France. The salons were seen by contemporary writers as a cultural hub, for the upper middle class and aristocracy, responsible for the dissemination of good manners and sociability. It was not merely manners that the salons spread, but also ideas, as the salons became a center of intellectual conversation, as well as a debate stage for social issues, playing host to many members of the Republic of Letters. In contrast to other Early Modern institutions, women played an important and visible role within the salons. Each woman, or Salonniere, played a different role within these Salons. Some were actively involved in conversation and debate, while others just used their connections to bring others together and spread Enlightenment ideas. Historiography of the Salons The historiography of the salons is far from straightforward. The salons have been studied in dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrien Baillet
Adrien Baillet (13 June 164921 January 1706) was a French scholar and critic. He is now best known as a biographer of René Descartes. Life He was born in the village of Neuville near Beauvais, in Picardy. His parents could only afford to send him to a small school in the village, but he picked up some Latin from the friars of a neighbouring convent, who brought him under the notice of the bishop of Beauvais. By his kindness Baillet received a thorough education at the theological seminary, and was afterwards appointed to a post as teacher in the college of Beauvais. In 1676 he was ordained priest and was presented to a small vicarage. The article contains this footnote: See the edition by M. de la Monnoye of the ''Jugemens des savans'' (Amsterdam, 4 vols. 1722), which contains the ''Anti-Baillet'' of Gilles Ménage, and an ''Abrégé de la vie de Mr Baillet''. He accepted in 1680 the appointment of librarian to François-Chrétien de Lamoignon, advocate-general to the parleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conseiller D'État (France)
In France, a Councillor of State (French: ''conseiller d'État'') is a high-level government official of administrative law in the French Council of State. Under the Ancien Régime Councillors of State were among the highest dignitaries of the French monarchy during the Ancien Régime. Being thirty in total, the Councillors of State included three clergymen, three from the old nobility (nobility "of the sword" or ''d'épée''), and twenty-four from the ''noblesse de robe'', or "administrative nobility". Ninety percent of the Councillors of State ''de robe'' were promoted from among the Masters of Requests, while the rest were chosen from among judges of the prerogative courts; often they had prior experience working as intendants. In 1789, their number was increased to 42: 25 full-time Councillors ordinary, 16 part-time consellors who functioned on a semester schedule, and the eldest of the Masters of Requests. Their title gave them great power, and in the administrative hierarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parlement
A ''parlement'' (), under the French Ancien Régime, was a provincial appellate court of the Kingdom of France. In 1789, France had 13 parlements, the oldest and most important of which was the Parlement of Paris. While both the modern French term ''parlement'' (for the legislature) and the English word ''parliament'' derive from this French term, the Ancien Régime parlements were not legislative bodies and the modern and ancient terminology are not interchangeable. History Parlements were judicial organizations consisting of a dozen or more appellate judges, or about 1,100 judges nationwide. They were the courts of final appeal of the judicial system, and typically wielded power over a wide range of subjects, particularly taxation. Laws and edicts issued by the Crown were not official in their respective jurisdictions until the parlements gave their assent by publishing them. The members of the parlements were aristocrats, called nobles of the robe, who had bought or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period of Roman occupation. It became an independent kingdom and then a duchy before being united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province governed as a separate nation under the crown. Brittany has also been referred to as Little Britain (as opposed to Great Britain, with which it shares an etymology). It is bordered by the English Channel to the north, Normandy to the northeast, eastern Pays de la Loire to the southeast, the Bay of Biscay to the south, and the Celtic Sea and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its land area is 34,023 km2 . Brittany is the site of some of the world's oldest standing architecture, home to the Barnenez, the Tumulus Saint-Michel and others, which date to the early 5th millennium BC. Today, the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
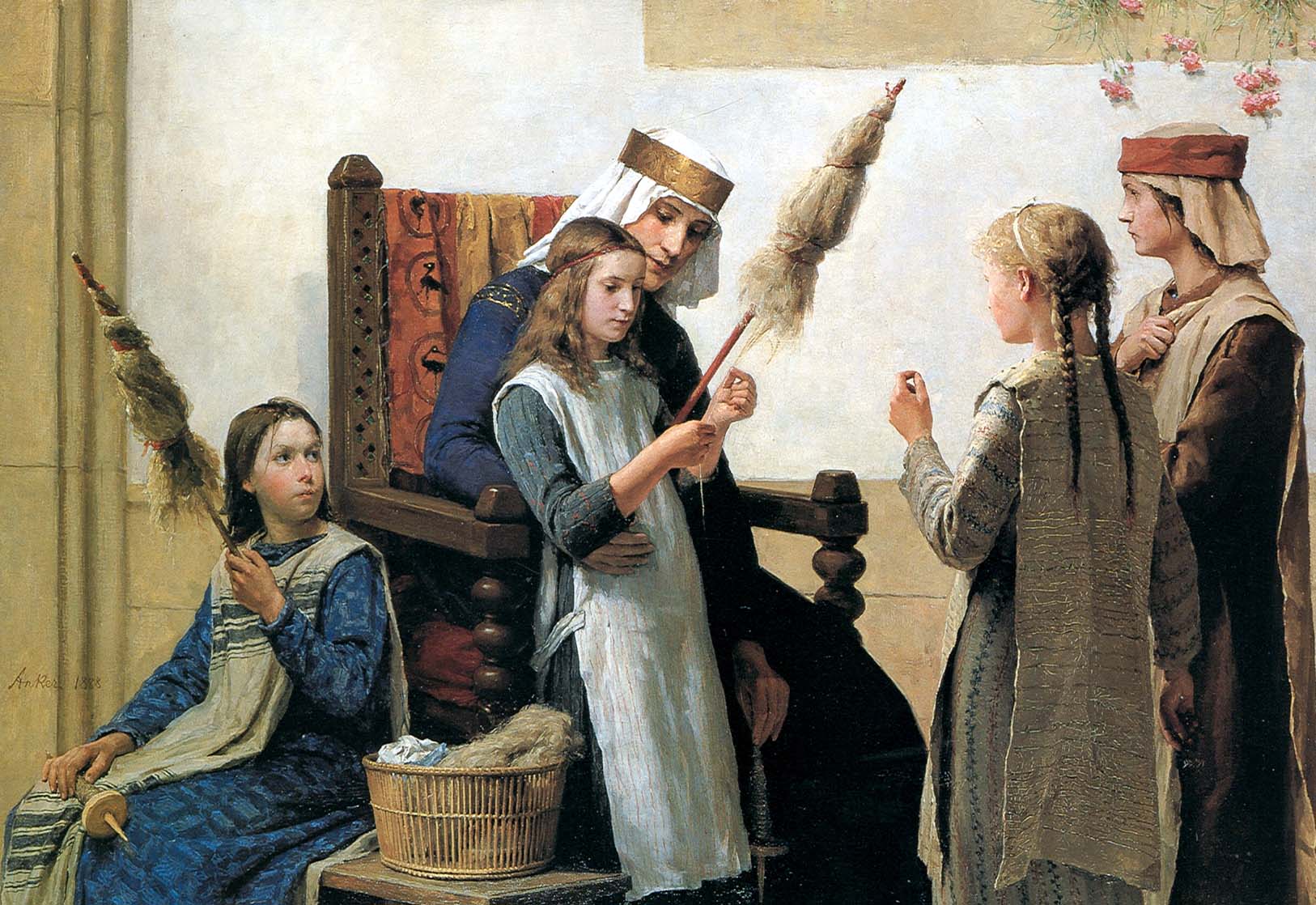
Distaff Side
A distaff (, , also called a rock"Rock." ''The Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd ed. 1989.), is a tool used in spinning. It is designed to hold the unspun fibers, keeping them untangled and thus easing the spinning process. It is most commonly used to hold flax and sometimes wool, but can be used for any type of fibre. Fiber is wrapped around the distaff and tied in place with a piece of ribbon or string. The word comes from Low German ''dis'', meaning a bunch of flax, connected with staff. As an adjective, the term ''distaff'' is used to describe the female side of a family. The corresponding term for the male side of a family is the "spear" side. Form In Western Europe, there were two common forms of distaves, depending on the spinning method. The traditional form is a staff held under one's arm while using a spindle – see the figure illustration. It is about long, held under the left arm, with the right hand used in drawing the fibres from it."Distaff." ''The Oxford Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine De Vivonne, Marquise De Rambouillet
Catherine de Vivonne, marquise de Rambouillet (1588 – 2 December 1665), known as Madame de Rambouillet, was a society hostess and a major figure in the literary history of 17th-century France. {{French literature sidebar Life Born in Rome, she was the daughter and heiress of Jean de Vivonne, marquis of Pisani, and Giulia Savelli, who belonged to a noble Roman family. She was married at the age of twelve to Charles d'Angennes, ''vidame du Mans'', and in 1612, ''marquis de Rambouillet''. They had seven children, two sons and five daughters. The young, beautiful and witty marquise found the coarseness and intrigues of the French court little to her taste and, in 1620, she began to gather around her the circle that gave its renown to her salon. She and her husband had taken residence in Paris at the Hôtel Pisani, later renamed ''Hôtel de Rambouillet'', and which she restored between 1618 and 1620. It was situated ''rue Saint-Thomas-du-Louvre'', between the Louvre and the Tuileri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie De Rabutin-Chantal, Marquise De Sévigné
Marie de Rabutin-Chantal, marquise de Sévigné (5 February 1626 – 17 April 1696), also widely known as Madame de Sévigné or Mme de Sévigné, was a French aristocrat, remembered for her letter-writing. Most of her letters, celebrated for their wit and vividness, were addressed to her daughter, Françoise-Marguerite de Sévigné. She is revered in France as one of the great icons of French 17th-century literature. Life Marie de Rabutin-Chantal was born in the fashionable Place des Vosges (then called the ''Place Royale''), Paris, to an old and distinguished family from Burgundy. Her father, Celse Bénigne de Rabutin, baron de Chantal, was the son of Saint Jeanne Françoise de Chantal, a friend and disciple of Saint Francis de Sales; her mother was Marie de Coulanges. Her father was killed during the English attack on the Isle of Rhé in July 1627, which began the Anglo-French War of 1627-1629. His wife did not survive him by many years, and Marie was left an orphan at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Françoise-Marguerite De Sévigné
Françoise-Marguerite de Sévigné, comtesse de Grignan (10 October 1646 – 13 August 1705), was a French aristocrat, remembered for the letters that her mother, Madame de Sévigné, wrote to her. Life Françoise-Marguerite was born in Paris, France, on 10 October 1646, in the fashionable Place des Vosges. She was the first child of Henri de Sévigné and his young wife, Marie de Rabutin-Chantal. Two years later, at the family's Château des Rochers-Sévigné in Brittany, her brother, Charles de Sévigné, was born. In 1651, Henri was killed in a duel over his mistress, Madame de Gondran. Now a widow, the Marquise de Sévigné took her children back to Paris where they came to live with her uncle, l'abbé de Coulanges, in the Marais district. After her mother became well-established in the royal court of Louis XIV, 17-year-old Françoise-Marguerite made her court debut in the Royal Ballets des Arts, dancing a lead role as a shepherdess alongside Louis, himself, as a shepherd. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeleine De Scudéry
Madeleine de Scudéry (15 November 1607 – 2 June 1701), often known simply as Mademoiselle de Scudéry, was a French writer. Her works also demonstrate such comprehensive knowledge of ancient history that it is suspected she had received instruction in Greek and Latin. In 1637, following the death of her uncle, Scudéry established herself in Paris with her brother, Georges de Scudéry, who became a playwright. Madeleine often used her older brother's name, George, to publish her works. She was at once admitted to the Hôtel de Rambouillet coterie of préciosité, and afterwards established a salon of her own under the title of the ''Société du samedi'' (''Saturday Society''). For the last half of the 17th century, under the pseudonym of Sapho or her own name, she was acknowledged as the first bluestocking of France and of the world. She formed a close romantic relationship with Paul Pellisson which was only ended by his death in 1693. She never married. Biography Born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |