|
Catalpa Fargesii
''Catalpa fargesii'', the Chinese bean tree, is a species of tree in the family Bignoniaceae, native to China. Growing to about 25 m tall, it is a deciduous tree which produces abundant pink blossom in spring, followed by narrow brown beans-like fruit in the autumn. Some sources place the species as a synonym of ''Catalpa bungei''. Description The tree can grow up to tall. It has a petiole (leaf-stems) which are long. It has leaves which are broadly ovate, straight or slightly heart-shaped at the base, or long and taper-pointed. They are long and wide. They have a soft, downy underside, which does fade at the end of the growing season. It blooms in summer, The flowers are similar in form to those of paulownia. The corolla is bell-shaped, two-lipped flowers are borne in corymbs or racemes, of between 7 and 15 individual flowers. They are long. They come in shades from lilac, pinkish, or pale red to pale purple. The throat is freckled with purple, brownish red, or brownish sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ãdouard Bureau
Louis Ãdouard Bureau (25 May 1830 in Nantes – 14 December 1918 in Paris) was a French physician and botanist. Ãdouard Bureau began his medical studies in Nantes in 1848, where he held the post of director of the Muséum de Nantes (Nantes Museum). He completed his medical degree in Paris in 1852. In 1872 he obtained a post as a naturalist assistant at the ''Muséum national d'histoire naturelle'' (French National Museum of Natural History) in the laboratory of Adolphe Brongniart, where he replaced Edmond Tulasne. In 1874 he received appointment to the new botany post dealing with classification. Beginning in 1875, he was a director of the herbaria at the museum. He was a professor at the museum from 1874 until he retired in 1905. Adrien Franchet was his assistant in the 80's. He was succeeded by Paul Henri Lecomte. Bureau was one of the founders of the ''Société botanique de France'' (''French Botanical Society'') and was the chairman in 1875, 1883, 1902 and 1905. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
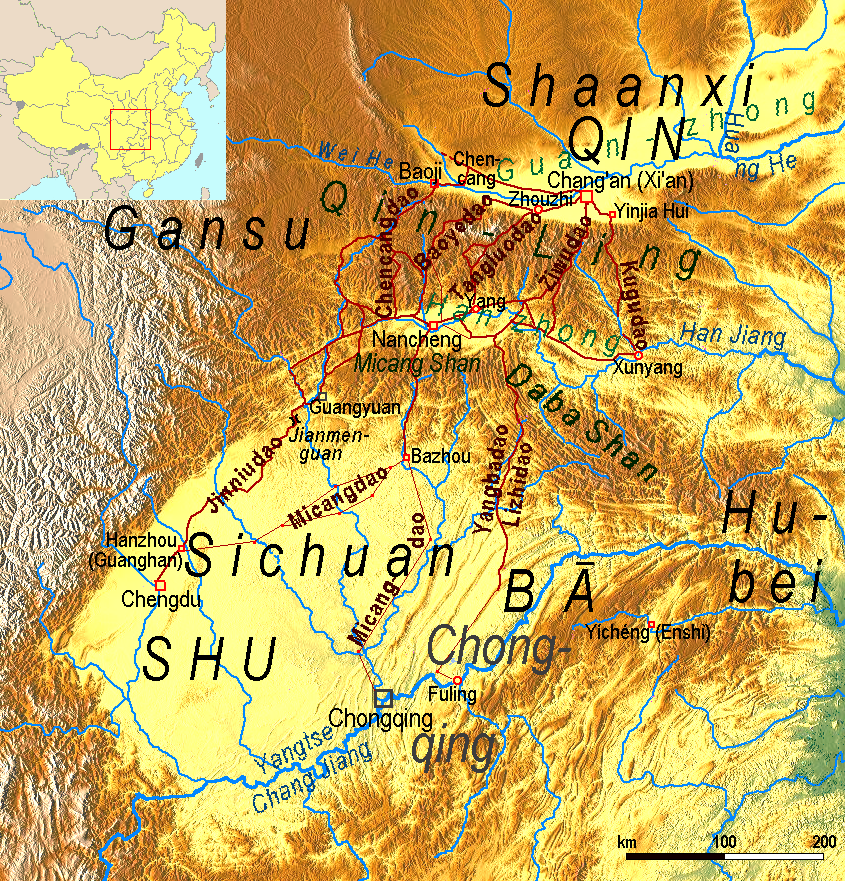
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=SìchuÄn; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalpa
''Catalpa'', commonly called catalpa or catawba, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to warm temperate and subtropical regions of North America, the Caribbean, and East Asia. Description Most ''Catalpa'' are deciduous trees; they typically grow to tall, with branches spreading to a diameter of about . They are fast growers and a 10-year-old sapling may stand about tall. They have characteristic large, heart-shaped leaves, which in some species are three-lobed. The appearance of the leaves sometimes causes confusion with species such as the unrelated tung tree (''Vernicia fordii'') and ''Paulownia tomentosa''. ''Catalpa'' species bear broad panicles of showy flowers, generally in summer. The flower colour generally is white to yellow. In late summer or autumn the fruit appear; they are siliques about long, full of small flat seeds, each with two thin wings to aid in wind dispersal. The large leaves and dense foliage of ''Catalpa'' species provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Award Of Garden Merit
The Award of Garden Merit (AGM) is a long-established annual award for plants by the British Royal Horticultural Society (RHS). It is based on assessment of the plants' performance under UK growing conditions. History The Award of Garden Merit is a mark of quality awarded, since 1922, to garden plants (including trees, vegetables and decorative plants) by the United Kingdom, Royal Horticultural Society (RHS). Awards are made annually after plant trials intended to judge the plants' performance under UK growing conditions. Trials may last for one or more years, depending on the type of plant being analyzed, and may be performed at Royal Horticulture Society Garden in Wisley and other gardens or after observation of plants in specialist collections. Trial reports are made available as booklets and on the website. Awards are reviewed annually in case plants have become unavailable horticulturally, or have been superseded by better cultivars. Similar awards The award should not b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Horticultural Society
The Royal Horticultural Society (RHS), founded in 1804 as the Horticultural Society of London, is the UK's leading gardening charity. The RHS promotes horticulture through its five gardens at Wisley (Surrey), Hyde Hall (Essex), Harlow Carr (North Yorkshire), Rosemoor (Devon) and Bridgewater (Greater Manchester); flower shows including the Chelsea Flower Show, Hampton Court Palace Flower Show, Tatton Park Flower Show and Cardiff Flower Show; community gardening schemes; Britain in Bloom and a vast educational programme. It also supports training for professional and amateur gardeners. the president was Keith Weed and the director general was Sue Biggs CBE. History Founders The creation of a British horticultural society was suggested by John Wedgwood (son of Josiah Wedgwood) in 1800. His aims were fairly modest: he wanted to hold regular meetings, allowing the society's members the opportunity to present papers on their horticultural activities and discoveries, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form (botany)
In botanical nomenclature, a ''form'' (''forma'', plural ''formae'') is one of the "secondary" taxonomic ranks, below that of variety, which in turn is below that of species; it is an infraspecific taxon. If more than three ranks are listed in describing a taxon, the "classification" is being specified, but only three parts make up the "name" of the taxon: a genus name, a specific epithet, and an infraspecific epithet. The abbreviation "f." or the full "forma" should be put before the infraspecific epithet to indicate the rank. It is not italicised. For example: * ''Acanthocalycium spiniflorum'' f. ''klimpelianum'' or ** ''Acanthocalycium spiniflorum'' forma ''klimpelianum'' (Weidlich & Werderm.) Donald * '' Crataegus aestivalis'' (Walter) Torr. & A.Gray var. ''cerasoides'' Sarg. f. ''luculenta'' Sarg. is a classification of a plant whose name is: ** ''Crataegus aestivalis'' (Walter) Torr. & A.Gray f. ''luculenta'' Sarg. A form usually designates a group with a noticeable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalpa Bignonioides
''Catalpa bignonioides'' is a species of '' Catalpa'' that is native to the southeastern United States in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, and Mississippi. Common names include southern catalpa, cigartree, and Indian-bean-tree (or Indian bean tree). It is commonly used as a garden and street tree. Description It is a medium-sized deciduous tree growing to tall, with a trunk up to diameter, with brown to gray bark, maturing into hard plates or ridges. The short thick trunk supports long and straggling branches which form a broad and irregular head. The roots are fibrous and branches are brittle, its juices are watery and bitter tasting. The leaves are large, bright green and heart shaped, being long and broad. They appear late, and as they are full-grown before the flower clusters open, they add much to the beauty of the blossoming tree. They secrete nectar, a most unusual characteristic for leaves, by means of groups of tiny glands in the axils of the primary veins. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinling
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major eastâwest mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow River systems, providing a natural boundary between North and South China and support a huge variety of plant and wildlife, some of which is found nowhere else on earth. To the north is the densely populated Wei River valley, an ancient center of Chinese civilization. To the south is the Han River valley. To the west is the line of mountains along the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. To the east are the lower Funiu and Dabie Shan which rise out of the coastal plain. The northern side of the range is prone to hot weather, however the physical barrier of the mountains mean that the land to the North has a semi-arid climate, with the lack of rich, fertile landscape that can not support a wealth of wildlife. The mountains also acte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of China
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects EastâWest cultural, ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small and usually only have precipitation changes. In temperate climates, not only do latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistency of frost. However, other climate classifications set the minimum at . Zones and climates The north temperate zone extends from the Tropic of Cancer (approximately 23.5° north latitude) to the Arctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital, Wuhan, serves as a major transportation hub and the political, cultural, and economic hub of central China. Hubei's name is officially abbreviated to "" (), an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the State of E of the Western Zhou dynasty of â771 BCE; a popular name for Hubei is "" () (suggested by that of the powerful State of Chu, which existed in the area during the Eastern Zhou dynasty of 770 â 256 BCE). Hubei borders the provinces of Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxi to the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province. Hubei is the 7th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)