|
Castration In Ancient Rome
Sexual attitudes and behaviors in ancient Rome are indicated by Roman art, art, Latin literature, literature, and Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum, inscriptions, and to a lesser extent by classical archaeology, archaeological remains such as erotic artifacts and Roman architecture, architecture. It has sometimes been assumed that "unlimited sexual license" was characteristic of ancient Rome, but sexuality was not excluded as a concern of the ''mos maiorum'', the traditional social norms that affected public, private, and military life. ''Pudor'', "shame, modesty", was a regulating factor in behavior, as were legal strictures on certain sexual transgressions in both the Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial periods. The Roman censor, censors—Roman magistrate, public officials who determined the Social class in ancient Rome, social rank of individuals—had the power to remove Roman citizenship, citizens from the Roman senate, senatorial or equestrian order for sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
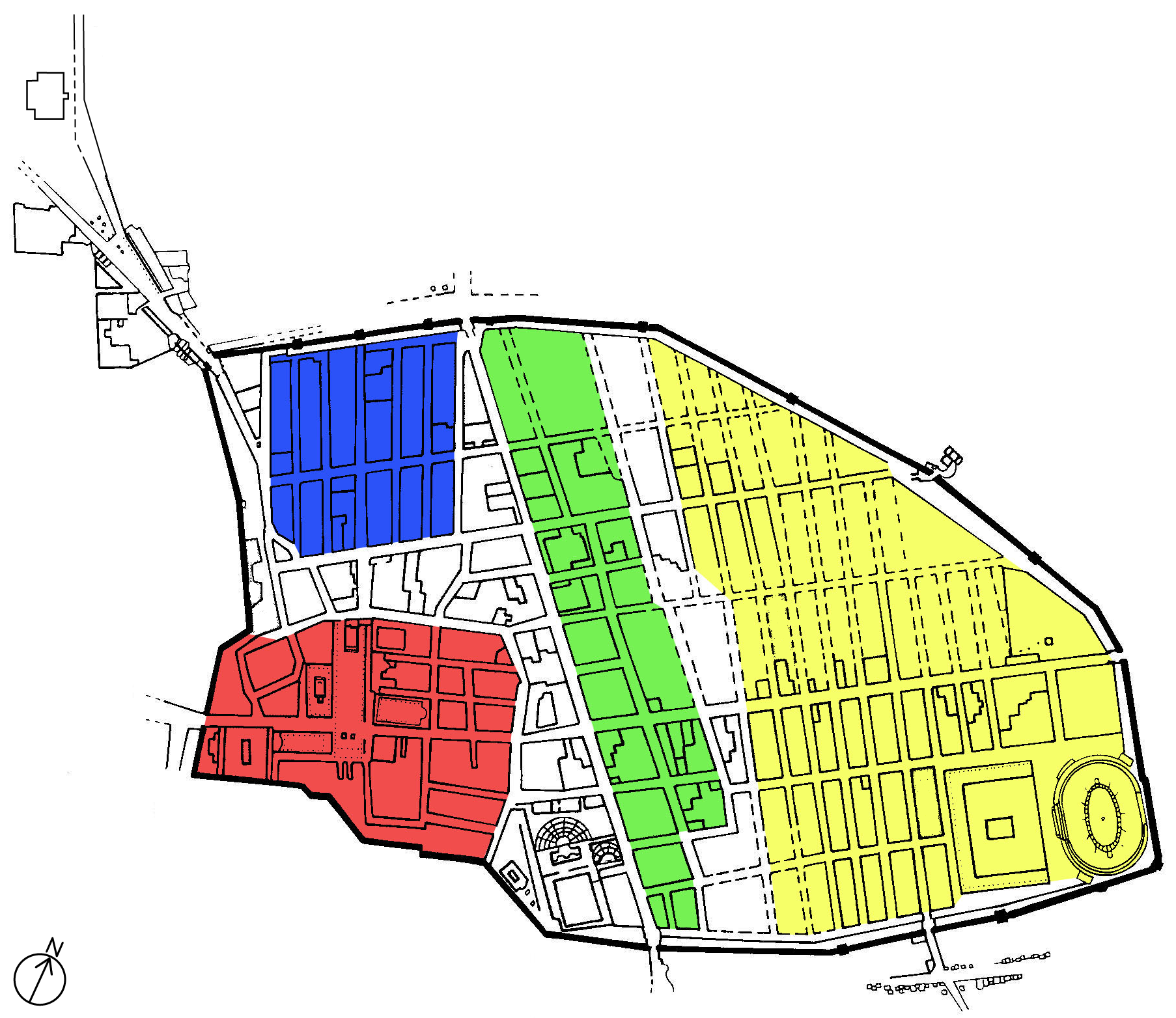
Pompeii - Casa Del Fauno - Satyr And Nymph - MAN
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash; their eventual decay allowed archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |