|
Castle Lake (California)
Castle Lake is a glacial lake (''cirque'' lake or tarn (lake), tarn) located in the Trinity Mountains, in Siskiyou County of northern California. It is west of Mount Shasta, California, Mount Shasta City and Mount Shasta peak. The outlet of the lake drains into Castle Lake Creek, and then into Lake Siskiyou reservoir, part of the headwaters of the Sacramento River. Nearly all of the lake's are within the Shasta-Trinity National Forest. Trails lead from Castle Lake into the adjacent Castle Crags Wilderness area, and on to Castle Crags State Park, including trails to Little Castle Lake and Heart Lake. Fishing, camping, and hiking are also available at or near the lake. Natural history Castle Lake and the surrounding area contain a wide variety of animals and plants including trout, bears, deer, otters, frogs, and osprey. The area is also well-known for early summer displays of flowers, including red Columbine (''Aquilegia truncata''), fawn lily (''Erythronium sp.''), and Shasta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
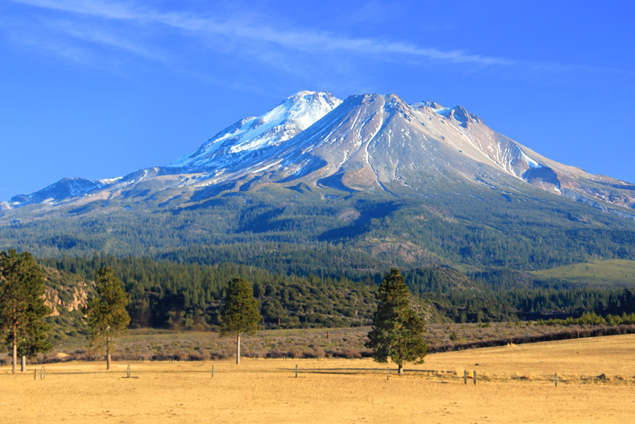
Mount Shasta
Mount Shasta ( ; Shasta people, Shasta: ''Waka-nunee-Tuki-wuki''; Karuk language, Karuk: ''Úytaahkoo'') is a Volcano#Volcanic activity, potentially active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. At an elevation of , it is the second-highest peak in the Cascades and the List of California fourteeners, fifth-highest in the state. Mount Shasta has an estimated volume of , which makes it the most voluminous stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanoes, Cascade Volcanic Arc. The mountain and surrounding area are part of the Shasta–Trinity National Forest. Description The origin of the name "Shasta people#Origin of name, Shasta" is vague, either derived from a Shasta people, people of a name like it or otherwise garbled by early Westerners. Mount Shasta is connected to its satellite cone of Shastina, and together they dominate the landscape. Shasta rises abruptly to tower nearly above its surroundings. On a clear winter day, the mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California At Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a public land-grant research university in Davis, California, United States. It is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The institution was first founded as an agricultural branch of the system in 1905 and became the sixth campus of the University of California in 1959. Founded as a primarily agricultural campus, the university has expanded over the past century to include graduate and professional programs in medicine (which includes the UC Davis Medical Center), engineering, science, law, veterinary medicine, education, nursing, and business management, in addition to 90 research programs offered by UC Davis Graduate Studies. The UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine is the largest veterinary school in the United States. UC Davis also offers certificates and courses, including online classes, for adults and non-traditional learners through its Division of Continuing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headwall
In physical geography and geology, the headwall of a glacier, glacial cirque (landform), cirque is its highest cliff. The term has been more broadly used to describe similar geomorphic features of non-glacial origin consisting of a concave depression with convergent slopes typically of 65 percent or greater forming the upper end of a drainage valley. In civil engineering, a headwall is a small retaining wall placed at the inlet or outlet of a stormwater pipe or culvert. In medicine, a headwall is the wall at the head end of a hospital bedspace. The bed abuts this headwall perpendicularly, which is furnished with equipment such as regulators for supplemental oxygen, regulators for suction, suction canisters, connections for the call bell system, lighting, electrical outlets, and often a vital signs monitor. References Glaciology {{Geo-term-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Fishing
Ice fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities. Shelters Longer fishing expeditions can be mounted with simple structures. Larger, heated structures can make multiple day fishing trips possible. A structure with various local names, but often called an ice shanty, ice shack, fish house, shack, icehouse, bobhouse, or ice hut, is sometimes used. These are dragged or towed onto the lake using a vehicle such as a snowmobile, ATV or truck. The two most commonly used types are portable and permanent. The portable houses are often made of a heavy material that is usually watertight. The two most common types of portable houses are those with a shelter that flips behind the user when not needed, or pop up shelters with a door as the only way out. The permanent shelters are made of wood or metal and usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowshoe
Snowshoes are specialized outdoor gear for walking over snow. Their large footprint spreads the user's weight out and allows them to travel largely on top of rather than through snow. Adjustable bindings attach them to appropriate winter footwear. Traditional snowshoes have a hardwood frame filled in with rawhide (material), rawhide latticework. Modern snowshoes are made of lightweight metal, plastic, and other synthetic materials. In the past, snowshoes were essential equipment for anyone dependent on travel in deep and frequent snowfall, such as Animal trapping, fur trappers. They retain that role in areas where motorized vehicles cannot reach or are inconvenient to use. However, their greatest contemporary use is for recreation. Snowshoeing is easy to learn and in appropriate conditions is a relatively safe and inexpensive recreational activity. However, doing so in icy, steep terrain requires both advanced skill and mountaineering-style pivoting-crampon snowshoes. Devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-country Skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing whereby skiers traverse snow-covered terrain without use of ski lifts or other assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreational activity; however, some still use it as a means of travel. Variants of cross-country skiing are adapted to a range of terrain which spans unimproved, sometimes mountainous terrain to groomed courses that are specifically designed for the sport. Modern cross-country skiing is similar to the original form of skiing, from which all skiing disciplines evolved, including alpine skiing, ski jumping and Telemark skiing. Skiers propel themselves either by striding forward (classic style) or side-to-side in a skating motion (skate skiing), aided by arms pushing on ski poles against the snow. It is practised in regions with snow-covered landscapes, including Europe, Canada, Russia, the United States, Australia and New Zealand. Cross-country skiing (sport), Competitive cross-country skiing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
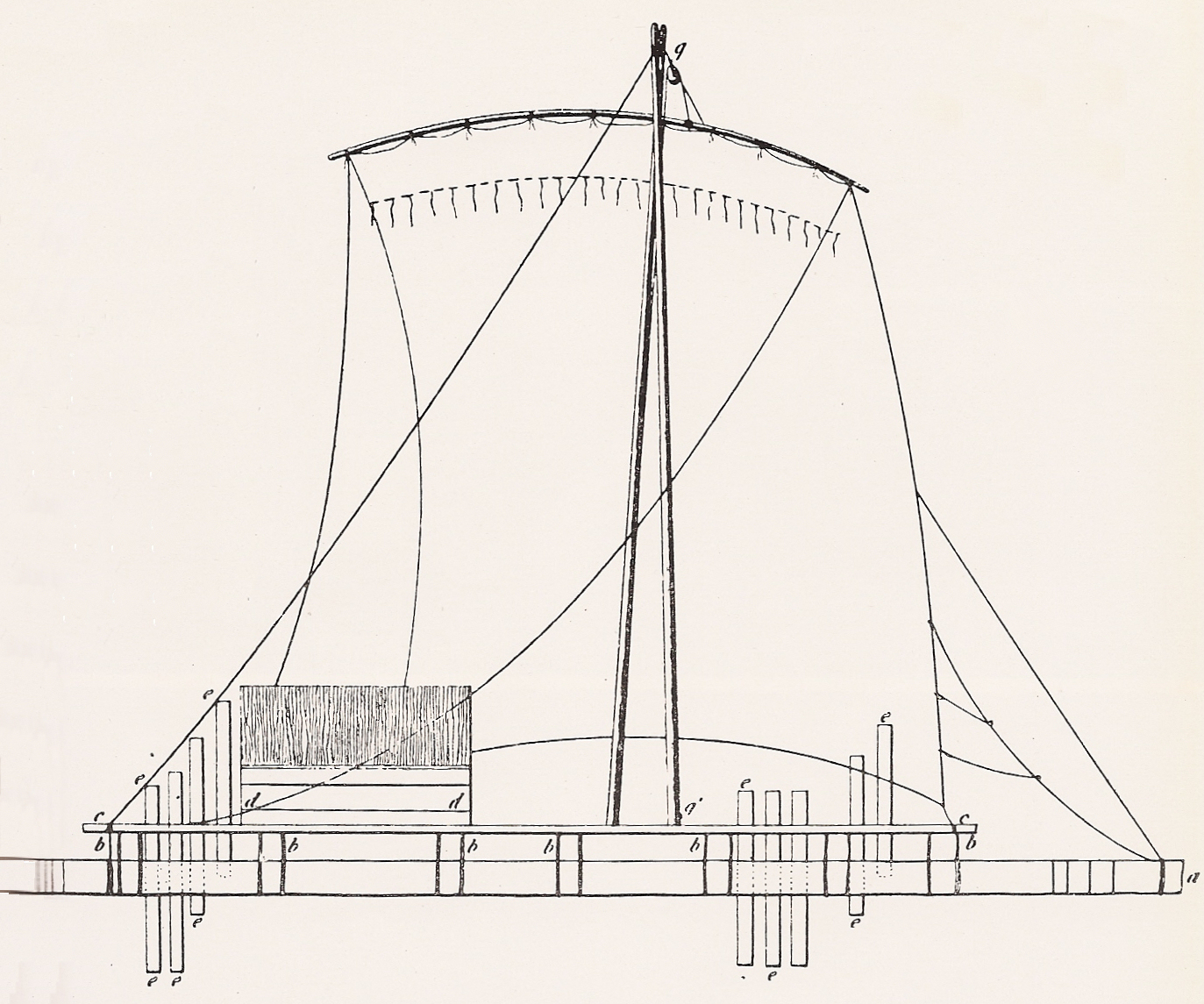
Raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, by tying them together into rafts and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayaking
Kayaking is the use of a kayak for moving over water. It is distinguished from canoeing by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. A kayak is a low-to-the-water, canoe-like boat in which the paddler sits facing forward, legs in front, using a double-bladed paddle to pull front-to-back on one side and then the other in rotation. Most kayaks have closed decks, although sit-on-top and inflatable kayaks are growing in popularity as well. History Kayaks were created thousands of years ago by Inuit of the northern Arctic regions. They used driftwood and sometimes the skeleton of whales, to construct the frame of the kayak, and animal skin, particularly seal skin was used to create the body. The main purpose for creating the kayak, which literally translates to "hunter's boat" was for hunting and fishing. The kayak's stealth capabilities allowed for the hunter to sneak up behind animals on the shoreline and successfully catch their prey. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, such as saltwater or freshwater environments, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Swimmers achieve locomotion by coordinating limb and body movements to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that results in directional motion. Newborns can instinctively hold their breath underwater and exhibit rudimentary swimming movements as part of a survival reflex. Swimming requires endurance, skill and efficient techniques to maximize speed and minimize energy consumption. Swimming is a popular activity and competitive sport where certain techniques are deployed to move through water. It offers numerous health benefits, such as strengthened cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and increased flexibility. It is suitable for people of all ages and fitness levels. Swimming is consistently among the top public recreational activities, and in some countries, swimming lessons are a compulsory part of the educational curriculum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Lake (California) - Swimmer With Mt
{{geodis ...
Castle Lake may refer to: *Castle Lake (California), a glacially-formed cirque lake in Siskiyou County * Castle Lake (Idaho), an alpine lake in Custer County * Castle Lake (Nevada), a glacial tarn in Elko County * Castle Lake (Washington), a barrier lake formed by the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens * Castle Lake (Park County, Montana), a lake in Park County * Castle Lake (Meagher County, Montana), a lake in Meagher County * Castle Lake, a reservoir in Henry County, Indiana Henry County is a county located in east central Indiana, United States. As of 2020, the population was 48,914. The county seat and largest and only city is New Castle. Henry County is the main setting of the novel '' Raintree County'' by Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shasta Springs
Shasta Springs was a popular summer resort during the late 19th and early 20th centuries on the Upper Sacramento River in northern California. It was located just north of the town of Dunsmuir, and just north of Upper Soda Springs along the Siskiyou Trail. The resort was on the main line of the Southern Pacific Railroad, where natural springs on the property were the original sources of the water and beverages that became known as the Shasta brand of soft drinks. The resort closed in the early 1950s when it was sold and continues to be owned by the Saint Germain Foundation, and is used as a major facility by that organization. It is no longer open to the public and the lower part of the resort – the bottling plant, the train station, the incline railway, the kiosk and the fountains – are all gone. The falls that were visible from the railroad tracks and what ruins are left of the lower part of the resort are all overgrown by blackberry bushes. Angel Trail and Mineral Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |