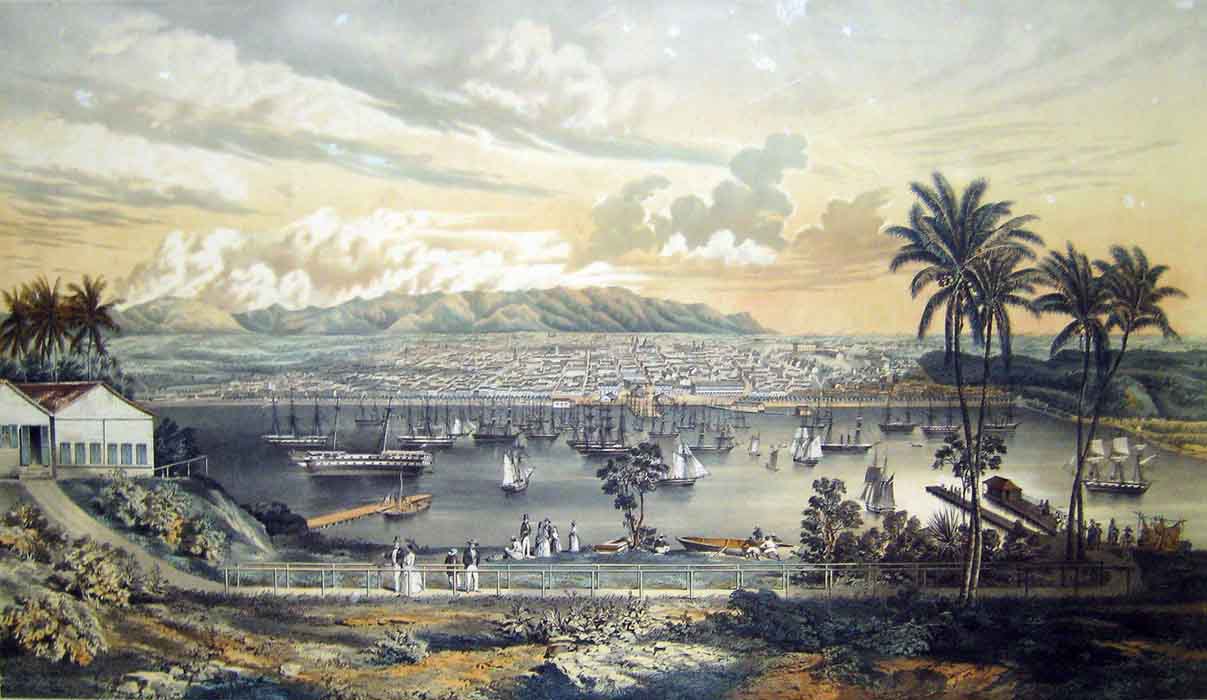|
Castillo De La Real Fuerza
The Castillo de la Real Fuerza (Castle of the Royal Force) is a bastion fort on the western side of the harbour in Havana, Cuba Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ..., set back from the entrance, and bordering the Plaza de Armas, Havana, Plaza de Armas. Originally built to defend against attack by pirates, it suffered from a poor location; it was too far inside the bay. The fort is considered to be the oldest stone fort in the Americas, and was listed in 1982 as part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of "Old Havana, Old Havana and its Fortifications". History A previous fort, the Fuerza Vieja (Old Fort), was damaged in 1555 during an attack on Havana by the French privateer Jacques de Sores, and eventually was demolished in 1582. In 1558 Bartolomé Sánchez, an eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castillo De La Real Fuerza, Havana, Cuba
Castillo (Spanish for 'castle') may refer to: * Castillo (surname), including a list of people with the name * Castillo, Dominican Republic * Castillo, Álava, Spain * Castillo CF, a Spanish football team See also * * Del Castillo (other) * El Castillo (other) * Castilho (other) * ''Castillo v. Texas'', a 2000 Texas court decision {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: "[16c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1454–1512). The name ''America'' first appeared on a map in 1507 by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, referring to the area now called Brazil]. Since the 16th century, the term "New World" has been used to describe the Western Hemisphere, often referred to as the Americas. Since the 18th century, it has come to represent the United States, which was initially colonial British America until it established independence following the American Revolutionary War. The second sense is now primary in English: ... However, the term is open to uncertainties: ..." The term arose in the early 16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Cuba (1741)
The invasion of Cuba took place between 4–5 August and 9 December 1741 during the War of Jenkins' Ear. A combined army and naval force under the command of Admiral Edward Vernon and Major-General Thomas Wentworth arrived off Cuba and fortified positions around their landing site at Cumberland Bay. Despite facing no serious opposition, neither commander felt prepared to advance on the Spanish settlement at Santiago de Cuba. Harassed by Spanish raids and with a mounting sick list, the British finally evacuated the island after several months of inactivity. Background Vernon had made an unsuccessful attempt to capture Cartagena in 1741, and after his repulse he directed the fragments of his sickly and dispirited followers against the island of Cuba. The south and east of Cuba were so little populated, and so far from the capital, Havana, that they might have made a permanent establishment there. Vernon's expedition The land forces consisted of the remnants of the troops from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King George's War in North America, the War of Jenkins' Ear, the First Carnatic War, and the First Silesian War, First and Second Silesian Wars. Its pretext was the right of Maria Theresa to succeed her father, Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Charles VI, as ruler of the Habsburg monarchy. Kingdom of France, France, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, and Electorate of Bavaria, Bavaria saw it as an opportunity to challenge Habsburg power, while Maria Theresa was backed by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, the Dutch Republic, and Electorate of Hanover, Hanover, collectively known as the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713, Pragmatic Allies. As the conflict widened, it drew in other participants, among them History of Spain (1700–1810), Spain, Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Vernon
Admiral Edward Vernon (12 November 1684 – 30 October 1757) was a Royal Navy officer and politician. He had a long and distinguished career, rising to the rank of admiral after 46 years service. As a vice admiral during the War of Jenkins' Ear, in 1739 he was responsible for the capture of Portobelo, Panama, seen as expunging the failure of Admiral Hosier there in a previous conflict. However, his amphibious operation against the Spanish port of Cartagena de Indias was a disastrous defeat. Vernon also served as a Member of Parliament (MP) on three occasions and was outspoken on naval matters in Parliament, making him a controversial figure. The origin of the name " grog" for rum diluted with water is attributed to Vernon. He was known for wearing coats made of grogram (also spelled grosgrain) cloth, earning him the nickname of "Old Grog", which in turn came to mean the diluted rum that he first introduced into his naval squadron. He is also the eponym of George Washingto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of Jenkins' Ear
The War of Jenkins' Ear was fought by Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and History of Spain (1700–1808), Spain between 1739 and 1748. The majority of the fighting took place in Viceroyalty of New Granada, New Granada and the Caribbean Sea, with major operations largely ended by 1742. It is considered a related conflict of the 1740 to 1748 War of the Austrian Succession. The name derives from Robert Jenkins (master mariner), Robert Jenkins, a British sea captain whose ear was allegedly severed in April 1731 by Spanish coast guards searching his ship for contraband. In 1738, opposition politicians in the Parliament of Great Britain, British Parliament used the incident to incite support for a war against Spain. The most significant operation of the war was a failed British attack on Battle of Cartagena de Indias, Cartagena in 1741, which resulted in heavy casualties and was not repeated. Apart from minor actions in Spanish Florida, Province of Georgia, Georgia, and Havan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guantánamo Bay
Guantánamo Bay (, ) is a bay in Guantánamo Province at the southeastern end of Cuba. It is the largest harbor on the south side of the island and it is surrounded by steep hills which create an enclave that is cut off from its immediate hinterland. The United States assumed territorial control over the southern portion of Guantánamo Bay under the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base#Permanent lease, 1903 Lease. The United States exercises jurisdiction and control over this territory as the home of the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base, while recognizing that Cuba retains ultimate sovereignty. Climate Guantánamo Bay has a hot semi-arid climate according to the Köppen climate classification, with high temperatures throughout the year. Rainfall is rather low, and it is one of the driest regions in Cuba. U.S. control of Guantánamo Bay The United States first seized Guantánamo Bay and established a naval base there in 1898 during the Spanish–American War in the Battle of Guantánamo Bay. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of Jamaica
The Crown Colony of Jamaica and Dependencies was a British colony from 1655, when it was Invasion of Jamaica (1655), captured by the The Protectorate, English Protectorate from the Spanish Empire. Jamaica became a British Empire, British colony from 1707 and a Crown colony in 1866. The Colony was primarily used for sugarcane production, and experienced many slave rebellions over the course of British rule. Jamaica was granted independence in 1962. History 17th century English conquest In late 1654, English leader Oliver Cromwell launched the ''Western Design'' armada against Spanish West Indies, Spain's colonies in the Caribbean. In April 1655, Robert Venables, General Robert Venables led the armada in an attack on Spain's fort at Santo Domingo, Hispaniola. However, the Spanish repulsed this poorly-executed attack, known as the Siege of Santo Domingo (1655), Siege of Santo Domingo, and the English troops were soon decimated by disease, injured badly or possibly killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago De Cuba
Santiago de Cuba is the second-largest city in Cuba and the capital city of Santiago de Cuba Province. It lies in the southeastern area of the island, some southeast of the Cuban capital of Havana. The municipality extends over , and contains the communities of Antonio Maceo, Bravo, Castillo Duany, Daiquirí, El Caney, El Cobre, Cuba, El Cobre, El Cristo, Guilera, Leyte Vidal, Moncada and Siboney, Cuba, Siboney. Historically Santiago de Cuba was the second-most important city on the island after Havana, and remains the second-largest. It is on a bay connected to the Caribbean Sea and an important sea port. In the 2022, the city of Santiago de Cuba recorded a population of 507,167 people. History Santiago de Cuba was the seventh village founded by Spanish conquistador Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar on 25 July 1515. The settlement was destroyed by fire in 1516, and was immediately rebuilt. This was the starting point of the expeditions led by Juan de Grijalba and Hernán Cort� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Myngs
Vice Admiral Sir Christopher Myngs (sometimes spelled ''Mings'', 1625–1666) was an English naval officer and privateer, most notably in the Colony of Jamaica. Life The date of Myngs's birth is uncertain, but is probably somewhere between 1620 and 1625. He came from a Norfolk family and was a relative of Admiral Sir Cloudesley Shovell. Samuel Pepys' story of Myngs' humble birth ("his father being always and at this day a shoemaker, and his mother a Hoyman’s daughter; of which he was used frequently to boast") has now been evaluated by historians as being mostly fictitious in nature. It is probable that he saw a good deal of sea-service before 1648. He first appears prominently as the captain of the ''Elisabeth'', which after it had undergone action during the First Anglo-Dutch War brought in a Dutch convoy with two men-of-war as prizes. From 1653 to 1655 he continued to command the ''Elisabeth'', when he was high in favour with the council of state and recommended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piet Heyn
Piet Pieterszoon Hein (25 November 1577 – 18 June 1629) was a Dutch admiral and privateer for the Dutch Republic during the Eighty Years' War. Hein was the first and the last to capture a large part of a Spanish treasure fleet which transported huge amounts of gold and silver from Spanish America to Spain. The amount of silver taken was so large that it resulted in the rise of the price of silver worldwide and the near bankruptcy of Spain. Early life Hein was born in Delfshaven (now part of Rotterdam), the son of a sea captain, and he became a sailor while he was still a teenager. During his first journeys he suffered from extreme motion sickness. In his twenties, he was captured by the Spanish, and served as a galley slave for about four years, probably between 1598 and 1602, when he was traded for Spanish prisoners. Between 1603 and 1607, he was again held captive by the Spanish, when captured near Cuba. Naval career Dutch East India Company In 1607, he joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |