|
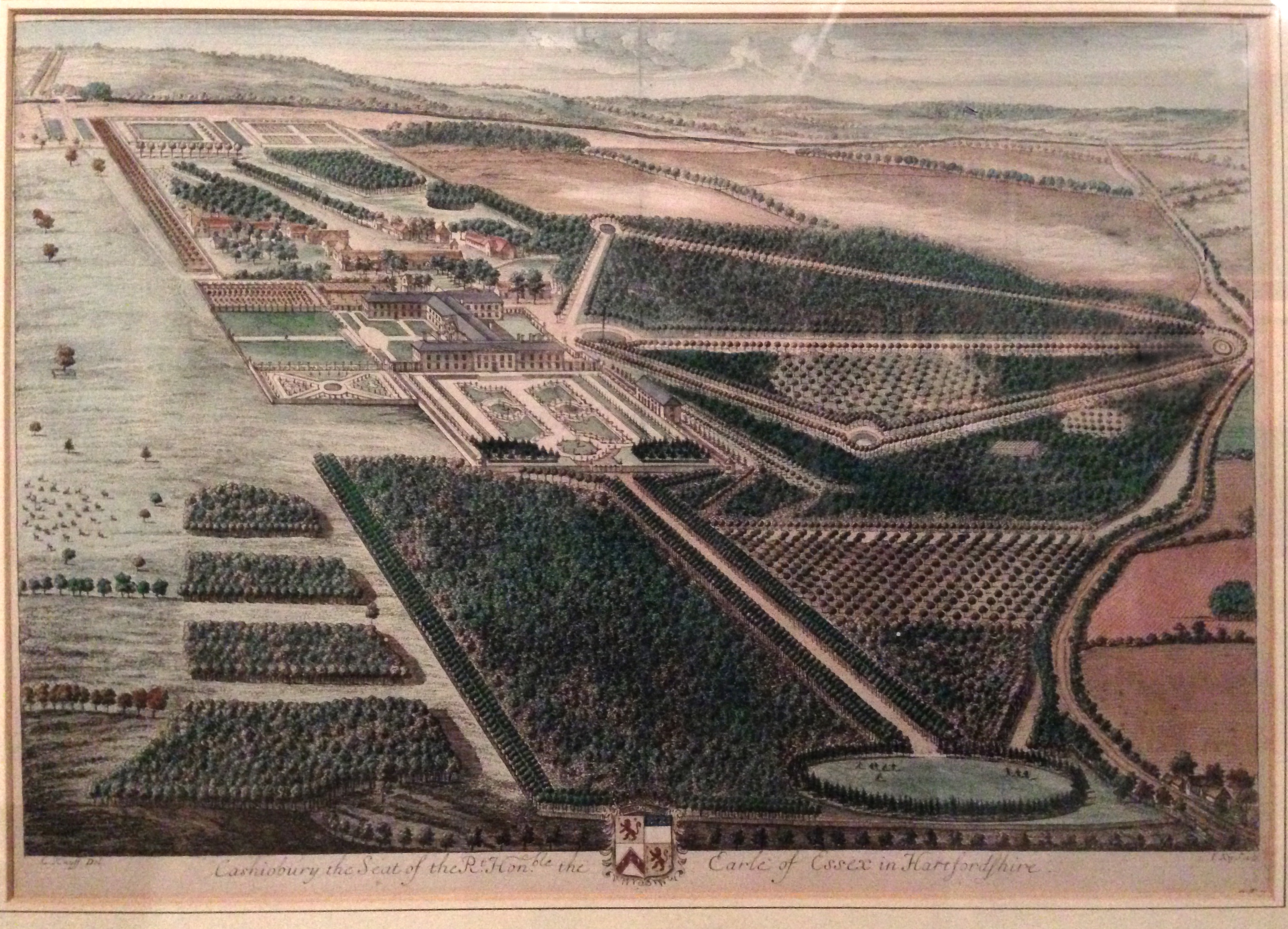
Cassiobury Park
Cassiobury Park is the principal public park in Watford, Hertfordshire, in England. It was created in 1909 from the purchase by Watford Borough Council of part of the estate of the Earl of Essex, Earls of Essex around Cassiobury House which was subsequently demolished in 1927.Lost Heritage It comprises over and extends from the A412 Rickmansworth Road in the east to the Grand Union Canal in the west, and lies to the south of the Watford suburb of Cassiobury, which was also created from the estate. The western part is a Local Nature Reserve managed by the Herts and Middlesex Wildlife Trust. The park hosts the free, weekly timed parkrun 5 km event every Saturday morning at 9 am, starting on the field near the Shepherds Road entrance to the park, and finishing by the bandstand. ...
|
Watford
Watford () is a town and non-metropolitan district with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in Hertfordshire, England, northwest of Central London, on the banks of the River Colne, Hertfordshire, River Colne. Initially a small market town, the Grand Junction Canal encouraged the construction of paper-making mills, print works, and brewery, breweries. While industry has declined in Watford, its location near London and transport links have attracted several companies to site their headquarters in the town. Cassiobury Park is a public park that was once the manor estate of the Earls of Essex. The town developed next to the River Colne on land belonging to St Albans Abbey. In the 12th century, a charter was granted allowing a market, and the building of St Mary's Church, Watford, St Mary's Church began. The town grew partly due to travellers going to Berkhamsted Castle and the royal palace at Kings Langley. A mansion was built at Cassiobury House, Cassiobury in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tudor Architecture
The Tudor architectural style is the final development of medieval architecture in England and Wales, during the Tudor period (1485–1603) and even beyond, and also the tentative introduction of Renaissance architecture to Britain. It followed the Late Gothic Perpendicular style and, gradually, it evolved into an aesthetic more consistent with trends already in motion on the continent, evidenced by other nations already having the Northern Renaissance underway Italy, and especially French Renaissance architecture, France already well into its revolution in art, architecture, and thought. A subtype of Tudor architecture is Elizabethan architecture, from about 1560 to 1600, which has continuity with the subsequent Jacobean architecture in the early Stuart period. In the much more slow-moving styles of vernacular architecture, "Tudor" has become a designation for half-timbering, half-timbered buildings, although there are cruck and frame houses with half-timbering that consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George London (landscape Architect)
George London (c. 1640–1714) was an English nurseryman and garden designer. George London's birth date is not certain but it was probably about 1640. Switzer tells us that he was trained by John Rose (d. 1677), gardener to Charles II. Rose had trained under André Le Nôtre and encouraged London's enthusiasm for the baroque style, which was reinforced by a visit to France. It was probably Rose who recommended London to Henry Compton, when he became Bishop of London in 1675 and began to stock the garden at Fulham Palace, Fulham. By 1681 London was also gardener to Henry Bennet, 1st Earl of Arlington and at two gardens in Bedfordshire, presumably ones he had designed. London was the principal founding partner in the Brompton Park Nursery, Kensington in 1681. The other partners were Moses Cook, Lucre, gardener to the Queen Dowager at Somerset House, and Field, gardener to the Earl of Bedford, at Bedford House, Strand, in London. The nursery's first major commission was for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Colburn
Henry Colburn (1784 – 16 August 1855) was a British publisher. Life Virtually nothing is known about Henry Colburn's parentage or early life, and there is uncertainty over his year of birth. He was well-educated and fluent in French and had the financial capital at a young age to enter publishing, giving credence to the hypothesis of Michael Sadleir that he may have been the illegitimate son of an Englishman by a French mother. He is first documented as an apprentice printer indentured for six years to William Earle, a bookseller in Albemarle Street, London, on 1 June 1800 for the sum of £1,000. Earle's was an established English and foreign language library. In 1806, Colburn acquired Morgan's circulating library based in Conduit Street, from where he published his first books, notably works by popular light novelists translated from French and German. Most of the French novels were published in the original language by ''Chez Colburn'' and then reissued in translation'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diary, diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society. John Evelyn's Diary, John Evelyn's diary, or memoir, spanned the period of his adult life from 1640, when he was a student, to 1706, the year he died. He did not write daily at all times. The many volumes provide insight into life and events at a time before regular magazines or newspapers were published, making diaries of greater interest to modern historians than such works might have been at later periods. Evelyn's work covers art, culture and politics, including the execution of Charles I, Oliver Cromwell's rise and eventual natural death, the last Great Plague of London, and the Great Fire of London in 1666. ''John Evelyn's Diary'' was first published posthumously in 1818, but over the years was overshadowed by that of Samuel Pepys. Pepys wrote a differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Verrio
Antonio Verrio (c. 1636 – 15 June 1707) was an Italian Baroque painter. He was responsible for introducing Baroque mural painting into England and served the Crown over a thirty-year period.British Art Journal, Volume X No. 3, Winter/Spring 2009/10 Career Verrio, born in Lecce, Kingdom of Naples, started his career in Lecce and was a pupil of Giovanni Andrea Coppola (1597–1659). Several works by Verrio still exist in the Apulian city, including ''S. Francesco Saverio appare al Beato Marcello Mastrilli'' – his first known signed work. Around 1665, Verrio moved to the region of Toulouse where he was commissioned to decorate the Château de Bonrepos, the property of Pierre-Paul Riquet, promoter of the Canal du Midi. He then settled in Toulouse itself where he worked for the Discalced Carmelites and the Capuchins. Today two of his paintings, ''Le Mariage de la Vierge'' and ''Saint-Félix de Cantalice'', are in the collection of the Musée des Augustins there. Around 167 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
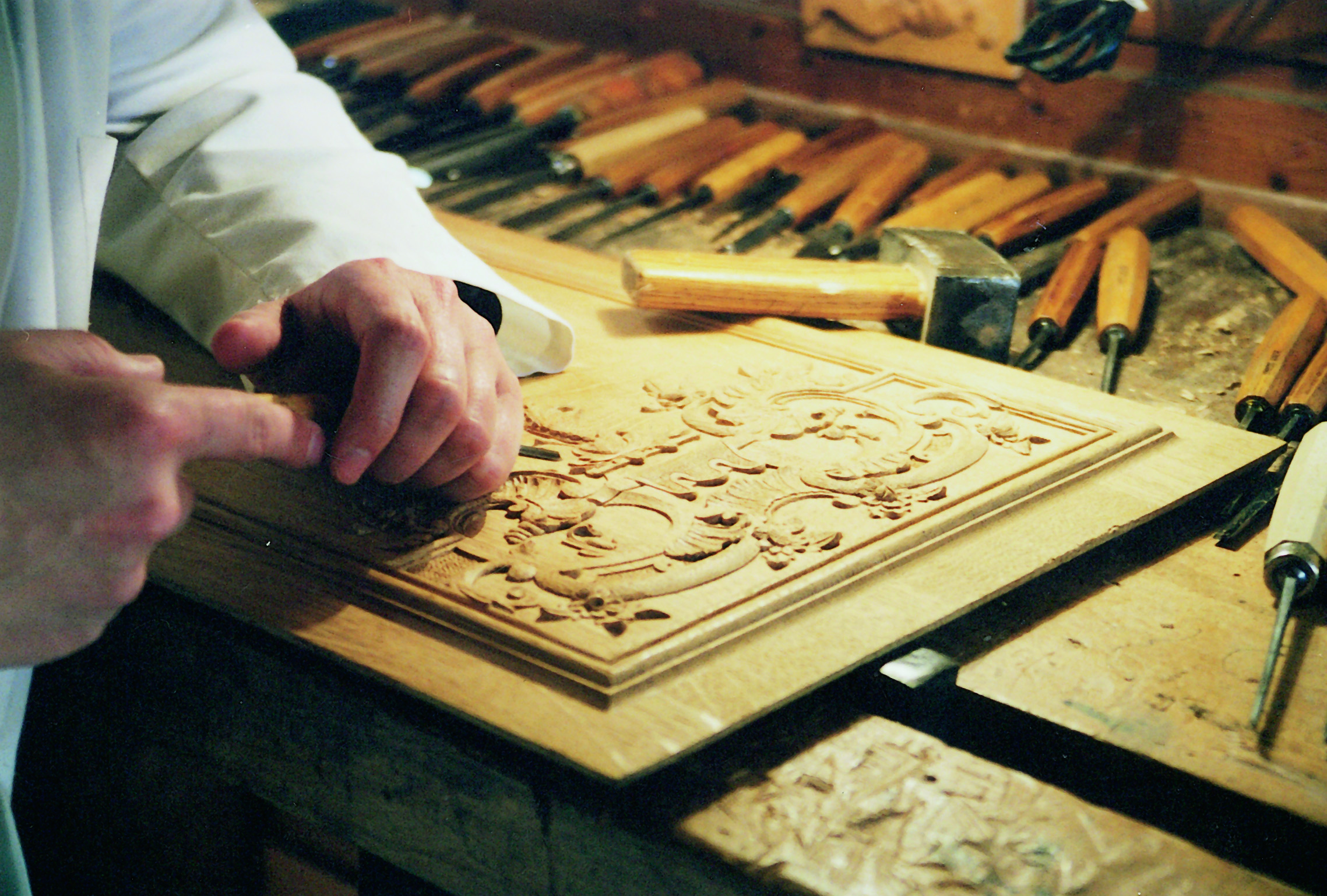
Grinling Gibbons
Grinling Gibbons (4 April 1648 – 3 August 1721) was an Anglo-Dutch sculptor and wood carver known for his work in England, including Windsor Castle, the Royal Hospital Chelsea and Hampton Court Palace, St Paul's Cathedral and other London churches, Petworth House and other country houses, Trinity College, Oxford and Trinity College, Cambridge. Gibbons was born to English parents in Holland, where he was educated. His father was a merchant. Gibbons was a member of the Drapers' Company of London; he is widely regarded as the finest wood carver working in England, and the only one whose name is widely known among the general public. Most of his work is in lime (''Tilia'') wood, especially decorative Baroque garlands made up of still-life elements at about life size, made to frame mirrors and decorate the walls of churches and palaces, but he also produced furniture and small relief plaques with figurative scenes. He also worked in stone, mostly for churches. By the time he was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Carver
Wood carving (or woodcarving) is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculptural ornamentation of a wooden object. The phrase may also refer to the finished product, from individual sculptures to hand-worked mouldings composing part of a tracery. The making of sculpture in wood has been extremely widely practised, but does not survive undamaged as well as the other main materials like stone and bronze, as it is vulnerable to decay, insect damage, and fire. Therefore, it forms an important hidden element in the art history of many cultures. Outdoor wood sculptures do not last long in most parts of the world, so it is still unknown how the totem pole tradition developed. Many of the most important sculptures of China and Japan, in particular, are in wood, and so are the great majority of African sculpture and that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from History of the British Isles, British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September 2004 in 60 volumes and online, with 50,113 biographical articles covering 54,922 lives. First series Hoping to emulate national biography, biographical collections published elsewhere in Europe, such as the (1875), in 1882 the publisher George Murray Smith, George Smith (1824–1901), of Smith, Elder & Co., planned a universal dictionary that would include biographical entries on individuals from world history. He approached Leslie Stephen, then editor of the ''Cornhill Magazine'', owned by Smith, to become the editor. Stephen persuaded Smith that the work should focus only on subjects from the United Kingdom and its present and former colonies. An early working title was the ''Biographia Britannica'', the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh May
Hugh May (1621 – 21 February 1684) was an English architect in the period after the Restoration of King Charles II. He worked in the era which fell between the first introduction of Palladianism into England by Inigo Jones, and the full flowering of English Baroque under John Vanbrugh and Nicholas Hawksmoor. His own work was influenced by both Jones' work, and by Dutch architecture. Although May's only surviving works are Eltham Lodge, and the east front, stables and chapel at Cornbury Park, his designs were influential. Together with his contemporary, Sir Roger Pratt, May was responsible for introducing and popularising an Anglo-Dutch type of house, which was widely imitated.Summerson, p.175 Biography Hugh May was the seventh son of John May of Rawmere, in Mid Lavant, West Sussex, by his wife, Elizabeth Hill, and was baptised on 2 October 1621.Colvin, pp.646–648 He was a first cousin of Baptist May, Charles II's Keeper of the Privy Purse. As a member of a Royalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Capell, 1st Earl Of Essex
Arthur Capell, 1st Earl of Essex (13 July 1683), also spelt Capel, of Cassiobury House, Watford, Hertfordshire, was an English statesman. Early life He was the son of Arthur Capell, 1st Baron Capell of Hadham (executed in 1649) by his wife Elizabeth Morrison, daughter and heiress of Sir Charles Morrison, 1st Baronet (1587–1628) of Cashiobury House, Watford, Hertfordshire. He was baptised on 2 January 1632. Youth In June 1648, then a sickly boy of sixteen, he was taken by Lord Fairfax's soldiers from Hadham to Colchester in Essex, which town his father was defending, and was carried every day around the works with the hope of inducing Lord Capell to surrender the town. Political career At the Restoration of the Monarchy, he was created on 20 April 1661 Viscount Malden and Earl of Essex, the latter earldom having become extinct on the death of Robert Devereux, 3rd Earl of Essex. It was granted with special remainder to the male issue of his father. Capell was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |