|
Carterinida
Carterinida is an order of multi-chambered foraminifera within the Globothalamea. Members of this order form hard tests out of thin calcite rods known as spicules, which are held together by a proteinaceous matrix. The spicules of carterinids have been a source of debate; as they are held together by a protein matrix, it has been suggested that the test is created by agglutinating spicules from the amoebozoan '' Trichosphaerium''. However, life observations of carterinids have failed to find evidence of agglutination, and members of the group have been found to grow on artificial substrates where such spicules were not available from the environment. This suggests the spicules are instead created by the carterinids themselves. The spicules of carterinids are formed of low-magnesium calcite and have "blebs" of organic matter within. Two sizes of spicules are present; smaller spicules are packed tightly between the larger spicules. Spicules appear to have been produced within the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globothalamea
Globothalamea comprises a class of multichambered foraminifera based in part on SSU rDNA evidence; the other is Tubothalamea. Six orders are included, which vary notably in composition, wall structure, and chamber arrangement. The Lituolida, Loftusiida, and Textulariida (as emended) have tests (shells) of agglutinated matter, glued together by various cements, but differ in chamber arrangement, wall structure, and complexity. In contrast the Carterinida, Robertinida and Rotaliida, with buliminids lumped into the Rotaliida, have calcareous tests. Those of rotaliid genera, which vary considerably, are of perforate hyaline (glassy) calcite. in contrast the Carterinida have tests composed of bundled calcite spicules. The Robertida differ in being composed, instead, of aragonite. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera Orders
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test, or shell, which can have either one or multiple chambers, some becoming quite elaborate in struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test, or shell, which can have either one or multiple chambers, some becoming quite elaborate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granuloreticulosa
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test, or shell, which can have either one or multiple chambers, some becoming quite elaborate in struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the stratigraphic column deposited during the corresponding age. Both age and stage bear the same name. As a unit of geologic time measure, the Cenomanian Age spans the time between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago (Mya). In the geologic timescale, it is preceded by the Albian and is followed by the Turonian. The Upper Cenomanian starts around at 95 Mya. The Cenomanian is coeval with the Woodbinian of the regional timescale of the Gulf of Mexico and the early part of the Eaglefordian of the regional timescale of the East Coast of the United States. At the end of the Cenomanian, an anoxic event took place, called the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli event", that is associated with a minor extinction event for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 (± 0.2) to 72.1 (± 0.2) million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian. The Campanian was an age when a worldwide sea level rise covered many coastal areas. The morphology of some of these areas has been preserved: it is an unconformity beneath a cover of marine sedimentary rocks. Etymology The Campanian was introduced in scientific literature by Henri Coquand in 1857. It is named after the French village of Champagne in the department of Charente-Maritime. The original type locality was a series of outcrop near the village of Aubeterre-sur-Dronne in the same region. Definition The base of the Campanian Stage is defined as a place in the stratigraphic col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 states and the Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese as an official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world; and the most populous Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of . It borders all other countries and territories in South America except Ecuador and Chile and covers roughly half of the continent's land area. Its Amazon basin includes a vast tropical forest, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochamminida
The Textulariida are an order of foraminifera that produce agglutinated shells or tests. An agglutinated test is one made of foreign particles glued together with an organic or calcareous cement to form an external shell on the outside of the organism. Commonly, the order had been made up of all species of Foraminifera with these types of shells, but genetic studies indicate these organisms do not form an evolutionary group, and several superfamilies in the order have been moved to the order Allogromiida. The remaining forms are sometimes divided into three orders: the Trochamminida and Lituolida, which have organic cement, and the Textulariida ''sensu stricto'', which use a calcareous cement. All three orders or superfamilies are known as fossils from the Cambrian The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediaca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
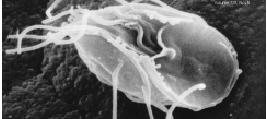
Trichosphaerium
The Tubulinea are a major grouping of Amoebozoa, including most of the more familiar amoebae genera like ''Amoeba'', ''Arcella'', ''Difflugia'' and ''Hartmannella''. Characteristics During locomotion most Tubulinea have a roughly cylindrical form or produce numerous cylindrical pseudopods. Each cylinder advances by a single central stream of cytoplasm, granular in appearance, and has no subpseudopodia. This distinguishes them from other amoeboid groups, although in some members this is not the normal type of locomotion. Classification This class was anticipated by some biologists like Jahn, who grouped all amoebae with granular pseudopodia together, but most split the lobose amoebae into testate Testacealobosia and naked Gymnamoebia. These latter are polyphyletic, but molecular trees by Bolivar ''et al.'' identified a core monophyletic subgroup. Subsequent studies showed the testate lobose amoebae belong to the same group, which was thus renamed Lobosea ''sensu stricto'' or Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German ''Calcit'', a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for lime, ''calx'' (genitive calcis) with the suffix "-ite" used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk. When applied by archaeologists and stone trade professionals, the term alabaster is used not just as in geology and mineralogy, where it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |