|
Carrier Striking Task Force
The , also known as the ''Kidō Butai'' ("Mobile Force"), was a combined carrier battle group comprising most of the aircraft carriers and carrier air groups of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the first eight months of the Pacific War. At the time of its best-known operation, the attack on Pearl Harbor, in December 1941, the 1st Air Fleet was the world's largest fleet of aircraft carriers. In its second generation, 1st Air Fleet was a land-based fleet of "kichi kōkūtai" (base air unit(s)). Origins In 1912, the British Royal Navy had established its own flying branch, the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). The IJN was modeled on the Royal Navy and the IJN Admiralty sought establishment of their own Naval Air Service. The IJN had also observed technical developments in other countries and saw military potential of the airplane. In 1913, the IJN seaplane carrier ''Wakamiya'' was converted into a seaplane tender and aircraft were purchased. The 1st and 2nd Air Fleet were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rising Sun Flag
The is a Japanese flag that consists of a red disc and sixteen red rays emanating from the disc. Like the Flag of Japan, Japanese national flag, the Rising Sun Flag symbolizes the Sun. The flag was originally used by daimyō, feudal warlords in Japan during the Edo period (1603–1868 AD). On May 15, 1870, as a policy of the Meiji government, it was adopted as the war flag of the Imperial Japanese Army; further, on October 7, 1889, it was adopted as the naval ensign of the Imperial Japanese Navy. At present, the flag is flown by the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force, and an eight-ray version is flown by the Japan Self-Defense Forces and the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force. The rising sun design is also seen in numerous scenes in daily life in Japan, such as in Tairyō-bata, fishermen's banners hoisted to signify large catches of fish, flags to celebrate childbirth, and in flags for seasonal festivities. The flag is controversial in most Asian and Pacific nations, mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Peattie
Mark R. Peattie (May 3, 1930 – January 22, 2014) was an American academic and Japanologist, renowned for his expertise in modern Japanese military, naval, and imperial history. Born in Nice, France, and later residing in San Rafael, California, Peattie made significant contributions to the study of Japan's wartime history. Throughout his career, he published extensively on the subject and was a respected figure in the field of Japanese studies.Hoover Institution, Stanford UniversityPeattie bio notes Early life Mark Peattie was born to Louise Redfield and Donald C. Peattie, an American botanist and author when they were living in southern France. His family later moved to Illinois and then California. The novelist Elia W. Peattie was his grandmother. Career Peattie was a professor emeritus at the University of Massachusetts Boston and a research fellow at Stanford University's Hoover Institution. He was a visiting professor at the University of Hawaii in 1995. Peattie was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jisaburō Ozawa
was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Ozawa held several important commands at sea throughout the duration of the conflict ( Southern Expeditionary Fleet, 3rd Fleet, 1st Mobile Fleet, and the Combined Fleet). Ozawa was noted for his innovative ideas in the employment of aircraft carriers. However, he could not, in his most important commands from 1943 onward, succeed in overcoming the superiority of American carrier aviation. In terms of quantity and quality of aircraft, as well as pilot training and experience, the Americans outmatched the Japanese carrier forces under Ozawa's command. Ozawa commanded Japanese carrier forces during some of the most significant naval battles that took place in the Pacific Theatre: the Battle of the Philippine Sea and the Battle of Leyte Gulf. He was the last Commander-in-Chief of the Combined Fleet. Ozawa has been noted for his unusual height for a Japanese man of his time period, measuring in at over tall, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force Concentration
Force concentration is the practice of concentrating a military force so as to bring to bear such overwhelming force against a portion of an enemy force that the disparity between the two forces alone acts as a force multiplier in favour of the concentrated forces. Mass of decision Force concentration became integral to the Prussian military operational doctrine of the ''mass of decision'', which aimed to cause disproportionate losses on the enemy and therefore destroy the enemy's ability to fight. From an empirical examination of past battles, the Prussian military theorist Carl von Clausewitz (1780–1831) concluded: ..we may infer, that it is very difficult in the present state of Europe, for the most talented General to gain a victory over an enemy double his strength. Now if we see double numbers prove such a weight in the scale against the greatest Generals, we may be sure, that in ordinary cases, in small as well as great combats, an important superiority of numbers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IJNAS
The (IJNAS) was the air arm of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). The organization was responsible for the operation of naval aircraft and the conduct of aerial warfare in the Pacific War. The Japanese military acquired its first aircraft in 1910 and followed the development of air combat during World War I with great interest. Japan initially built European aircraft under license, but by the early 1930s Japanese factories were producing domestic designs. The Japanese also embarked on an ambitious aircraft carrier building program, launching the world's first purpose-built aircraft carrier, , in 1922. Several excess battlecruisers and battleships were converted into aircraft carriers as well. As the organization assigned to the IJN's aircraft carriers, the Navy Air Service was tasked with the missions of national air defence, deep strike, naval warfare, and so forth. It retained this mission until its dissolution at the end of the Second World War. The Japanese pilot training ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaplane Tender
A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are regarded by some as the first aircraft carriers and appeared just before the First World War. Terminology In maritime parlance a tender is a vessel that is used to support the operation of other vessels. In British usage, the term tender was used for small craft, with the term depot ship being used for large seagoing vessels. Flying boats and float planes even when based at home in ports and harbour had a need for small support vessels to operate.p British tenders were small craft of launch to pinnace size. These were used to ferry crews, stores and supplies between shore and the aircraft, to maintain the buoys used to mark out "taxiways" and "runways" and to keep these clear of debris to prevent foreign object damage, and in the case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
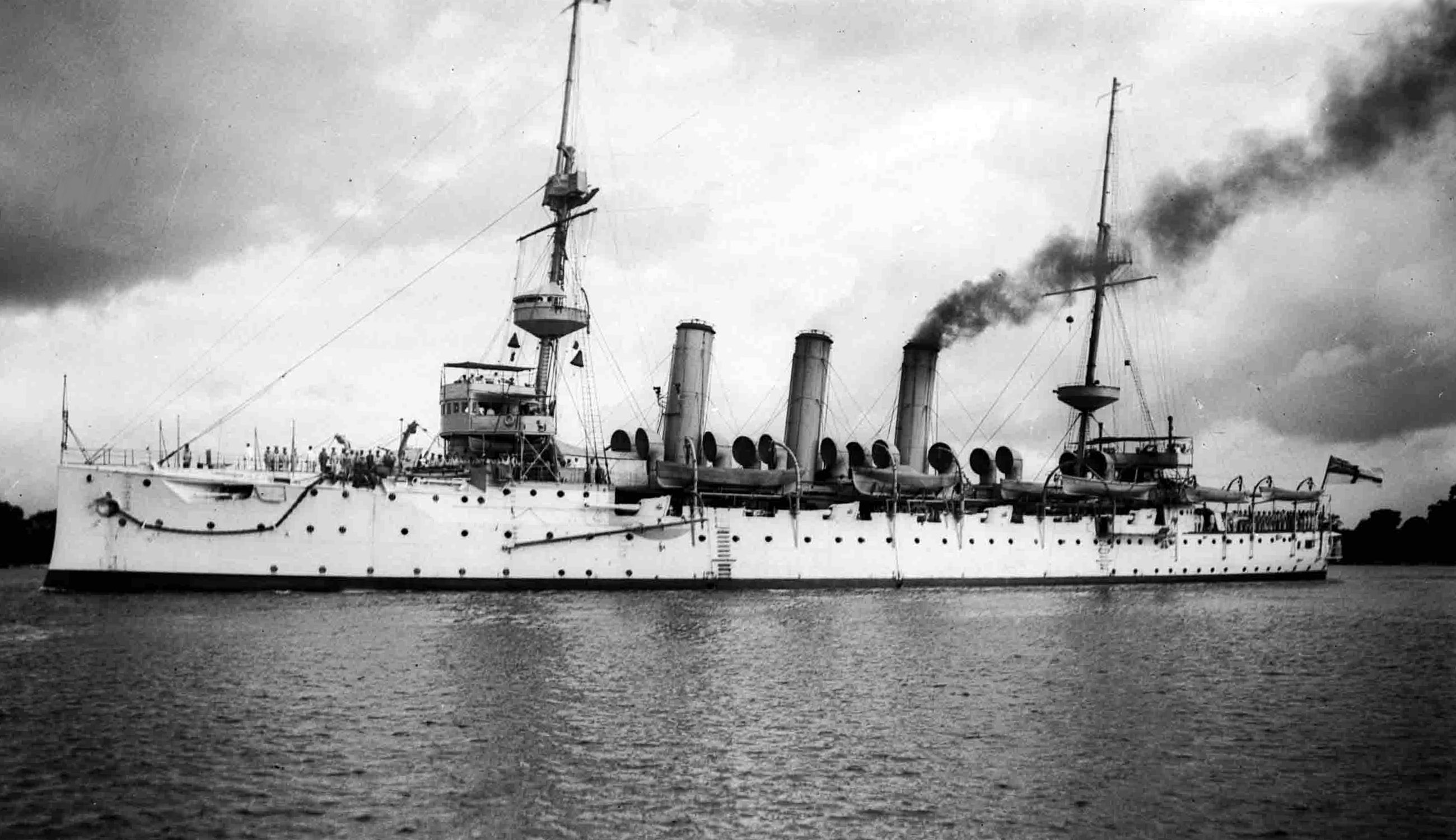
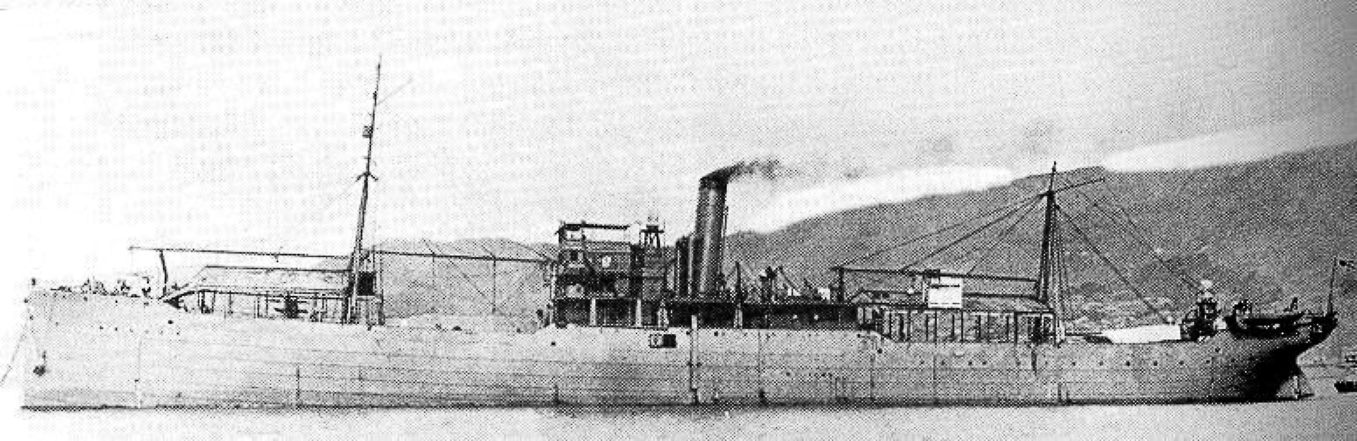
Japanese Seaplane Carrier Wakamiya
''Wakamiya'' (, later ) was a seaplane carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy and the first Japanese aircraft carrier. She was converted from a transport ship into a seaplane carrier and commissioned in August 1914. She was equipped with four Japanese-built French Maurice Farman seaplanes (powered by Renault engines). In September 1914, she conducted the world's first naval-launched air raids. Early career ''Wakamiya'' was initially the Russian freighter ''Lethington'', built by Duncan in Port Glasgow, United Kingdom, laid down in 1900 and launched 21 September 1900. She was captured on a voyage from Cardiff to Vladivostok during the Russo-Japanese War near Okinoshima in 1905 by the Japanese torpedo boat ''TB No. 72''. She was acquired by the Japanese government, renamed ''Takasaki-Maru'' until given the official name of ''Wakamiya-Maru'' on 1 September, and from 1907 was managed as a transport ship by NYK. In 1913 she was transferred to the Imperial Japanese Navy and conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty (United Kingdom), Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps to form the Royal Air Force (RAF), the world's first independent air force. It was replaced by the Fleet Air Arm, initially consisting of those RAF units that normally operated from ships, but emerging as a separate unit similar to the original RNAS by the time of the Second World War. History Background On 21 July 1908 Captain Reginald Bacon, who was a member of the Aerial Navigation Sub-Committee, submitted to the First Sea Lord John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Sir John Fisher that a rigid airship based on the Imperial Germany, German Zeppelin be designed and constructed by the firm of Vickers. After much discussion on the Committee of Imperial Defence the suggestion was approved on 7 May 1909. Though Bacon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakamiya
Wakamiya may refer to: Places * Wakamiya, Fukuoka, a town located in Kurate District, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan that in 2006, along with the town of Miyata (also from Kurate District), was merged to create the city of Miyawaka * Wakamiya Station, a railway station on the Tadami Line in the town of Aizubange, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan, operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East). * Keta Wakamiya Shrine, a Shinto shrine located in the city of Hida, Gifu Prefecture, Japan also commonly referred to as "Sugimoto-sama" *Wakamiya Ōji is a 1.8 km street in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura, a city in Kanagawa Prefecture in Japan, unusual because it is at the same time the city's main avenue and the approach () of its largest Shinto shrine, Tsurugaoka Hachiman-gū. Over the cen ..., a 1.8 km street in Kamakura, a city in Kanagawa Prefecture in Japan, unusual because it is at the same time the city's main avenue and the approach (sandō (参道)) of its largest Shinto shrine, Tsurug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of Hawaii, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941. At the time, the U.S. was a Neutral powers during World War II, neutral country in World War II. The air raid on Pearl Harbor, which was launched from Aircraft carrier, aircraft carriers, resulted in the U.S. entering the war on the side of the Allies of World War II, Allies on the day following the attack. The Imperial General Headquarters, Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. The attack on Pearl Harbor was preceded by months of negotiations between the U.S. and Japan over the future of the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. Japanese demands included that the U.S. ABCD line, end its sanctions against Japan, cease aidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |