|
Carl Wilhelm Wirtz
Carl Wilhelm Wirtz (24 August 1876 in Krefeld – 18 February 1939 in Hamburg) was an astronomer who studied astronomy at Bonn University (1895-1898) obtaining his doctorate there after which he spent his time between the Kiel Observatory in Germany and the Observatory of Strasbourg, France. He is known for statistically showing the existence of a redshift-distance correlation for spiral galaxies. Scientific career As already Vesto Slipher in 1912, Wirtz in 1918 observed a systematic redshift of spiral nebulae, which was difficult to interpret in terms of a cosmological model in which the Universe is filled more or less uniformly with stars and nebulae. Wirtz additionally used the equivalent in German of '' K correction''. The term continues to be used in present-day observational cosmology, but Wirtz's observational evidence that the Universe is expanding is not often mentioned. He wrote: In 1922, he wrote a paper where he argued that the observational results sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krefeld
Krefeld ( , ; ), also spelled Crefeld until 1925 (though the spelling was still being used in British papers throughout the Second World War), is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany. It is located northwest of Düsseldorf, its center lying just a few kilometers to the west of the river Rhine; the borough of Uerdingen is situated directly on the Rhine. Because of its economic past, Krefeld is often referred to as the "Velvet and Silk City". It is accessed by the autobahns A57 (Cologne– Nijmegen) and A44 (Aachen–Düsseldorf– Dortmund– Kassel). Krefeld's residents now speak ', or standard German, but the native dialect is a Low Franconian variety, sometimes locally called ', ', or sometimes simply '. The Uerdingen line isogloss, separating general dialectical areas in Germany and neighboring Germanic-speaking countries, runs through and is named after Krefeld's Uerdingen district, originally an independent municipality. History Early history left, up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Dilation
Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either because of a relative velocity between them (special relativity), or a difference in gravitational potential between their locations (general relativity). When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity. The dilation compares "wristwatch" clock readings between events measured in different inertial frames and is not observed by visual comparison of clocks across moving frames. These predictions of the theory of relativity have been repeatedly confirmed by experiment, and they are of practical concern, for instance in the operation of satellite navigation systems such as GPS and Galileo. Invisibility Time dilation is a relationship between clock readings. Visually observed clock readings involve delays due to the propagation speed of light from the clock to the observer. Thus there is no direct way to observe time dilation. As an example of time dilation, two expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1939 Deaths
This year also marks the start of the World War II, Second World War, the largest and deadliest conflict in human history. Events Events related to World War II have a "WWII" prefix. January * January 1 ** Coming into effect in Nazi Germany of: *** The Protection of Young Persons Act (Germany), Protection of Young Persons Act, passed on April 30, 1938, the Working Hours Regulations. *** The small businesses obligation to maintain adequate accounting. *** The Jews name change decree. ** With his traditional call to the New Year in Nazi Germany, Führer and Reich Chancellor Adolf Hitler addresses the members of the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP). ** The Hewlett-Packard technology and scientific instruments manufacturing company is founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard, in a garage in Palo Alto, California, considered the birthplace of Silicon Valley. ** Philipp Etter takes over as President of the Swiss Confederation. ** The Third Soviet Five Year P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1876 Births
Events January * January 1 ** The Reichsbank opens in Berlin. ** The Bass Brewery Red Triangle becomes the world's first registered trademark symbol. *January 27 – The Northampton Bank robbery occurs in Massachusetts. February * February 2 ** The National League of Professional Base Ball Clubs is formed at a meeting in Chicago; it replaces the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players. Morgan Bulkeley of the Hartford Dark Blues is selected as the league's first president. ** Third Carlist War (Spain): Battle of Montejurra – The new commander General Fernando Primo de Rivera marches on the remaining Carlist stronghold at Estella, where he meets a force of about 1,600 men under General Carlos Calderón, at nearby Montejurra. After a courageous and costly defence, Calderón is forced to withdraw. * February 14 – Alexander Graham Bell applies for a U.S. patent for the telephone, as does Elisha Gray. * February 19 – Third Carlist War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics Data System
The SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS) is a digital library portal for researchers on astronomy and physics, operated for NASA by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. ADS maintains three bibliographic collections containing over 15 million records, including all arXiv e-prints. Abstracts and full-text of major astronomy and physics publications are indexed and searchable through the portal. Historical context Johann Friedrich Weidler published the first comprehensive history of astronomy in 1741 and the first astronomical bibliography in 1755. This was an effort to archive and classify earlier astronomical knowledge and works. This effort was continued by Jérôme de La Lande who published his ''Bibliographie astronomique'' in 1803, a work that covered the period from 480 BCE to the year of publication. The ''Bibliographie générale de l’astronomie, Volume I and Volume II'', published by J.C. Houzeau and A. Lancaster, followed in 1882 until 1889. As the numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Function The Minor Planet Center is the official worldwide organization in charge of collecting observational data for minor planets (such as asteroids), calculating their orbits and publishing this information via the '' Minor Planet Circulars''. Under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory. The MPC runs a number of free online services for observers to assist them in observing minor planets and comets. The complete catalogue of minor planet orbits (sometimes referred to as the "Minor Planet Catalogue") may also be freely downloaded. In addition to astrometric data, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitschrift Für Astrophysik
''Astronomy & Astrophysics (A&A)'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering theoretical, observational, and instrumental astronomy and astrophysics. It is operated by an editorial team under the supervision of a board of directors representing 27 sponsoring countries plus a representative of the European Southern Observatory. The journal is published by EDP Sciences and the current editors-in-chief are Thierry Forveille and João Alves. History Origins ''Astronomy & Astrophysics'' was created as an answer to the publishing situation found in Europe in the 1960s. At that time, multiple journals were being published in several countries around the continent. These journals usually had a limited number of subscribers, and articles were written in languages other than English. They were less widely read than American and British journals and the research they reported had therefore less impact in the community. Starting in 1963, conversations between astronomers from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
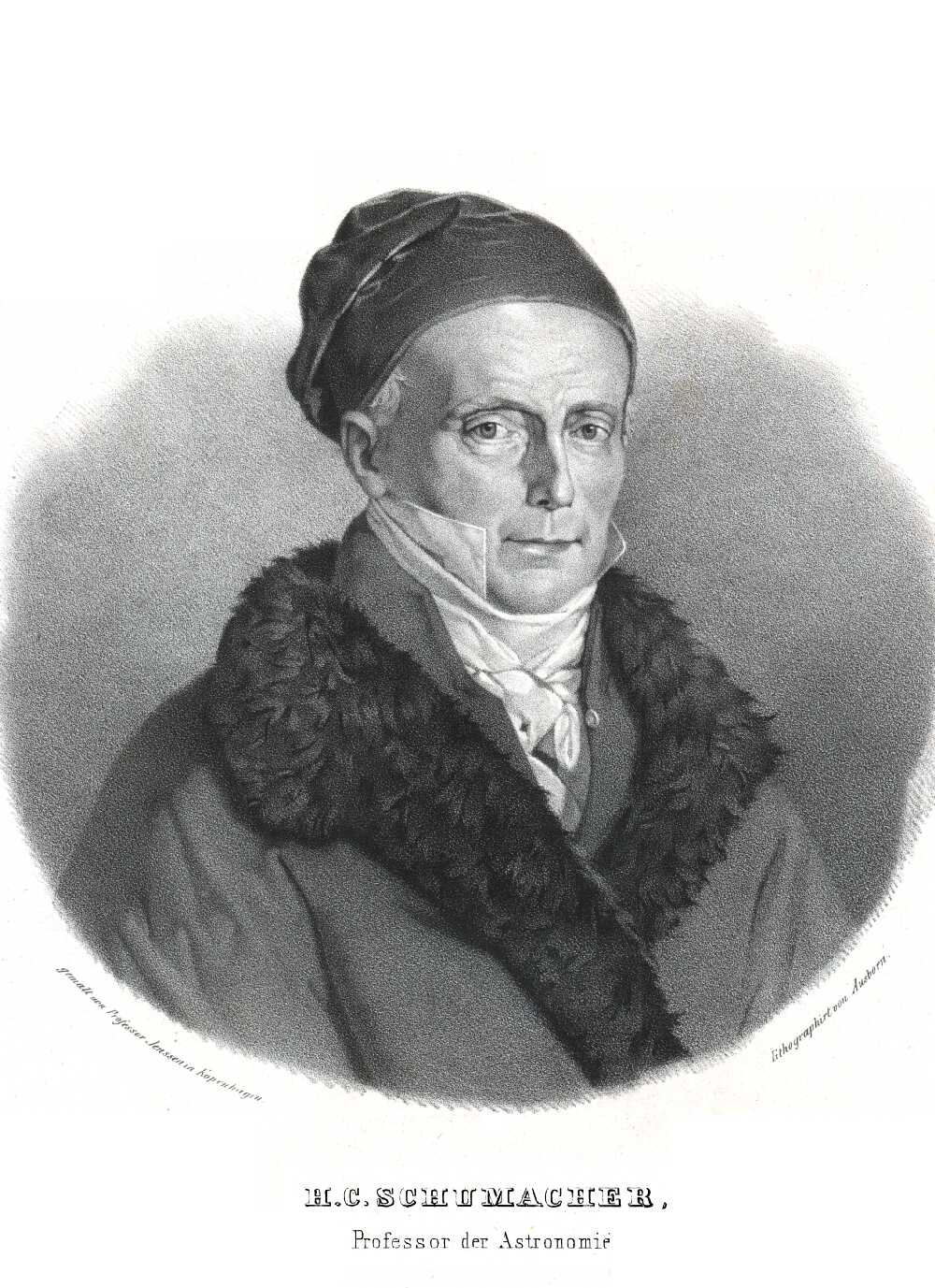
Astronomische Nachrichten
''Astronomische Nachrichten'' (''Astronomical Notes''), one of the first international journals in the field of astronomy, was established in 1821 by the German astronomer Heinrich Christian Schumacher. It claims to be the oldest astronomical journal in the world that is still being published. The publication today specializes in articles on solar physics, extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, geophysics, and instrumentation for these fields. All articles are subject to peer review. Early history The journal was founded in 1821 by Heinrich Christian Schumacher,''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'', page 60, v.7 (1895) under the patronage of Christian VIII of Denmark, and quickly became the world's leading professional publication for the field of astronomy. Schumacher edited the journal at the Altona Observatory, then under the administration of Denmark, later part of Prussia, and today part of the German city of Hamburg. Schumacher edited the first 31 issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'' (''ApJ'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and became an electronic-only journal in 2015. Since 1953, ''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series'' (''ApJS'') has been published in conjunction with ''The Astrophysical Journal'', with generally longer articles to supplement the material in the journal. It publishes six volumes per year, with two 280-page issues per volume. ''The Astrophysical Journal Letters'' (''ApJL''), established in 1967 by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar as Part 2 of ''The Astrophysical Journal'', is now a separate journal focusing on the rapid publication of high-impact astronomical research. The three journals were published by the University of Chicago Press for the American Astronomical Society until, in January 2009, publication was transferred to IOP Publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Science (journal)
''History of Science'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that covers the history of science, medicine, and technology. The editor-in-chief is Lissa L. Roberts (University of Twente). It was established in 1962 and is published by SAGE Publications. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Scopus and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', its 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... is 1.0371. References External links * SAGE Publishing academic journals English-language journals History of science journals Philosophy of science journals Academic journals established in 1962 Quarterly journals {{science-philo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bibliographical Encyclopedia Of Astronomers
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |