|
Carinodens
''Carinodens'' is an extinct genus of Cretaceous marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. "''Carinodens''" means "keel teeth" and was named in 1969 as a replacement name for ''Compressidens'', "compressed teeth", which was already in use for a gadilidan scaphopod mollusk. ''Carinodens'' is widely considered a sister taxon to '' Globidens'' classified within the tribe Globidensini. Like its close relative, ''Carinodens'' also possesses distinctive round, blunt teeth for crushing primitive clams and oysters. Most of the cranial elements known from the genus have been recovered from deposits in the Netherlands and Belgium, with the only known postcranial material being known from deposits of latest Maastrichtian age in Jordan. Other materials have been discovered in Europe, North America, South America and North Africa. Description ''Carinodens'' measured about in length and is one of the smallest known mosasaurs. It was closely related to '' Globidens'', though is scan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globidensini
The Globidensini or Globidentatini are a tribe of mosasaurine mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the tribe, known as "globidensins" or "globidensine mosasaurs", have been recovered from North America, Europe, Africa and Asia. The tribe contains the genera '' Globidens'' (the best studied genus by far), '' Carinodens'', '' Igdamanosaurus'',Schulp, Anne S., et al. "New mosasaur material from the Maastrichtian of Angola, with notes on the phylogeny, distribution and palaeoecology of the genus Prognathodon." On Maastricht Mosasaurs. Publicaties van het Natuurhistorisch Genootschap in Limburg 45.1 (2006): 57-67/ref>Lindgren, Johan. "Dental and vertebral morphology of the enigmatic mosasaur Dollosaurus (Reptilia, Mosasauridae) from the lower Campanian (Upper Cretaceous) of southern Sweden." Bulletin of the Geological Society of Denmark 52.17 (2005): e25/ref> ''Harranasaurus'' and '' Xenodens''. Features of the maxilla and digits make the placemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
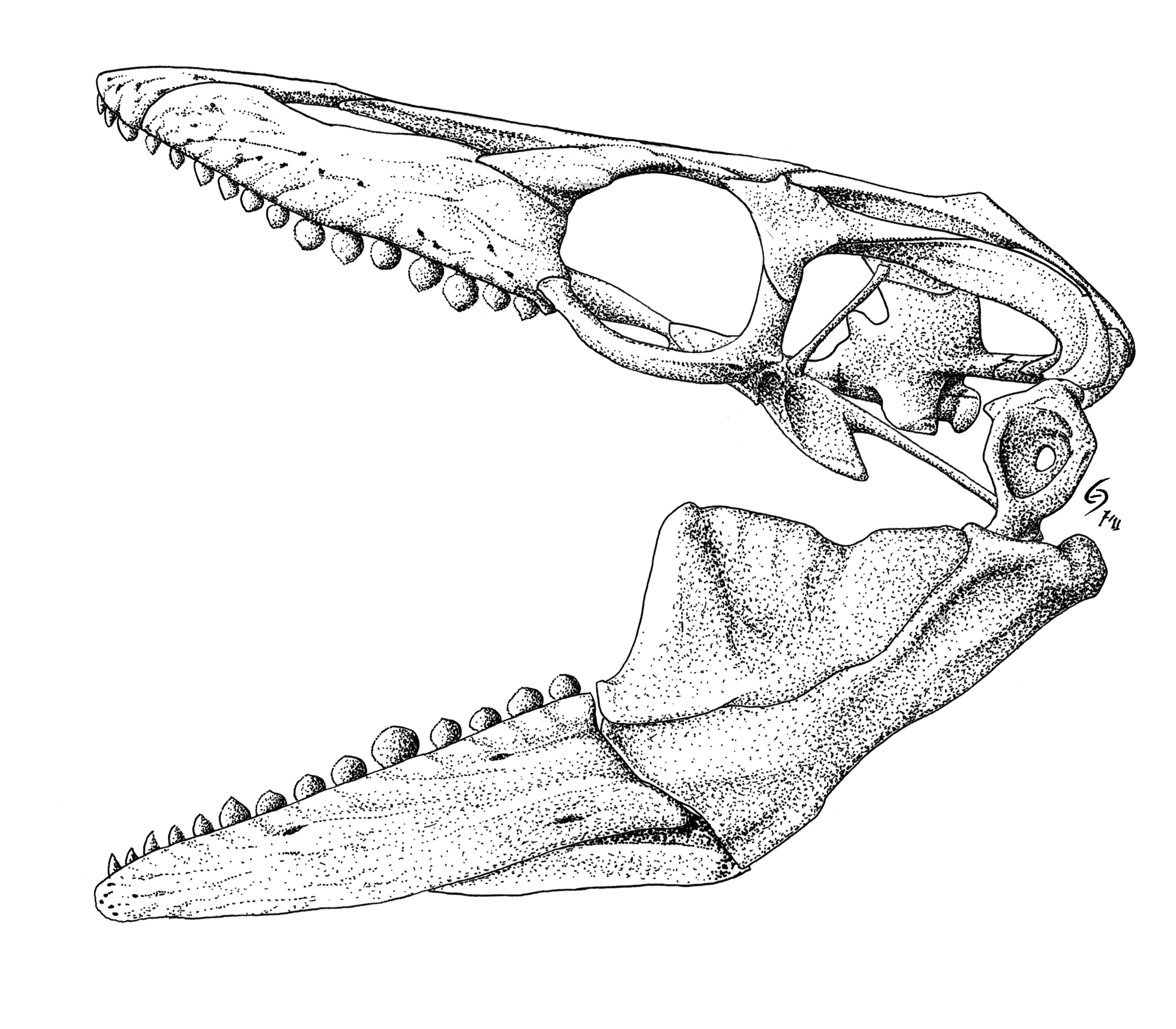
Globidens
''Globidens'' ("Globe tooth") is an extinct genus of mosasaurid oceanic lizard classified as part of the Globidensini tribe in the Mosasaurinae subfamily. ''Globidens'' belongs to the family Mosasauridae, which consists of several genera of predatory marine lizards of various sizes that were prevalent during the Late Cretaceous. Specimens of ''Globidens'' have been discovered in Angola, Brazil, Colombia, Morocco, Syria and the United States. Among mosasaurs, ''Globidens'' is probably most well known for the highly rounded, globe-like teeth that give it its name. ''Globidens alabamaensis'' was the first species of ''Globidens'' described, in a publication by Charles W. Gilmore (1912). It is used as the type specimen for ''Globidens''. Description ''Globidens'' was a relatively medium-sized mosasaur, measuring about long. It was similar in appearance to other mosasaurs, with its streamlined body, flippers, a laterally flattened tail, and powerful jaws. The teeth of ''Globidens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globidens Alabamaensis
''Globidens'' ("Globe tooth") is an extinct genus of mosasaurid oceanic lizard classified as part of the Globidensini tribe in the Mosasaurinae subfamily. ''Globidens'' belongs to the family Mosasauridae, which consists of several genera of predatory marine lizards of various sizes that were prevalent during the Late Cretaceous. Specimens of ''Globidens'' have been discovered in Angola, Brazil, Colombia, Morocco, Syria and the United States. Among mosasaurs, ''Globidens'' is probably most well known for the highly rounded, globe-like teeth that give it its name. ''Globidens alabamaensis'' was the first species of ''Globidens'' described, in a publication by Charles W. Gilmore (1912). It is used as the Type (biology), type specimen for ''Globidens''. Description ''Globidens'' was a relatively medium-sized mosasaur, measuring about long. It was similar in appearance to other mosasaurs, with its streamlined body, flipper (anatomy), flippers, a laterally flattened tail, and powerfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes. During the last 20 million years of the Cretaceous period (Turonian–Maastrichtian ages), with the extinction of the ichthyosaurs and Pliosauridae, pliosaurs, mosasaurids became the dominant marine predators. They themselves became extinct as a result of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, K-Pg event at the end of the Cretaceous period, about 66 million years ago. Description Mosasaurs breathed air, were powerful swimmers, and were well-adapted to living in the warm, shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas prevalent during the Late Cretaceous period. Mosasaurs were so well adapted to thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of the Americas. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Drake Passage; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. The Dutch Caribbean ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao) and Trinidad and Tobago are geologically located on the South-American continental shel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of the Western Sahara in the west, to Egypt and Sudan's Red Sea coast in the east. The most common definition for the region's boundaries includes Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, and Western Sahara, the territory territorial dispute, disputed between Morocco and the list of states with limited recognition, partially recognized Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The United Nations’ definition includes all these countries as well as Sudan. The African Union defines the region similarly, only differing from the UN in excluding the Sudan and including Mauritania. The Sahel, south of the Sahara, Sahara Desert, can be considered as the southern boundary of North Africa. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodont
In anatomy, a heterodont (from Greek, meaning 'different teeth') is an animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology. Human dentition is heterodont and diphyodont as an example. In vertebrates, heterodont pertains to animals where teeth are differentiated into different forms. For example, members of the Synapsida generally possess incisors, canines ("dogteeth"), premolars, and molars. The presence of heterodont dentition is evidence of some degree of feeding and or hunting specialization in a species. In contrast, homodont or isodont dentition refers to a set of teeth that possess the same tooth morphology. In invertebrates, the term heterodont refers to a condition where teeth of differing sizes occur in the hinge plate, a part of the Bivalvia Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing Temporomandibular joint, joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower Human tooth, teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic Revolution, Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be Human jaw shrinkage, smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to Mandibular fracture, fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |