|
Cardiosporidium Cionae
''Cardiosporidium'' is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. It infects the ascidian ''Ciona intestinalis''. History This genus was first described by Van Gaver and Stephan in 1907. It was redescribed by Ciancio ''et al'' in 2008. Taxonomy There is one known species in this genus: ''Cardiosporidium cionae''. It appears to be related to the genera ''Babesia'', ''Cytauxzoon'' and ''Theileria ''Theileria'' is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to ''Plasmodium''. Two ''Theileria'' species, ''T. annulata'' and ''T. parva'', are important cattle parasites. ''T. annulata'' causes tropical ...''. Description The parasite infects the pericardial body of the host. Like other members of this phylum it possesses apicoplasts, rhoptry and subpellicular microtubules. This Apicomplexan parasite is occasionally itself "parasitised" by an alphaproteobacteria from the order ''Rickettsiales''. The symbiont is termed a "pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
SAR is a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and rhizarians. It is a node-based taxon (under the Sar name), including all descendants of the three groups' last common ancestor, and comprises most of the now-rejected Chromalveolata. Their sister group has been found to be telonemids, with which they make up the TSAR clade. Harosa is sometimes used synonymously with TSAR. Etymology The name SAR is an acronym derived from the first letters of its three constituent clades; it has been alternatively spelled RAS. The term Harosa (at the subkingdom level) has also been used, with Stramenopiles replaced by its synonym Heterokonta in this variant of the acronym. History of discovery Before the discovery of the SAR supergroup, stramenopiles and alveolates were classified in the supergroup Chromalveolata alongside haptophytes and cryptomonads, being believed to have acquired plastids th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia; single: apicomplexan) are organisms of a large phylum of mainly parasitic alveolates. Most possess a unique form of organelle structure that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplastwith an apical complex membrane. The organelle's apical shape is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetrating a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. Most are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus, and the Chromerida, some of which are photosynthetic partners of corals. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis ('' Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aconoidasida
The Aconoidasida are a Class (biology), class of apicomplexan parasites coined by Mehlhorn ''et al'' in 1980. Description Organisms in this class bear a tip at one end of their outer membrane. This apical complex includes vesicles called rhoptries and micronemes, which open at the anterior of the cell. These secrete enzymes that allow the parasite to enter other cells. The tip is surrounded by a band of microtubules, called the polar ring. As the name indicates, Aconoidasida (from Greek language, Greek: negative prefix ''a-'' = "lacking") lack a conoid (organelle), conoid (they do have one only during the ookinete stage) in contrast to the class Conoidasida which have one throughout their life cycle. See also *Haemosporidiasina References Aconoidasida, Apicomplexa classes {{Apicomplexa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatorida
Achromatorida is an order of non-pigmented intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates belonging to the subclass Haemosporidiasina. The order was created by Jacques Euzéby in 1988. The taxonomy of these organisms has been one of some controversy. Weylon in 1926 grouped many of these genera into the genus ''Babesia'' - given what is now known about these genera this was probably an error. Agreement on the organisation of these genera probably cannot be regarded as being settled. Description These are minute rounded or pyriform parasites found within erythrocytes, or other circulating or endothelial cells of vertebrates. The parasites reproduce by merogony without oocysts or spores. The apical complex has a polar ring and rhoptries. A conoid is lacking and most species lack the associated pellicular microtubules. Flagellae are lacking. The trophozoite stage is separated from erythrocyte by single membrane (in the other groups there usually 2 or more). Vectors include ticks and leec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiosporidium Cionae
''Cardiosporidium'' is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. It infects the ascidian ''Ciona intestinalis''. History This genus was first described by Van Gaver and Stephan in 1907. It was redescribed by Ciancio ''et al'' in 2008. Taxonomy There is one known species in this genus: ''Cardiosporidium cionae''. It appears to be related to the genera ''Babesia'', ''Cytauxzoon'' and ''Theileria ''Theileria'' is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to ''Plasmodium''. Two ''Theileria'' species, ''T. annulata'' and ''T. parva'', are important cattle parasites. ''T. annulata'' causes tropical ...''. Description The parasite infects the pericardial body of the host. Like other members of this phylum it possesses apicoplasts, rhoptry and subpellicular microtubules. This Apicomplexan parasite is occasionally itself "parasitised" by an alphaproteobacteria from the order ''Rickettsiales''. The symbiont is termed a "pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciona Intestinalis
''Ciona intestinalis'' (sometimes known by the common name of vase tunicate) is an ascidian (sea squirt), a tunicate with very soft tunic. Its Latin name literally means "pillar of intestines", referring to the fact that its body is a soft, translucent column-like structure, resembling a mass of intestines sprouting from a rock. It is a globally distributed cosmopolitan species. Since Linnaeus described the species, ''Ciona intestinalis'' has been used as a model invertebrate chordate in developmental biology and genomics. Studies conducted between 2005 and 2010 have shown that there are at least two, possibly four, sister species. More recently it has been shown that one of these species has already been described as '' Ciona robusta''. By anthropogenic means, the species has invaded various parts of the world and is known as an invasive species. Although Linnaeus first categorised this species as a kind of mollusk, Alexander Kovalevsky found a tadpole-like larval stage durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babesia
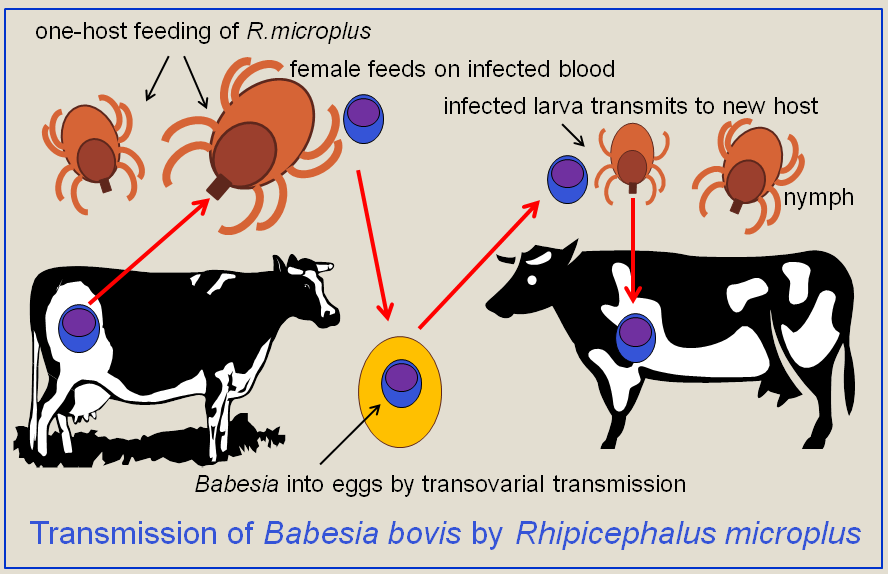
''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888; over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since been identified. ''Babesia'' comprises more than 100 species of tick-borne parasites that infect erythrocytes (red blood cells) in many vertebrate hosts. ''Babesia'' species infect livestock worldwide, wild and domestic vertebrate animals, and occasionally humans, where they cause the disease babesiosis. In the United States, ''B. microti'' is the most common strain of the few that have been documented to cause disease in humans. Classification ''Babesia'' is a protozoan parasite found to infect vertebrate animals, mostly livestock mammals and birds, but also occasionally humans. Common names of the disease that ''B. microti'' causes are Texas cattle fever, redwater fever, tick fever, and Nantucket fever. The disease it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytauxzoon
''Cytauxzoon'' is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. The name is derived from the Greek meaning an increase in the number of cells in an animal. History This genus was created in 1948 when Neitz and Thomas proposed the name ''Cytauxzoon'' to accommodate the ''Theileria'' like parasites with preerythrocytic schizogony in histiocytes. This is in contrast to schizogony in lymphocytes with the latter being characteristic for ''Theileria''. This genus was originally described in African ruminants but is now known to be common in felids including the domestic cat (''Felis catus''). It was first described in the African grey duiker ('' Sylvicapra grimmia''). ''C. felis'' was first described by Kier in 1979. Taxonomy This genus is closely related to ''Theileria'' but differs from it by replicating in macrophages rather than lymphocytes. Description Life cycle The parasites are transmitted by tick bite. After a cat or other host is bitten by an infected tic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theileria
''Theileria'' is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to ''Plasmodium''. Two ''Theileria'' species, ''T. annulata'' and ''T. parva'', are important cattle parasites. ''T. annulata'' causes tropical theileriosis and ''T. parva'' causes East Coast fever. ''Theileria'' species are transmitted by ticks. The genomes of ''T. orientalis'' Shintoku'', Theileria equi'' WA, ''Theileria annulata'' Ankara and ''Theileria parva'' Muguga have been sequenced and published. ''Theileria equi'' infects equid blood cells causing equine piroplasmosis. The disease presents with a variety of clinical conditions, such as fever, depression, jaundice, cramps, haemolytic anaemia, hemoglobinuria and even death, but asymptomatic infections are frequently observed. The most common vectors are the ticks ''Dermacentor nitens'' and ''Rhipicephalus microplus'' but ''Amblyomma cajennense'' was also implicated in the disease transmission. Vaccines against ''Theiler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |