|
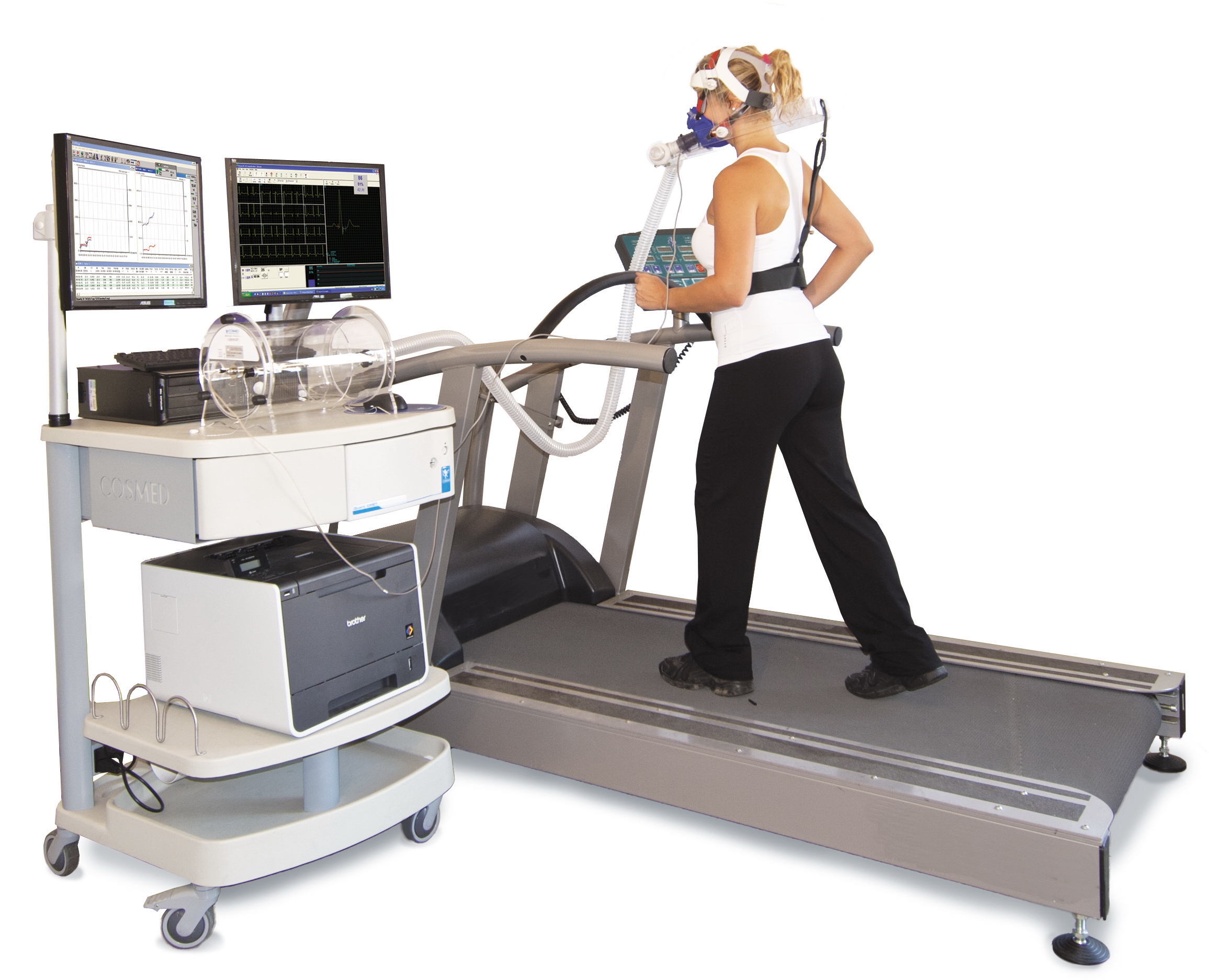
Cardiorespiratory Distress
Cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) refers to the ability of the circulatory and respiratory systems to supply oxygen to skeletal muscles during sustained physical activity. Scientists and researchers use CRF to assess the functional capacity of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. These functions include ventilation, perfusion, gas exchange, vasodilation, and delivery of oxygen to the body's tissues. As these body's functions are vital to an individual's health, CRF allows observers to quantify an individual's morbidity and mortality risk as a function of cardiorespiratory health. In 2016, the American Heart Association published an official scientific statement advocating that CRF, quantifiable as V̇O2 max/peak, be categorized as a clinical vital sign and should be routinely assessed as part of clinical practice. Low levels of CRF have been shown to increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and all-cause mortality. Some medical researchers claim that CRF is an even s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. subarachnoid hemorrhage, Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontinence, loss of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Physiology
Cardiovascular physiology is the study of the cardiovascular system, specifically addressing the physiology of the heart ("cardio") and blood vessels ("vascular"). These subjects are sometimes addressed separately, under the names cardiac physiology and circulatory physiology. Although the different aspects of cardiovascular physiology are closely interrelated, the subject is still usually divided into several subtopics. Heart * Cardiac output (= heart rate * stroke volume. Can also be calculated with Fick principle, palpating method.) ** Stroke volume (= end-diastolic volume − end-systolic volume) ** Ejection fraction (= stroke volume / end-diastolic volume) ** Cardiac output is mathematically ` to systole ** Inotropic, chronotropic, and dromotropic states ** Cardiac input (= heart rate * suction volume Can be calculated by inverting terms in Fick principle) ** Suction volume (= end-systolic volume + end-diastolic volume) ** Injection fraction (=suction volum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise professionals and utilise education, lifestyle intervention and specific forms of exercise to rehabilitate and manage acute and chronic injuries and conditions. Understanding the effect of exercise involves studying specific changes in muscular, cardiovascular, and Neuro-hormonal, neurohormonal Biological system, systems that lead to changes in functional capacity and Physical strength, strength due to endurance training or strength training. The effect of training on the body has been defined as the reaction to the adaptive responses of the body arising from exercise or as "an elevation of metabolism produced by exercise". Exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Governor
The central Governor (device), governor is a proposed process in the brain that regulates exercise in regard to a neurally calculated safe exertion by the body. In particular, physical activity is controlled so that its intensity cannot threaten the body’s homeostasis by causing Hypoxia (medical), anoxic damage to the Myocardial ischemia, heart muscle. The central governor limits exercise by reducing the neural recruitment of muscle fibers. This reduced recruitment causes the sensation of muscle fatigue, fatigue. The existence of a central governor was suggested to explain fatigue after prolonged strenuous exercise in long-distance running and other endurance sports, but its ideas could also apply to other causes of exertion-induced fatigue. The existence of a central governor was proposed by Tim Noakes in 1997, but a similar idea was suggested in 1924 by Archibald Hill. It was first published as a full theory by Tim Noakes, Alan St Clair Gibson and Vicki Lambert in five lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Conditioning
Aerobic conditioning is the use of continuous, rhythmic movement of large muscle groups to strengthen the heart and lungs ( cardiovascular system), as well as changes to the skeletal muscles. Improvement in aerobic conditioning occurs when athletes expose themselves to an increase in oxygen uptake and metabolism, but to keep this level of aerobic conditioning, the athletes must keep or progressively increase their training to increase their aerobic conditioning. Aerobic conditioning is usually achieved through aerobic exercise such as running, swimming, rowing machine, elliptical, treadmill, cycling, etc. A stronger heart does not pump more blood by beating faster but by beating more efficiently, primarily via increased stroke volume and left ventricular mass. Trained endurance athletes can have resting heart rates as low as a reported 28 beats per minute ( Miguel Indurain) or 32 beats per minute ( Lance Armstrong), both of whom were professional cyclists at the highest lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the ventricle (heart), ventricle per beat. Stroke volume is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an Echocardiography, echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat (called end-systolic volume) from the volume of blood just prior to the beat (called end-diastolic volume). The term ''stroke volume'' can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although when not explicitly stated it refers to the left ventricle and should therefore be referred to as left stroke volume (LSV). The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 90 mL in a healthy 70-kg man. Any persistent difference between the two stroke volumes, no matter how small, would inevitably lead to venous congestion of either the systemic or the pulmonary circulation, with a corresponding state of hypotension in the other circulatory sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. It is also modulated by numerous factors, including (but not limited to) genetics, physical fitness, Psychological stress, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness, as well as the interaction between these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse rate measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. An ultra-trained athlete would have a resting heart rate of 37–38 bpm. ''Tachycardia'' is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. ''Bradycardia'' is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by a single Ventricle (heart), ventricle of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). Cardiac output (CO) is the product of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm), and the stroke volume (SV), which is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat; thus giving the formula: :CO = HR \times SV Values for cardiac output are usually denoted as L/min. For a healthy individual weighing 70 kg, the cardiac output at rest averages about 5 L/min; assuming a heart rate of 70 beats/min, the stroke volume would be approximately 70 mL. Because cardiac output is related to the quantity of blood delivered to various parts of the body, it is an important com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Flow
Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. Blood flow ensures the transportation of nutrients, hormones, metabolic waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide throughout the body to maintain cell-level metabolism, the regulation of the pH, osmotic pressure and temperature of the whole body, and the protection from microbial and mechanical harm. Blood is a non-Newtonian fluid, and is most efficiently studied using rheology rather than hydrodynamics. Because blood vessels are not rigid tubes, classic hydrodynamics and fluids mechanics based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |