|
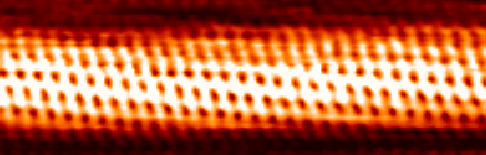
Carbon Peapod
Carbon peapod is a hybrid nanomaterial consisting of spheroidal fullerenes encapsulated within a carbon nanotube. It is named due to their resemblance to the seedpod of the pea plant. Since the properties of carbon peapods differ from those of nanotubes and fullerenes, the carbon peapod can be recognized as a new type of a self-assembled graphitic structure. Possible applications of nano-peapods include nanoscale lasers, single electron transistors, spin-qubit arrays for quantum computing, nanopipettes, and data storage devices thanks to the memory effects and superconductivity of nano-peapods. History Single-walled nanotubes (SWNTs) were first seen in 1993 as cylinders rolled from a single graphene sheet. In 1998, the first peapod was observed by Brian Smith, Marc Monthioux and David Luzzi. The idea of peapods came from the structure that was produced inside a transmission electron microscope in 2000. They were first recognized in fragments obtained by a pulsed-laser vaporiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanobud3
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (Molecular diffusion, particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, statistics, data science, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, data and price v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotubes
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range (nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized: * ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') have diameters around 0.5–2.0 nanometer, nanometres, about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. They can be idealised as cutouts from a two-dimensional graphene sheet rolled up to form a hollow cylinder. * ''Multi-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consist of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes in a nested, tube-in-tube structure. Double- and triple-walled carbon nanotubes are special cases of MWCNT. Carbon nanotubes can exhibit remarkable properties, such as exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity because of their nanostructure and bond strength, strength of the bonds between carbon atoms. Some SWCNT structures exhibit high electrical conductivity while others are semiconductors. In addition, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored. Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Structure In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Level
The Fermi level of a solid-state body is the thermodynamic work required to add one electron to the body. It is a thermodynamic quantity usually denoted by ''μ'' or ''E''F for brevity. The Fermi level does not include the work required to remove the electron from wherever it came from. A precise understanding of the Fermi level—how it relates to electronic band structure in determining electronic properties; how it relates to the voltage and flow of charge in an electronic circuit—is essential to an understanding of solid-state physics. In band structure theory, used in solid state physics to analyze the energy levels in a solid, the Fermi level can be considered to be a hypothetical energy level of an electron, such that at thermodynamic equilibrium this energy level would have a ''50% probability of being occupied at any given time''. The position of the Fermi level in relation to the band energy levels is a crucial factor in determining electrical properties. The Fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names for the elements in some languages, such as German and Russian. rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute Group (periodic table)#Group names, group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of periodic trends, group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised Homologous series, homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element. The alkali metals are all shiny, hardness, sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Room Temperature
Room temperature, colloquially, denotes the range of air temperatures most people find comfortable indoors while dressed in typical clothing. Comfortable temperatures can be extended beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation, and other factors. In certain fields, like science and engineering, and within a particular context, room temperature can mean different agreed-upon ranges. In contrast, ambient temperature is the actual temperature, as measured by a thermometer, of the air (or other medium and surroundings) in any particular place. The ambient temperature (e.g. an unheated room in winter) may be very different from an ideal ''room temperature''. Food and beverages may be served at "room temperature", meaning neither heated nor cooled. Comfort temperatures Comfort temperature is interchangeable with neutral temperature in the scientific literature, which can be calculated through regression analysis between thermal sensation votes and indoor temperature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fullerides
Fullerides are chemical compounds containing fullerene anions. Common fullerides are derivatives of the most common fullerenes, i.e. C60 and C70. The scope of the area is large because multiple charges are possible, i.e., 60sup>''n''− (''n'' = 1, 2...6), and all fullerenes can be converted to fullerides. The suffix "-ide" implies their negatively charged nature. Fullerides can be isolated as derivatives with a wide range of cations. Most heavily studied derivatives are those with alkali metals, but fullerides have been prepared with organic cations. Fullerides are typically dark colored solids that generally dissolve in polar organic solvents. Structure and bonding According to electronic structure calculations, the LUMO of C60 is a triply degenerate orbital of t1u symmetry. Using the technique cyclic voltammetry, C60 can be shown to undergo six reversible reductions starting at −1 V referenced to the Fc+/Fc couple. Reduction causes only subtle changes in the str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Gap
In solid-state physics and solid-state chemistry, a band gap, also called a bandgap or energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap refers to the energy difference (often expressed in electronvolts) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The resulting conduction-band electron (and the electron hole in the valence band) are free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as charge carriers to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Transformation
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition States of matter Phase transitions commonly refer to when a substance transforms between one of the four states of matter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphous Carbon
Amorphous carbon is free, reactive carbon that has no crystalline structure. Amorphous carbon materials may be stabilized by terminating dangling-π bonds with hydrogen. As with other amorphous solids, some short-range order can be observed. Amorphous carbon is often abbreviated to ''aC'' for general amorphous carbon, ''aC:H'' or ''HAC'' for hydrogenated amorphous carbon, or to ''ta-C'' for tetrahedral amorphous carbon (also called diamond-like carbon). In mineralogy In mineralogy, amorphous carbon is the name used for coal, carbide-derived carbon, and other impure forms of carbon that are neither graphite nor diamond. In a crystallographic sense, however, the materials are not truly amorphous but rather polycrystalline materials of graphite or diamond within an amorphous carbon matrix. Commercial carbon also usually contains significant quantities of other elements, which may also form crystalline impurities. In modern science With the development of modern thin f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |