|
Capture Of The Sloop Anne
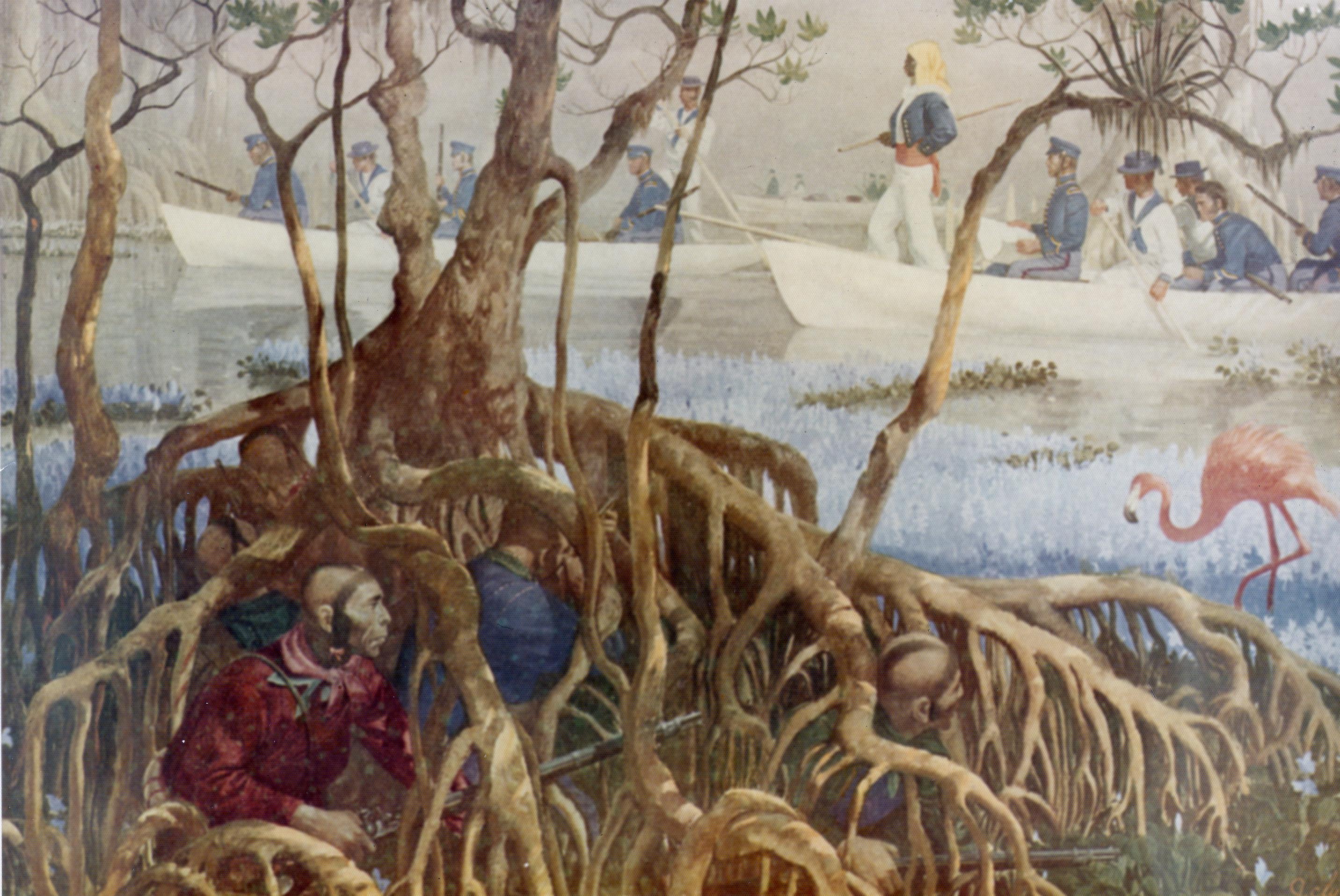
The capture of the sloop ''Anne'' was the result of a naval campaign carried out by an alliance between the Spanish Empire forces in Puerto Rico, the Danish government in Saint Thomas and the United States Navy. The powers pursued Roberto Cofresí's pirate flotilla in March 1825 because of the economic losses suffered by the parties to the pirates, as well as diplomatic concerns caused by their use of the flags of Spain and Gran Colombia which menaced the fragile peace between the naval powers. Several of those involved had been attacked by the freebooters. Among the diplomatic concerns caused by Cofresí was a robbery carried out by several of his subordinates, the catalyst of an incident that threatened war between Spain and the United States known as "The Foxardo Affair", eventually leading to the resignation of his rival, pirate hunter David Porter. Sailing under the authorization of the Danish West Indies, the coalition employed two local ships, including a former victi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Navy Marines
The Marine Infantry () are the marines of the Spanish Navy. Responsible for conducting amphibious warfare. Fully integrated into the Spanish Navy's structure, the branch's history dates back to 1537 when Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor formed the , making it the oldest Marines, marine unit in existence. History First period The (Navy Infantry) was created by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V in 1537, when he permanently assigned the (Old Sea Companies of Kingdom of Naples, Naples) to the (Mediterranean Galley Squadrons). But it was Philip II of Spain, Philip II who established today's concept of a Landing operation, landing force. This was a pure naval power projection ashore by forces deployed from ships that could maintain their ability to fight despite being based on board. This is the period of the famous Tercios (literally "One Third", due to its organisation: one third of musketeers, one third of swordsmen and the final third of Pike (weapon), pikemen):''La Inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of navy, naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest quality, best known, or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahía De Jobos
Bahía de Jobos ( English: ''Jobos Bay'') or Reserva Natural de Investigación Estuarina de Bahía de Jobos ( English: ''Jobos Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve'') is a federally protected estuary in Aguirre, Salinas, Puerto Rico. The bay is an intertidal tropical ecosystem dominated by seagrass beds, coral reefs, and mangroves.JOBOS BAY ESTUARINE PROFILE: A NATIONAL ESTUARINE RESEARCH RESERVE. 2002. Editor: Raph Field Authors: Pedro O. Robles, Carmen M. Gonzalez, Eddie N. Laboy, and Jorge Capella. In an area of , the reserve contains five distinct habitat types and provides sanctuary to several endangered species. Bahía de Jobos is one of 28 reserves that comprise the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) National Estuarine Research Reserve System. The reserve is operated in conjunction with the Puerto Rico Department of Natural and Environmental Resources (DRNA). History Jobos Bay is located on the south coast of Puerto Rico in Aguirre barr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies Squadron (United States)
The West Indies Squadron, or the West Indies Station, was a United States Navy squadron that operated in the West Indies in the early nineteenth century. It was formed due to the need to suppress piracy in the Caribbean Sea, the Antilles and the Gulf of Mexico region of the Atlantic Ocean. This unit later engaged in the Second Seminole War until being combined with the Home Squadron in 1842. From 1822 to 1826 the squadron was based out of Saint Thomas Island until the Pensacola Naval Yard was constructed. Formation United States Navy ships had for years operated against piracy and the slave trade in the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico but it was not until 1822 that a permanent squadron was formed. American warships were assigned to anti-piracy operations in the West Indies as early as 1817 but after a September 1821 attack by pirates, in which three American merchant ships were captured, the United States Congress authorized Commodore James Biddle to dispatch a fleet to the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Ship
United States Ship (abbreviated as USS or U.S.S.) is a ship prefix used to identify a commissioned ship of the United States Navy and applies to a ship only while it is in commission. Before commissioning, the vessel may be referred to as a " pre-commissioning unit" (PCU), but is officially referred to by name with no prefix. After decommissioning, it is referred to by name with no prefix, though people commonly refer to those ships with the prefix "ex-", as in ex-''ship name''. In-service but non-commissioned Navy ships go by the prefix USNS, which stands for United States Naval Ship. From the early beginnings of the U.S. Navy there had been no standard method of referring to U.S. Navy ships until 1907 when President Theodore Roosevelt Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Porter (naval Officer)
David Porter (February 1, 1780 – March 3, 1843) was an American naval officer and diplomat. Porter commanded a number of U.S. naval ships. He saw service in the First Barbary War, the War of 1812 and in the West Indies. On July 2, 1812, Porter hoisted the banner "Free trade and sailors' rights" as captain of .Gilje, Paul A. Free Trade and Sailors' Rights in the War of 1812', Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2013, , p. 1. The phrase resonated with many Americans. Porter was later court martialed; he resigned and then joined and became commander-in-chief of the Mexican Navy. Porter County, Indiana was named after him. Early life Born in Boston, Massachusetts, Porter served in the Quasi-War with France first as midshipman aboard , participating in the capture of '' L'Insurgente'' on February 9, 1799; then as 1st lieutenant of ; and finally in command of USS ''Amphitheatre''. During the First Barbary War (1801–07), Porter was first lieutenant of , , and and was take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), also known as Greater Colombia and officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and parts of Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador (i.e. excluding the Galápagos Islands), Panama, and Venezuela, along with the Caribbean coasts of Nicaragua and Costa Rica, parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil, and Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute, claimed the Essequibo region. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiography, historiographically to distinguish it from the current Colombia, Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state. However, Diplomatic recognition, international recognition of the legitimacy of the Gran Colombian state ran afoul of European opposition to the independence of states in the Americas. Austrian Empire, Austria, Bourb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, and vessels used for piracy are called pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples of such areas include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish West Indies
The Danish West Indies () or Danish Virgin Islands () or Danish Antilles were a Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas with , Saint John () with , Saint Croix with , and Water Island. The islands of St Thomas, St John, and St Croix were purchased by United States in 1917 and became known as the United States Virgin Islands. Water Island was sold in 1905 to the Danish East Asiatic Company and bought by the U.S. Government in 1944. In 1996, it also became part of the U.S. Virgin Islands. Historical overview Acquisition The Danish West India-Guinea Company annexed uninhabited St. Thomas in 1672. It annexed St. John in 1718 and bought St. Croix from France (King Louis XV) on 28 June 1733. When the Danish West India-Guinea Company went bankrupt in 1754, King Frederik V of Denmark–Norway assumed direct control of the three islands. Although, during the Napoleonic Wars, Britain twice occupied the Danish West Indies, first in 1801� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa, various islands in Asia and Oceania, as well as territory in other parts of Europe. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming known as "the empire on which the sun never sets". At its greatest extent in the late 1700s and early 1800s, the Spanish Empire covered , making it one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history. Beginning with the 1492 arrival of Christopher Columbus and continuing for over three centuries, the Spanish Empire would expand across the Caribbean Islands, half of South America, most of Central America and much of North America. In the beginning, Portugal was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |