|
Capricorn Seamount
Capricorn Seamount is a seamount in Tonga. It rises to a depth of about and is capped off by a wide summit platform. It appears to be a submerged volcano of Miocene age that may be part of a volcanic chain with Niue. Capricorn Seamount is located on the eastern flank of the Tonga Trench and is in the process of breaking up; in turn the trench has been altered by the interaction with the downgoing seamount. Geography, research history and name The Capricorn Seamount lies east of Vava'u Island in Tonga and inside of Tonga's exclusive economic zone. First examined by the during the Capricorn Expedition of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, it was successfully dredged in 1958 by the during the Pacific Cruise of the New Zealand Oceanographic Institute. It is also known as Capricorn guyot, Gora Kaprikorn and Capricorn tablemount. Geomorphology and geology The large guyot rises over from the eastern flank of the Tonga Trench to a depth of . It features a wide flat t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seamount
A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form.IHO, 2008. Standardization of Undersea Feature Names: Guidelines Proposal form Terminology, 4th ed. International Hydrographic Organization and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Monaco. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface, such flat-top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron ( mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flows that can spread over great areas before cooling and solidifying. Flood basalts are thick s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
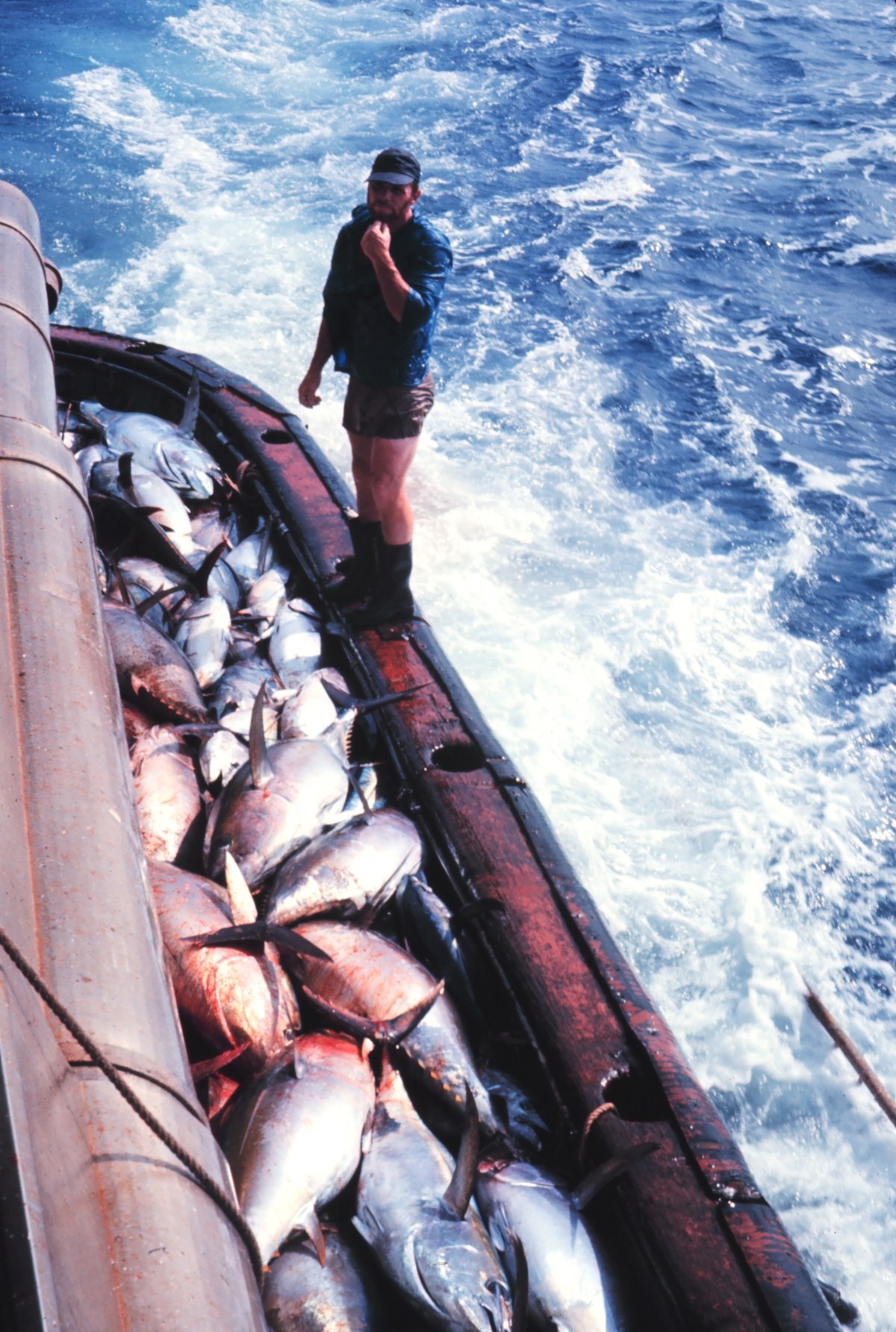
Yellowfin Tuna
The yellowfin tuna (''Thunnus albacares'') is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide. Yellowfin is often marketed as ahi, from the Hawaiian , a name also used there for the closely related bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus''). The species name, ''albacares'' ("white meat") can also lead to confusion: in English, the albacore (''Thunnus alalunga'') is a different species, while yellowfin is officially designated ''albacore'' in French and referred to as ''albacora'' by Portuguese fishermen. Description The yellowfin tuna is among the larger tuna species, reaching weights over , but is significantly smaller than the Atlantic and Pacific bluefin tunas, which can reach over , and slightly smaller than the bigeye tuna and the southern bluefin tuna. The second dorsal fin and the anal fin, as well as the finlets between those fins and the tail, are bright yellow, giving this fish its common name. The second dorsal and anal fins can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigeye Tuna
The bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus'') is a species of true tuna of the genus ''Thunnus'', belonging to the wider mackerel family (biology), family Scombridae. In Hawaiian language, Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ahi, the other being the yellowfin tuna. Bigeye tuna are found in the open waters of all tropical and temperate oceans, but not in the Mediterranean Sea. Description Bigeye tuna can grow up to in length. Maximum weight of individuals probably exceeds , with the all-tackle angling record standing at . They are large, deep-bodied, streamlined fish with large heads and eyes. The pectoral fins are very long, reaching back beyond the start of the second dorsal fin in juveniles and the space between the first and second dorsal fin in adults. They have 13 or 14 Dorsum (biology), dorsal spines. Physiology Bigeye tuna have a unique physiology which allows them to forage in deeper colder waters and tolerate oxygen-poor waters. Bigeye tuna are reported to tolerate ambie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Scombriformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct stocks known globally in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans, as well as the Mediterranean Sea. The albacore has an elongate, fusiform body with a conical snout, large eyes, and remarkably long pectoral fins. Its body is a deep blue dorsally and shades of silvery white ventrally. Individuals can reach up to in length. Albacore are pelagic predators that eat a wide variety of foods, including but not limited to fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. They are unique among tuna in that their primary food source is cephalopods, with fish making up a much smaller portion of their diet. Reproduction usually occurs from November to February and is oviparous. An adult female can release over two million eggs in a single cycle. Fry (juvenile fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plio-Pleistocene
The Plio-Pleistocene is an informally described geological pseudo-period, which begins about 5 million years ago (Mya) and, drawing forward, combines the time ranges of the formally defined Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs—marking from about 5 Mya to about 12 kya. Nominally, the Holocene epoch—the last 12 thousand years—would be excluded, but most Earth scientists would probably treat the current times as incorporated into the term "Plio-Pleistocene"; see below. In the contexts of archaeology, paleontology, and paleoanthropology, the Plio-Pleistocene is a very useful period to which scientists may assign the long and continuous run in East Africa of datable sedimentary layers and their contents (e.g. the Bouri Formation). These contents collectively present a focused view of the continuous evolution of the region's large vertebrates, especially the evolution of some African apes ( hominids) to the earliest hominins; and then the development of the early humans and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule and utricle, in turn, together make the ''otolith organs''. These organs are what allows an organism, including humans, to perceive linear acceleration, both horizontally and vertically (gravity). They have been identified in both extinct and extant vertebrates. Counting the annual growth rings on the otoliths is a common technique in estimating the age of fish. Description Endolymphatic infillings such as otoliths are structures in the saccule and Utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the Labyrinth (inner ear), vestibular labyrinth of all vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds). In vertebrates, the saccule and utricle together make the ''otolith organs''. Both statoconia and otoliths are used as gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese Dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cell batteries, such as the alkaline battery and the zinc–carbon battery, although it is also used for other battery chemistries such as aqueous zinc-ion batteries.. is also used as a pigment and as a precursor to other manganese compounds, such as . It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, for example, for the oxidation of allylic alcohols. has an α- polymorph that can incorporate a variety of atoms (as well as water molecules) in the "tunnels" or "channels" between the manganese oxide octahedra. There is considerable interest in as a possible cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Structure Several polymorphs of are claimed, as well as a hydrated form. Like many other dioxides, crystallizes in the rutile crystal structure (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and from the land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and sea slug, slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda is a diverse and highly successful class of mollusks within the phylum Mollusca. It contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Furongian, Late Cambrian. , 721 family (taxonomy), families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently neontology, extant living fossil, with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are unicellular organism, single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class (biology), class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "Test (biology), test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and ''Textularia'' in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthos, benthic, with different sized species playing a role within the macrobenthos, meiobenthos, and Benthos, microbenthos), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecal Pellet
Feces (also known as faeces or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially-altered bilirubin and dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. Feces are discharged through the anus or cloaca during defecation. Feces can be used as fertilizer or soil conditioner in agriculture. They can also be burned as fuel or dried and used for construction. Some medicinal uses have been found. In the case of human feces, fecal transplants or fecal bacteriotherapy are in use. Urine and feces together are called excreta. Characteristics The distinctive odor of feces is due to skatole, and thiols (sulfur-containing compounds), as well as amines and carboxylic acids. Skatole is produced from tryptophan via indoleacetic acid. Decarboxylation gives skatole. The perceived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |