|
Capmatinib
Capmatinib, sold under the brand name Tabrecta, is an anticancer medication used for the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors have a mutation that leads to the exon 14 skipping of the ''MET'' gene, which codes for the membrane receptor HGFR. The most common adverse reactions are peripheral edema, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, dyspnea, and decreased appetite. Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant cancer cells form in the tissues of the lung. It is the most common type of lung cancer with up to 90% of all lung carcinomas falling into the non-small cell category. Non-small cell lung cancer occurs when healthy cells become abnormal and grow rapidly. One danger of this form of cancer is that there's a high likelihood that the cancer cells will spread from the lungs to other organs and body parts. Cancer metastasis consists of a sequential series of events, and MET exon 14 skipping is recognized as a critical event for metastasis of carci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priority Review
Priority review is a program of the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to expedite the review process for drugs that are expected to have a particularly great impact on the treatment of a disease. The priority review voucher program is a program that grants a voucher for priority review to a drug developer as an incentive to develop treatments for disease indications with limited profitability. Priority review vouchers are currently earned by pharmaceutical companies for the development and approval of drugs treating neglected tropical diseases, rare pediatric diseases, and "medical countermeasures" for terrorism. The voucher can be used for future drugs that could have wider indications for use, but the company is required to pay a fee (approximately $2.8 million) to use the voucher. When seeking approval for a drug, manufacturers can apply to the FDA for priority review. This is granted when a drug is intended to treat a serious condition and would "provide a sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal organs of the organism. The cells of each of the three germ layers undergo differentiation, a process where less-specialized cells become more-specialized through the expression of a specific set of genes. Cell differentiation is driven by cell signaling cascades. Differentiation is influenced by extracellular signals such as growth factors that are exchanged to adjacent cells which is called juxtracrine signaling or to neighboring cells over short distances which is called paracrine signaling. Intracellular signals – a cell signaling itself ( autocrine signaling) – also play a role in organ formation. These signaling pathways allow for cell rearrangement and ensure that organs form at specific sites within the organism. The organogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineoplastic Drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard regimen A regimen is a plan, or course of action such as a Diet (nutrition), diet, exercise or medical treatment. A salt#Health effects, low-salt diet is a regimen. A course of penicillin is a regimen, and there are many chemotherapy regimens in the trea .... Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim only to prolong life or to Palliative care, reduce symptoms (Palliative care, palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''oncology#Specialties, medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' now means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of pharmaceutical products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee For Medicinal Products For Human Use
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), formerly known as the Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP), is the European Medicines Agency's committee responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding medicinal product Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...s for human use. See also * Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use References External links Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Health and the European Union {{eu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combination wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a medication, pharmaceutical agent that is developed to treat certain rare medical conditions. An orphan drug would not be profitable to produce without government assistance, due to the small population of patients affected by the conditions. The conditions that orphan drugs are used to treat are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy that depends on the legislation (if there is any) of the country. Designation of a drug as an orphan drug has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug medical research, research and development. Examples of this can be that in the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Approval (FDA)
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) initiated the FDA Accelerated Approval Program in 1992 to allow faster approval of drugs for serious conditions that fill an unmet medical need. The faster approval relies on use of surrogate endpoints. Drug approval typically requires clinical trials with endpoints that demonstrate a clinical benefit, such as increased survival for cancer patients. Drugs with accelerated approval can initially be tested in clinical trials that use a surrogate endpoint, or something that is thought to predict clinical benefit. Surrogate endpoints typically require less time, and in the case of a cancer patient, it is much faster to measure a reduction in tumor size, for example, than overall patient survival. Drugs approved under the FDA Accelerated Approval Program still need to be tested in clinical trials using endpoints that demonstrate clinical benefit, and those trials are known as phase 4 confirmatory trials. If the drug later proves unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
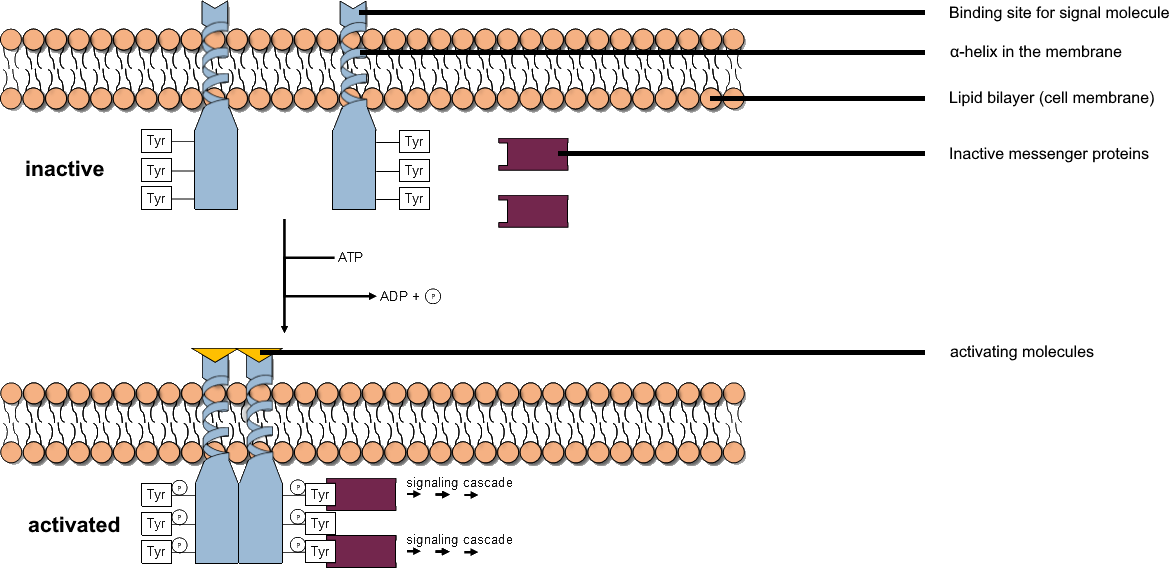
Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticancer Medication
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy regimen, regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a cure, curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim only to prolong life or to Palliative care, reduce symptoms (Palliative care, palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''oncology#Specialties, medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' now means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to induce DNA damage (naturally occurring), DNA damage (so that DNA repair can augment chemotherapy). This meaning excludes the more-selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Met
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGF receptor) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MET'' gene. The protein possesses tyrosine kinase activity. The primary single chain precursor protein is post-translationally cleaved to produce the alpha and beta subunits, which are disulfide linked to form the mature receptor. HGF receptor is a single pass tyrosine kinase receptor essential for embryonic development, organogenesis and wound healing. Hepatocyte growth factor/Scatter Factor (HGF/SF) and its splicing isoform (NK1, NK2) are the only known ligands of the HGF receptor. MET is normally expressed by cells of epithelial origin, while expression of HGF/SF is restricted to cells of mesenchymal origin. When HGF/SF binds its cognate receptor MET it induces its dimerization through a not yet completely understood mechanism leading to its activation. Sometimes MET is misunderstood as of an abbreviation of Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition. It is incorrect. The three letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |