|
Capillary Pressure
In fluid statics, capillary pressure () is the pressure between two immiscible fluids in a thin tube (see capillary action), resulting from the interactions of forces between the fluids and solid walls of the tube. Capillary pressure can serve as both an opposing or driving force for fluid transport and is a significant property for research and industrial purposes (namely microfluidic design and oil extraction from porous rock). It is also observed in natural phenomena. Definition Capillary pressure is defined as: :p_c=p_-p_ where: :p_ is the capillary pressure :p_ is the pressure of the non-wetting phase :p_ is the pressure of the wetting phase The wetting phase is identified by its ability to preferentially diffuse across the capillary walls before the non-wetting phase. The "wettability" of a fluid depends on its surface tension, the forces that drive a fluid's tendency to take up the minimal amount of space possible, and it is determined by the contact angle of the fluid.F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Statics
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear force applied to them. Although the term ''fluid'' generally includes both the liquid and gas phases, its definition varies among branches of science. Definitions of '' solid'' vary as well, and depending on field, some substances can have both fluid and solid properties. Non-Newtonian fluids like Silly Putty appear to behave similar to a solid when a sudden force is applied. Substances with a very high viscosity such as pitch appear to behave like a solid (see pitch drop experiment) as well. In particle physics, the concept is extended to include fluidic matters other than liquids or gases. A fluid in medicine or biology refers to any liquid constituent of the body ( body fluid), whereas "liquid" is not used in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrochemical Industry
file:Jampilen Petrochemical Co. 02.jpg, 300px, Jampilen Petrochemical co., Asaluyeh, Iran The petrochemical industry is concerned with the production and trade of petrochemicals. A major part is constituted by the plastics industry, plastics (polymer) industry. It directly interfaces with the petroleum industry, especially the downstream (petroleum industry), downstream sector. Companies The top global petrochemical companies based on different KPIs: Countries and sites *Marun petrochemical complex Technology Conferences *Asia Petrochemical Industry Conference *International Petrochemical Conference by the American Fuel and Petrochemical Manufacturers, AFPM Associations *American Fuel and Petrochemical Manufacturers (AFPM) *European Petrochemical Association (EPCA) *Gulf Petrochemicals and Chemicals Association (GPCA) *Petrochemicals Europe (industry sector of Cefic) Awards *Medal "For the Tapping of the Subsoil and Expansion of the Petrochemical Complex of Western Siberia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannulation
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; : cannulae or cannulas) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces of a trocar needle thus extending the effective needle length by at least half the length of the original needle. Its size mainly ranges from 14 to 26 gauge. Different-sized cannula have different colours as coded. Decannulation is the permanent removal of a cannula ( extubation), especially of a tracheostomy cannula, once a physician determines it is no longer needed for breathing. Medicine Cannulas normally come with a trocar inside. The trocar is a needle, which punctures the body in order to get into the intended space. Intravenous cannulas are the most common in hospital use. A variety of cannulas are used to establish cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery. A nasal cannula is a piece of plastic tubing that runs un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
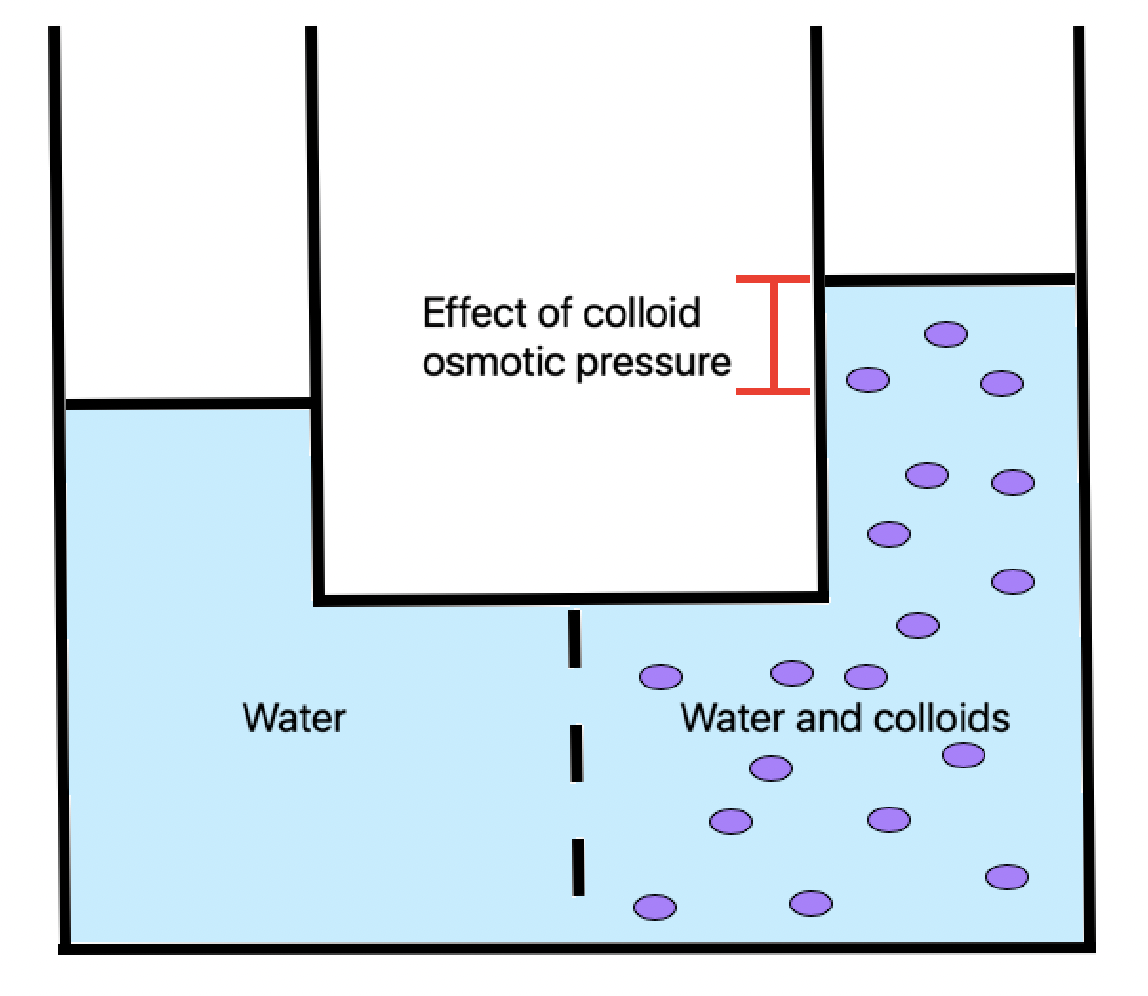
Oncotic Pressure
Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a type of osmotic pressure induced by the plasma proteins, notably albumin, in a blood vessel's plasma (or any other body fluid such as blood and lymph) that causes a pull on fluid back into the capillary. It has an effect opposing both the hydrostatic blood pressure, which pushes water and small molecules out of the blood into the interstitial spaces at the arterial end of capillaries, and the interstitial colloidal osmotic pressure. These interacting factors determine the partitioning of extracellular water between the blood plasma and the extravascular space. Oncotic pressure strongly affects the physiological function of the circulatory system. It is suspected to have a major effect on the pressure across the glomerular filter. However, this concept has been strongly criticised and attention has shifted to the impact of the intravascular glycocalyx layer as the major player. Etymology The word 'oncotic' by definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrostatics
Hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and "the pressure in a fluid or exerted by a fluid on an immersed body". The word "hydrostatics" is sometimes used to refer specifically to water and other liquids, but more often it includes both gases and liquids, whether compressible or incompressible. It encompasses the study of the conditions under which fluids are at rest in stable equilibrium. It is opposed to ''fluid dynamics'', the study of fluids in motion. Hydrostatics is fundamental to ''hydraulics'', the engineering of equipment for storing, transporting and using fluids. It is also relevant to geophysics and astrophysics (for example, in understanding plate tectonics and the anomalies of the Earth's gravitational field), to meteorology, to medicine (in the context of blood pressure), and many other fields. Hydrostatics offers physical explanations for many phenomena of everyday life, such as why atmospheric pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
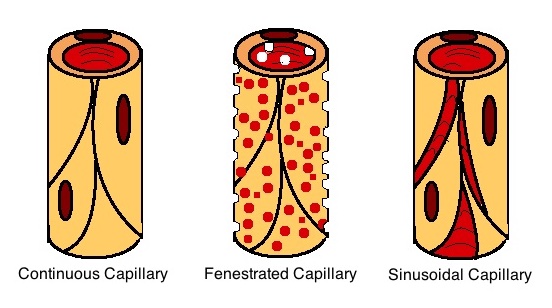
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frost Heaving
Frost heaving (or a frost heave) is an upwards swelling of soil during freezing conditions caused by an increasing presence of ice as it grows towards the surface, upwards from the depth in the soil where freezing temperatures have penetrated into the soil (the freezing front or freezing boundary). Ice growth requires a water supply that delivers water to the freezing front via capillary action in certain soils. The weight of overlying soil restrains vertical growth of the ice and can promote the formation of lens-shaped areas of ice within the soil. Yet the force of one or more growing ice lenses is sufficient to lift a layer of soil, as much as or more. The soil through which water passes to feed the formation of ice lenses must be sufficiently porous to allow capillary action, yet not so porous as to break capillary continuity. Such soil is referred to as "frost susceptible". The growth of ice lenses continually consumes the rising water at the freezing front. Differential fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Ice
Needle ice is a needle-shaped column of ice formed by groundwater. Needle ice forms when the temperature of the soil is above and the surface temperature of the air is below . Liquid water underground rises to the surface by capillary action, and then freezes and contributes to a growing needle-like ice column. The process usually occurs at night when the air temperature reaches its minimum. The ice needles are typically a few centimetres long. While growing, they may lift or push away small soil particles. On sloped surfaces, needle ice may be a factor contributing to soil creep.Isbell, D.: Needle Ice on Mt. Osceola'', EPOD of July 10, 2005. URL last accessed 2007-12-07.Pidwirny, M. URL last accessed 2007-12-07. Alternate names for needle ice are "frost pillars" ("Säuleneis" in German), "frost column", "Spew Ice", "Kammeis" (a German term meaning "comb ice"), "Stängeleis" (another German term referring to the stem-like structures), "shimobashira" (霜柱, a Japanese term m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Ice Showing Distinct Strands
Needle or Needles may refer to: Crafting * Crochet needle, a tool for making loops in thread or yarn * Knitting needle, a tool for knitting, not as sharp as a sewing needle * Sewing needle, a long slender tool with a pointed tip * Trussing needle, a long slender tool, sometimes with a flattened point, to tie poultry for cooking * Upholstery needle, a tool for upholstery, generally thick and curved Science and technology Botany * Needle (botany), of conifers Medicine * Acupuncture needle, in alternative medicine * Hypodermic needle, a hollow needle commonly used with a syringe to inject fluid into or extract fluid from the body * Surgical needle, several types of needles used for surgical suture * Tuohy needle, a needle used to administer epidural catheters Technology * Gramophone needle, used for playing records * Indicator needle, of a measuring instrument * Needle valve People * Dave Needle (1947–2016), American engineer * Sharon Needles (born 1981), American drag queen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifuge Method For Measuring Capillary Pressure
A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to subject a specimen to a specified constant force - for example, to separate various components of a fluid. This is achieved by spinning the fluid at high speed within a container, thereby separating fluids of different densities (e.g. cream from milk) or liquids from solids. It works by causing denser substances and particles to move outward in the radial direction. At the same time, objects that are less dense are displaced and moved to the centre. In a laboratory centrifuge that uses sample tubes, the radial acceleration causes denser particles to settle to the bottom of the tube, while low-density substances rise to the top. A centrifuge can be a very effective filter that separates contaminants from the main body of fluid. Industrial scale centrifuges are commonly used in manufacturing and waste processing to sediment suspended solids, or to separate immiscible liquids. An example is the cream separator found in dairies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |