|
Capell Lofft
Capel Lofft (sometimes spelled Capell; 14 November 1751 – 26 May 1824) was a British lawyer, writer and amateur astronomer. Life Born in London, he was educated at Eton College and Peterhouse, Cambridge. He trained as a lawyer at Lincoln's Inn, where he was called to the bar (qualified as a barrister) in 1775. In addition to his legal practice, he became a prolific writer on the law and political topics. In politics, he was an advocate of parliamentary and other reforms, identifying with the Foxite Whig faction. He also engaged in voluminous correspondence with prominent authors. His legal career was ended by a case in Stanton, Suffolk. On the night of 3 October 1799, Sarah Lloyd, a 22 year old servant, was incited by a suitor to steal 40 shillings. She was caught, tried, and sentenced to death by hanging. Capel Lofft fought strenuously but unsuccessfully for a reprieve. Lloyd was to be executed on 23 April 1800 in Bury St Edmunds. Lofft accompanied the cart transporting L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Astronomer
Amateur astronomy is a hobby where participants enjoy observing or imaging celestial objects in the sky using the unaided eye, binoculars, or telescopes. Even though scientific research may not be their primary goal, some amateur astronomers make contributions in doing citizen science, such as by monitoring variable stars, double stars, sunspots, or occultations of stars by the Moon or asteroids, or by discovering transient astronomical events, such as comets, galactic novae or supernovae in other galaxies. Amateur astronomers do not use the field of astronomy as their primary source of income or support, and usually have no professional degree in astrophysics or advanced academic training in the subject. Most amateurs are hobbyists, while others have a high degree of experience in astronomy and may often assist and work alongside professional astronomers. Many astronomers have studied the sky throughout history in an amateur framework; however, since the beginning of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbrella
An umbrella or parasol is a folding canopy supported by wooden or metal ribs that is mounted on a wooden, metal, or plastic pole. It is usually designed to protect a person against rain. The term ''umbrella'' is traditionally used when protecting oneself from rain, while ''parasol'' is used when protecting oneself from sunlight, though the terms continue to be used interchangeably. Often the difference is the material used for the canopy; some parasols are not waterproof, and some umbrellas are transparent. Umbrella canopies may be made of fabric or flexible plastic. There are also combinations of parasol and umbrella that are called ''en-tout-cas'' (French for "in any case"). Generally speaking, parasols and umbrellas are small, handheld, personal use items. Golf umbrellas are the biggest hand-portable umbrellas available. There are two types of umbrellas: completely collapsible umbrellas, which can be folded up into a small enough bag because of the supporting metal pole's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
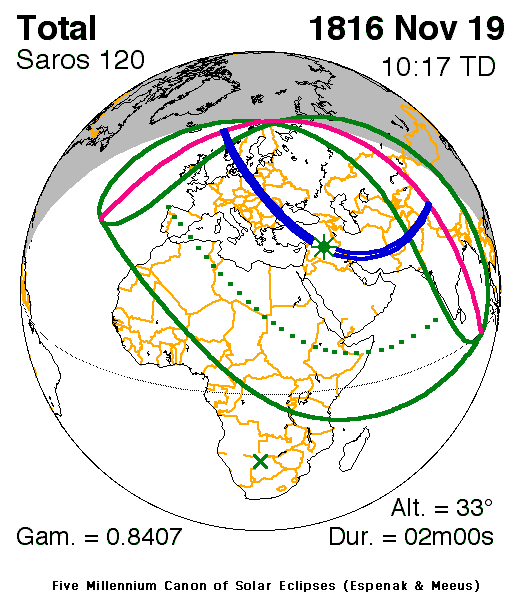
Solar Eclipse Of November 19, 1816
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, November 19, 1816, with a magnitude of 1.0233. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.7 days before perigee (on November 17, 1816, at 17:10 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. The path of totality was visible from parts of modern-day Norway, Sweden, Poland, western Ukraine, Romania, Turkey, Syria, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, northern India, and western China. A partial solar eclipse was also visible for parts of Europe, North Africa, Northeast Africa, the Middle E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of June 16, 1806
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's Lunar node, descending node of orbit on Monday, June 16, 1806 (sometimes dubbed Tecumseh's Eclipse), with a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 1.0604. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.7 days before Apsis, perigee (on June 18, 1806, at 9:30 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. The path of totality was visible from parts of modern-day northwestern Mexico, the states of Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, northwestern Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Missouri, southeastern Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, Penn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season in its new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to Ecliptic, the plane of Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In #Types, partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years. If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit and in the same orbital plane as Earth, there would be total solar eclipses once a month, at every new moon. Instead, because the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit Of Mercury
file:Mercury transit symbol.svg, frameless, upright=0.5 A transit of Mercury across the Sun takes place when the planet Mercury (planet), Mercury passes directly between the Sun and a superior planet. During a Astronomical transit, transit, Mercury appears as a tiny black dot moving across the Sun as the planet obscures a small portion of the solar disk. Because of orbital alignments, transits viewed from Earth occur in May or November. The last four such transits occurred on May 7, 2003; November 8, 2006; May 9, 2016; and November 11, 2019. The next will occur on November 13, 2032. A typical transit lasts several hours. Mercury transits are much more frequent than transit of Venus, transits of Venus, with about 13 or 14 per century, primarily because Mercury is closer to the Sun and orbits it more rapidly. On June 3, 2014, the Mars rover ''Curiosity (rover), Curiosity'' observed the planet Mercury transiting the Sun, marking the first time a planetary transit has been observed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipses
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three celestial objects is known as a ''syzygy''. An eclipse is the result of either an ''occultation'' (completely hidden) or a ''transit'' (partially hidden). A "deep eclipse" (or "deep occultation") is when a small astronomical object is behind a bigger one. "What is a deep eclipse? The smaller star is behind the bigger star" The term ''eclipse'' is most often used to describe either a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow crosses the Earth's surface, or a lunar eclipse, when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. However, it can also refer to such events beyond the Earth–Moon system: for example, a planet moving into the shadow cast by one of its moons, a moon passing into the shadow cast by its host planet, or a moon passing into the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit (astronomy)
In astronomy, a transit (or astronomical transit) is the passage of a astronomical object, celestial body directly between a larger body and the observer. As viewed from a particular vantage point, the transiting body appears to move across the face of the larger body, eclipse, covering a small portion of it. The word "transit" refers to cases where the nearer object apparent size, appears smaller than the more distant object. Cases where the nearer object appears larger and completely hides the more distant object are known as occultation, ''occultations''. However, the probability of seeing a transiting planet is low because it is dependent on the alignment of the three objects in a nearly perfectly straight line. Many parameters of a planet and its parent star can be determined based on the transit. In the Solar System One type of transit involves the motion of a planet between a Earth, terrestrial observer and the Sun. This can happen only with inferior and superior pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maecenas
Gaius Cilnius Maecenas ( 13 April 68 BC – 8 BC) was a friend and political advisor to Octavian (who later reigned as emperor Augustus). He was also an important patron for the new generation of Augustan poets, including both Horace and Virgil. In many languages, his name is an eponym for "patron of arts". During the reign of Augustus, Maecenas served as a quasi-culture minister to the Roman emperor but in spite of his wealth and power he chose not to enter the Roman Senate, Senate, remaining of Equites, equestrian rank. Life Expressions in Propertius seem to imply that Maecenas had taken some part in the campaigns of Battle of Mutina, Mutina, Battle of Philippi, Philippi, and Battle of Perugia, Perugia. He prided himself on his ancient Etruscan civilization, Etruscan lineage, and claimed descent from the princely house of the Cilnia (gens), Cilnii, who excited the jealousy of their townsmen by their preponderant wealth and influence at Arretium in the 4th century BC. Horace mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gordon Byron, Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-known works are the lengthy narratives ''Don Juan'' and ''Childe Harold's Pilgrimage''; many of his shorter lyrics in ''Hebrew Melodies'' also became popular. Byron was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, before he travelled extensively in Europe. He lived for seven years in Italy, in Venice, Ravenna, Pisa and Genoa after he was forced to flee England due to threats of lynching. During his stay in Italy, he would frequently visit his friend and fellow poet Percy Bysshe Shelley. Later in life, Byron joined the Greek War of Independence to fight the Ottoman Empire, for which Greeks revere him as a folk hero. He died leading a campaign in 1824, at the age of 36, from a fever contracted after the first and second sieges of Missolonghi. His o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bloomfield
Robert Bloomfield (3 December 1766 – 19 August 1823) was an English labouring-class poet, whose work is appreciated in the context of other self-educated writers, such as Stephen Duck, Mary Collier and John Clare. Life Robert Bloomfield was born into a poor family in the village of Honington, Suffolk.David Kaloustian, "Bloomfield, Robert (1766–1823)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 200Retrieved 4 March 2012/ref> His father was a tailor, who died of smallpox when his son was a year old. It was from his mother Elizabeth, who kept the village school, that he received the rudiments of education. Bloomfield was apprenticed at the age of eleven to his mother's brother-in-law, and worked on a farm that was part of the estate of the Duke of Grafton, his future patron. Four years later, owing to his small and weak stature (in adulthood just five feet tall), he was sent to London to work as a shoemaker under his elder brother George. One of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |