|
Cape Berg
Cape Berg (russian: Мыс Берга, ''Mys Berga'') is a headland in Severnaya Zemlya, Russia. This cape was named after prominent Soviet geographer and biologist Lev Berg (1876 – 1950). Geography Stretching out towards the Laptev Sea east of the Rusanov Glacier, Cape Berg is the northeasternmost point of October Revolution Island. History The shore of present-day Severnaya Zemlya was discovered by Boris Vilkitsky in 1913 during the Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition on behalf of the Russian Hydrographic Service. On 3 September 1913 —22 August 1913 in the Julian calendar The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematics, Greek mathematicians and Ancient Greek astronomy, as ... used by Russia at the time, members of the expedition went to the shore near Cape Berg, on what is now known as October Revolution Island. They raised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai ( rus, Красноя́рский край, r=Krasnoyarskiy kray, p=krəsnɐˈjarskʲɪj ˈkraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), with its administrative center in the city of Krasnoyarsk, the third-largest city in Siberia (after Novosibirsk and Omsk). Comprising half of the Siberian Federal District, Krasnoyarsk Krai is the largest krai in the Russian Federation, the second largest federal subject (after neighboring Sakha) and the third largest subnational governing body by area in the world, after Sakha and the Australian state of Western Australia. The krai covers an area of , which is nearly one quarter the size of the entire country of Canada (the next-largest country in the world after Russia), constituting roughly 13% of the Russian Federation's total area and containing a population of 2,828,187 (more than a third of them in the city of Krasnoyarsk), or just under 2% of its population, per the 2010 Census. Geography The krai lies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition
The Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition (GESLO) (1910–1915) was a scientific expedition organized by Russia for the purpose of the development of the Northern Sea Route. This expedition accomplished its goal of exploring the uncharted areas of the continental side of the Northern Sea Route in what was seen as the culmination of the Great Northern Expedition, an ambitious enterprise initially conceived by emperor Peter I the Great to map the whole of the northern coast of Russia to the east. Expedition Two icebreaking steamers Vaigach and Taimyr were used for the venture. The plan of the expedition was developed with the active participation of A.V. Kolchak and F. A. Matisen. The 32 man expedition was headed by Boris A. Vilkitsky and was staffed with military seamen and hydrographers, such as Konstantin Neupokoev. The biological and geological collections were performed by military doctors L. M. Starokadomsky on icebreaker "Taimyr" and E. E. Arnold on icebreaker "Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlands Of Severnaya Zemlya
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severnaya Zemlya - Raising Of The Russian Flag In 1913
Severny (Russian: ''Северный'', 'northern') (masculine), Severnaya (''Северная'') (feminine), or Severnoye (''Северное'') (neutral) may refer to: People *Andrei Severny (astronomer) (1913–1987), Soviet astronomer *Andrei Severny (filmmaker) (born 1977), Russian filmmaker and photographer *Arkady Severny (1939–1980), performer of Russian criminal songs *Count and Countess Severny, pseudonyms of Tsar Paul I of Russia and Tsaritsa Maria Feodorovna Places *Severny District, several districts and city districts in Russia *Severny Okrug (other), various divisions in Russia * Severny Urban Settlement, several municipal urban settlements in Russia *Severny (inhabited locality) (''Severnaya'', ''Severnoye''), several inhabited localities in Russia *Severny Island, Russia * Severny (volcano), a volcano on the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia *Severny (air base), Orsk, Russia *Severny Airport, Novosibirsk, Russia *Severny mine, a copper mine in Murmansk Oblas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Nicholas II Land 1913-map-arctic
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother (empress dowager), or a woman who rules in her own right and name (empress regnant). Emperors are generally recognized to be of the highest monarchic honor and rank, surpassing kings. In Europe, the title of Emperor has been used since the Middle Ages, considered in those times equal or almost equal in dignity to that of Pope due to the latter's position as visible head of the Church and spiritual leader of the Catholic part of Western Europe. The Emperor of Japan is the only currently reigning monarch whose title is translated into English as "Emperor". Both emperors and kings are monarchs or sovereigns, but both emperor and empress are considered the higher monarchical titles. In as much as there is a strict definition of emperor, it is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland, ruling from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. During his reign, Nicholas gave support to the economic and political reforms promoted by his prime ministers, Sergei Witte and Pyotr Stolypin. He advocated modernization based on foreign loans and close ties with France, but resisted giving the new parliament (the Duma) major roles. Ultimately, progress was undermined by Nicholas's commitment to autocratic rule, strong aristocratic opposition and defeats sustained by the Russian military in the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. By March 1917, public support for Nicholas had collapsed and he was forced to abdicate the throne, thereby ending the Romanov dynasty's 304-year rule of Russia (1613 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematics, Greek mathematicians and Ancient Greek astronomy, astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandria. The calendar became the predominant calendar in the Roman Empire and subsequently most of the Western world for more than 1,600 years until 1582, when Pope Gregory XIII promulgated #Replacement by the Gregorian calendar, a minor modification to reduce the average length of the year from 365.25 days to 365.2425 days and thus corrected the Julian calendar's drift against the Tropical year, solar year. adoption of the Gregorian calendar, Worldwide adoption of this revised calendar, which became known as the Gregorian calendar, took place over the subsequent centuries, first in Catholic Church, Catholic countries and subsequently in Protestantism, Protestant countries of the Western Christianity, West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; ) is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya entsiklopediya'' (or ''Great Russian Encyclopedia'') in an updated and revised form. The GSE claimed to be "the first Marxist–Leninist general-purpose encyclopedia". Origins The idea of the ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' emerged in 1923 on the initiative of Otto Schmidt, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. In early 1924 Schmidt worked with a group which included Mikhail Pokrovsky, (rector of the Institute of Red Professors), Nikolai Meshcheryakov (Former head of the Glavit, the State Administration of Publishing Affairs), Valery Bryusov (poet), Veniamin Kagan (mathematician) and Konstantin Kuzminsky to draw up a proposal which was agreed to in April 1924. Also involved was Anatoly Lunacharsky, People's Commissar of Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Hydrographic Service
The Russian Hydrographic Service, full current official name Department of Navigation and Oceanography of the Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation ( rus, Управление навигации и океанографии Министерства обороны Российской Федерации), is Russia's hydrographic office, with responsibility to facilitate navigation, performing hydrographic surveys and publishing nautical charts. Since the Russian state is of such a vast size and nature that it includes many different seas, long and indented coastlines and a great number of islands, as well as a complex system of waterways and lakes, surveying has been an indispensable activity for the Russian Navy since its modernization at the time of Czar Peter the Great in the 17th century. The hydrographic service has been historically attached to the Russian Navy and the agents and supervisors of hydrographic works have been largely naval officers throughout its history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
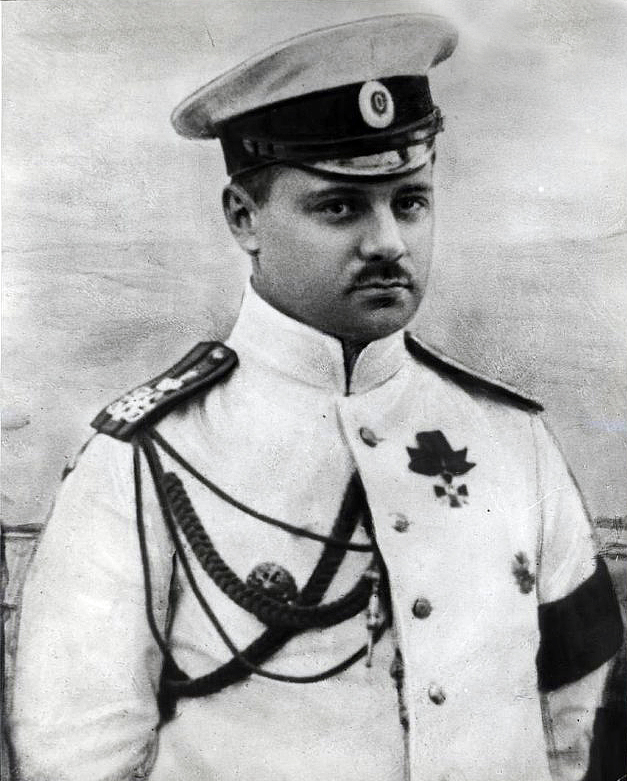
Boris Vilkitsky
Boris Andreyevich Vilkitsky (russian: Бори́с Андре́евич Вильки́цкий) (22 March (3 April N.S.) 1885, Pulkovo – 6 March 1961) was a Russian hydrographer and surveyor. He was the son of Andrey Ippolitovich Vilkitsky. Career Born in Pulkovo, Tsarskoselsky Uyezd (now part of Saint Petersburg), Vilkitsky graduated from the Naval Academy in Saint Petersburg in 1908. He participated in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. In 1913—1915 he led the Arctic hydrographic expedition on the ships ''"Taimyr"'' and ''"Vaigach"'' with the purpose of further exploration of the Northern Sea Route. In 1913, Vilkitsky's expedition discovered Emperor Nicholas II Land (russian: Земля Императора Николая II, ''Zemlya Imperatora Nikolaya II'') —later renamed 'Severnaya Zemlya', perhaps one of the most important Russian discoveries in the Arctic at the time. Other discoveries were an island that now bears his name ( Vilkitsky Island), as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
October Revolution Island
October Revolution Island (Russian: Остров Октябрьской Революции, ''Ostrov Oktyabrskoy Revolyutsii'') is the largest island of the Severnaya Zemlya group in the Russian Arctic. It is named after the October Revolution which led to the former Russian Empire becoming a Socialist country. The area of this island has been estimated at making it the 59th largest island in the world. It rises to a height of on Mount Karpinsky. Half the island is covered with glaciers reaching down into the sea. In the sections free from ice, the vegetation is desert or tundra. Geography October Revolution Island houses five domed ice caps; clockwise from north, they are named: Rusanov, Karpinsky, University, Vavilov and Albanov. The Rusanov and Karpinsky ice caps, located on the eastern side of the island, feed with glaciers the Matusevich Fjord of the Laptev Sea and the Marat Fjord of the Shokalsky Strait.Mark Nuttall, ''Encyclopedia of the Arctic'', p. 1887 The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rusanov Glacier
Rusanov (russian: Русанов) is a Russian masculine surname, its feminine counterpart is Rusanova. It may refer to: * Anatoly Rusanov (born 1932), Russian chemist * Dmitri Rusanov (born 1987), Russian football player * Lyubov Rusanova (born 1954), Russian swimmer * Nikolay Rusanov (1859–1939), Russian revolutionary *Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Alexandrovich Rusanov (russian: Влади́мир Алекса́ндрович Руса́нов; – ca. 1913) was a Russian geologist and Arctic explorer. Early life Rusanov was born in a merchant's family in Oryol, Russia. His early ... (1875–c. 1913), Russian geologist * Vladislav Rusanov (born 1966), Ukrainian fantasy writer * Yuliya Rusanova (born 1986), Russian runner See also * Mount Rusanov in Antarctica Russian-language surnames {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_(cropped).jpg)