|
Cannonville
Cannonville is a town in Garfield County, Utah, United States, along Utah Scenic Byway 12. As of the 2020 census, the population was 186. History Cannonville was laid out in 1874. A post office called Cannonville was established in 1879, and remained in operation until 1966. The community bears the name of George Q. Cannon, a Mormon official. Geography Cannonville is located near the southern border of Garfield County, in the valley of the Paria River. Via State Route 12 it is east to Henrieville and north to Tropic. Bryce Canyon National Park is in a straight line to the west, by road. According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , all land. Climate The climate in this area features a large daily and annual temperature range, with cold, dry winters and hot summers. Rainfall is highly seasonal, with most precipitation falling during the late-summer monsoon season and average annual precipitation of nine inches. According to the Köppen Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah State Route 12
State Route 12 or Scenic Byway 12 (SR-12), also known as ''"Highway 12 — A Journey Through Time Scenic Byway"'', is a state highway designated an All-American Road located in Garfield County and Wayne County, Utah, United States. Route description Proceeding west to east for 123 miles (nearly 200 km), the highway starts south of Panguitch at an intersection with US-89, crosses part of Dixie National Forest and Bryce Canyon National Park, continues through the small towns of Tropic, Cannonville, and Henrieville. It crosses various parts of Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument (GS-ENM), continues northeast through Escalante and over the Escalante River, then over "The Hogback", a narrow ridge with no guardrails or shoulders and steep drop-offs on each side. It then proceeds north through more of GS-ENM, Boulder, the Aquarius Plateau, and Grover, ending in Torrey at an intersection with SR-24, five miles (8 km) west of Capitol Reef National Park. The lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henrieville, Utah
Henrieville is a town in Garfield County, Utah, Garfield County, Utah, United States, along Utah State Route 12, Utah Scenic Byway 12. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the town population was 221. The community was named after James Henrie, a Mormon leader. Geography Henrieville is in southern Garfield County, along Utah State Route 12. It is southeast of Bryce Canyon City, Utah, Bryce Canyon City and southwest of Escalante, Utah, Escalante. Cannonville, Utah, Cannonville, the closest neighboring town, is to the west on Route 12. According to the United States Census Bureau, Henrieville has a total area of , all land. Climate The climate in this area has mild differences between highs and lows, and there is adequate rainfall year-round. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Henrieville has a hot and cold arid desert climate, abbreviated "BWk" on climate maps. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 159 people, 57 households ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropic, Utah
Tropic is a town in Garfield County, Utah, United States, along Utah State Route 12 (A Journey Through Time Scenic Byway / Scenic Byway 12). As of the 2020 census, the town had a population of 486. Tropic was founded in 1891. Geography Tropic is in southern Garfield County along Utah Route 12, southeast of Bryce Canyon City and north of Cannonville. It is in the Tropic Valley, drained by the Paria River, a tributary of the Colorado River. According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , of which , or 0.26%, are water. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 508 people in the town, organized into 160 households and 132 families. The population density was 60.6 people per square mile (23.4/km2). There were 206 housing units at an average density of 24.6 per square mile (9.5/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 96.06% White, 0.39% Native American, 1.38% from other races, and 2.17% from two or more races. There were no African Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garfield County, Utah
Garfield County is a county in south central Utah, United States. As of the 2020 United States census the population was 5,083, making it the fifth-least populous county in Utah; with about one inhabitant per square mile, it is also the least densely populated county in Utah. Its county seat and largest city is Panguitch. History The Utah Territory legislature created the county on March 9, 1882, with areas partitioned from Iron County. It was named for James A. Garfield, the twentieth President of the United States, who had died six months earlier. The border with Iron County was adjusted in 1884, and Garfield County's boundaries have remained intact since then. Geography The Colorado River, flowing southwestward through a deep gorge, forms the eastern boundary. The Dirty Devil River flows southward through the east end of the county to discharge into Colorado at the county's border. Westward, the cliffs of tributary canyons give way to the barren stretches of the San R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
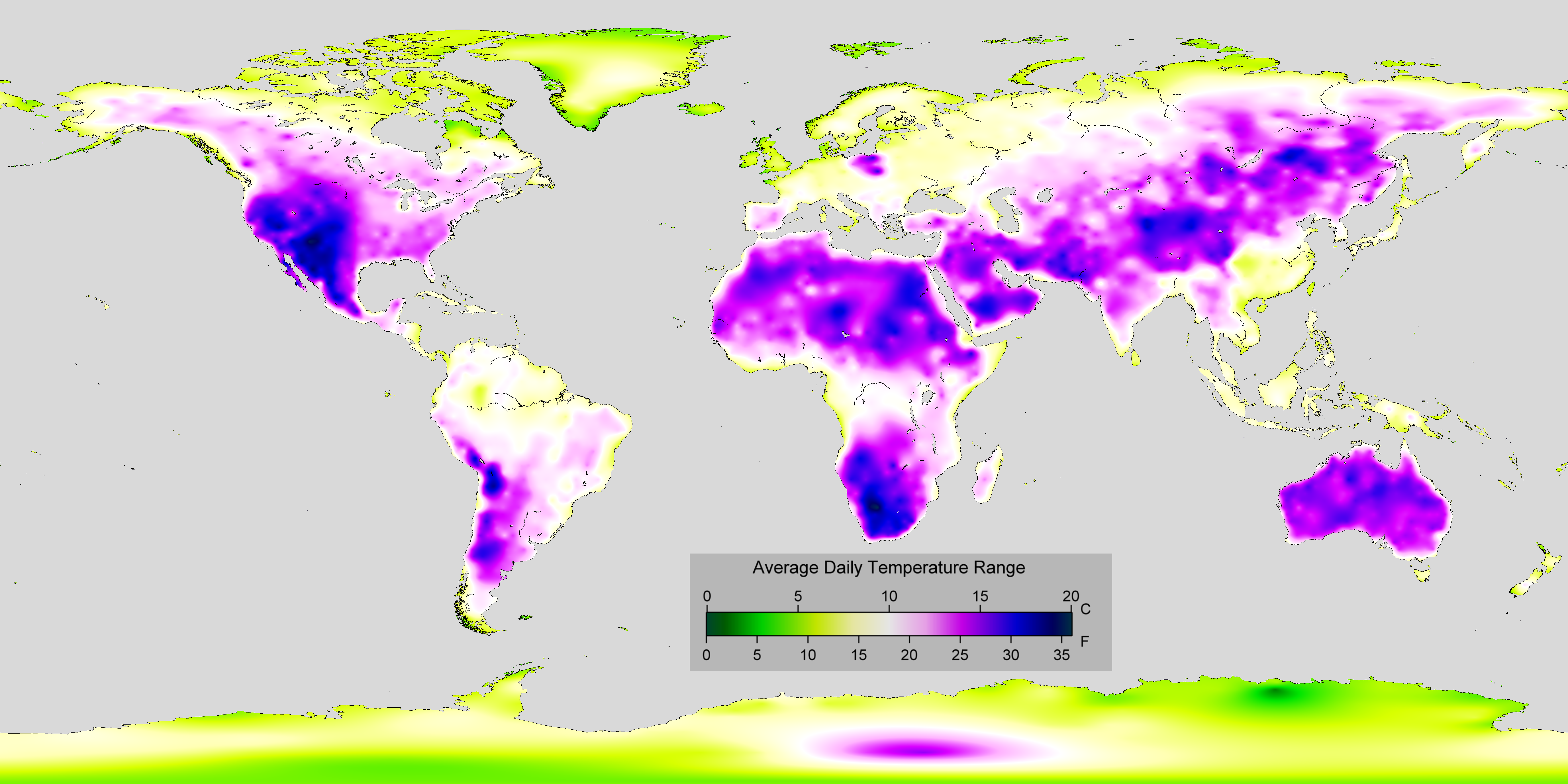
Diurnal Temperature Variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day. Temperature lag Temperature lag, also known as thermal inertia, is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation. Peak daily temperature generally occurs ''after'' noon, as air keeps absorbing net heat for a period of time from morning through noon and some time thereafter. Similarly, minimum daily temperature generally occurs substantially after midnight, indeed occurring during early morning in the hour around dawn, since heat is lost all night long. The analogous annual phenomenon is seasonal lag. As solar energy strikes the Earth's surface each morning, a shallow layer of air directly above the ground is heated by conduction. Heat exchange between this shallow layer of warm air and the cooler air above is very inefficient. On a warm summer's day, for example, air temperatures may vary by from just above the ground t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paria River
The Paria River is a tributary of the Colorado River, approximately long, in southern Utah and northern Arizona in the United States. It drains a rugged and arid region northwest of the Colorado, flowing through roadless slot canyons along part of its course. Geography It is formed in southern Utah, in southwestern Garfield County from several creeks that descend from the edge of the Paunsaugunt Plateau, meeting just north of Tropic. It flows SSE across Kane County and Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument. Along the Arizona state line, it descends through the Vermilion Cliffs in the Paria Canyon and onto the Paria Plateau. It joins the Colorado from the northwest approximately 5 mi (8 km) southwest of Page, Arizona and the Glen Canyon Dam. The lower 20 mi (32 km) of the river are within the Paria Canyon-Vermilion Cliffs Wilderness, which is administered by the Bureau of Land Management; a permit is required for any overnight visit. The Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryce Canyon National Park
Bryce Canyon National Park () is a national park of the United States located in southwestern Utah. The major feature of the park is Bryce Canyon, which despite its name, is not a canyon, but a collection of giant natural amphitheaters along the eastern side of the Paunsaugunt Plateau. Bryce is distinctive due to geological structures called hoodoos, formed by frost weathering and stream erosion of the river and lake bed sedimentary rock. The red, orange, and white colors of the rocks provide spectacular views for park visitors. Bryce Canyon National Park is much smaller and sits at a much higher elevation than nearby Zion National Park. The rim at Bryce varies from . The area is in portions of Garfield County and Kane County. The Bryce Canyon area was settled by Mormon pioneers in the 1850s and was named after Ebenezer Bryce, who homesteaded in the area in 1874. The area was originally designated as a national monument by President Warren G. Harding in 1923 and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative status, or historical significance. In some regions, towns are formally defined by legal charters or government designations, while in others, the term is used informally. Towns typically feature centralized services, infrastructure, and governance, such as municipal authorities, and serve as hubs for commerce, education, and cultural activities within their regions. The concept of a town varies culturally and legally. For example, in the United Kingdom, a town may historically derive its status from a market town designation or City status in the United Kingdom, royal charter, while in the United States, the term is often loosely applied to incorporated municipality, municipalities. In some countries, such as Australia and Canada, distinction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highway 12 Cannonville Utah
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It includes not just major roads, but also other public roads and rights of way. In the United States, it is also used as an equivalent term to controlled-access highway, or a translation for ''motorway'', ''Autobahn'', ''autostrada'', ''autoroutes of France, autoroute'', etc. According to Merriam-Webster, the use of the term predates the 12th century. According to Online Etymology Dictionary, Etymonline, "high" is in the sense of "main". In North American English, North American and Australian English, major roads such as controlled-access highways or arterial (road), arterial roads are often state highways (Canada: provincial highways). Other roads may be designated "county highways" in the US and Ontario. These classifications refer to the level of government (state, provincial, county) that maintains the roadway. In British English, "highway" is primarily a legal term. Everyday use normally implies roads, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (other), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopulation Density Geography.about.com. March 2, 2011. Retrieved on December 10, 2011. Biological population densities Population density is population divided by total land area, sometimes including seas and oceans, as appropriate. Low densities may cause an extinction vortex and further reduce fertility. This is called the Allee effect after the scientist who identified it. Examples of the causes of reduced fertility in low population densities are: * Increased problems with locating sexual mates * Increased inbreeding Human densities Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually transcribed as "per square kilometre" or square mile, and which may include or exclude, for example, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |