|
Canggadai
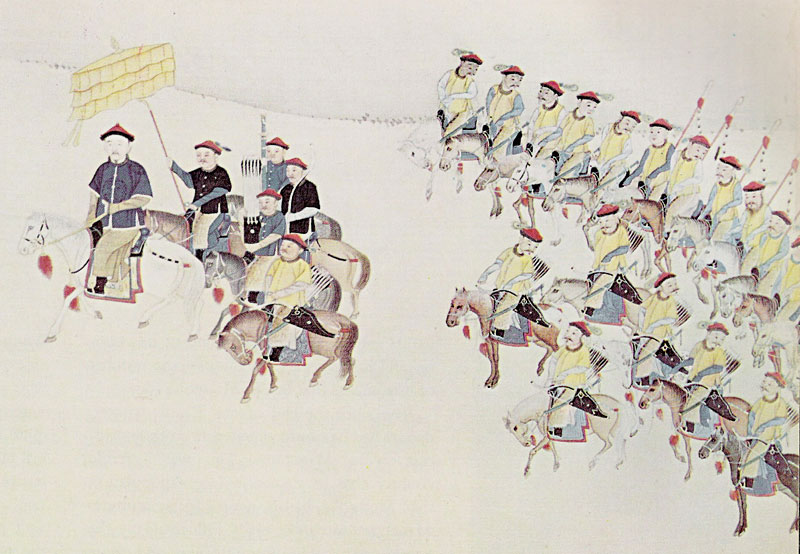
Canggadai (; 21 November 1643 - 29 May 1665), formally the Prince Huaimin of the Third Rank (懷愍貝勒), was an imperial prince of the Qing dynasty of China. He was the son of Mandahai and his primary consort, Lady Khorchin Borijit. Life Canggadai was born in the last year of Huang Taiji's reign as Mandahai's seventh son. He had a full brother named Huse. In the 9th year of the Shunzhi Emperor's reign (1652), his father passed away and he inherited the title of " Prince Xun". However, in the 16th year of Shunzhi's reign (1659), it was found that his father had confiscated a part of former Prince Regent Dorgon's property, which lead to Canggadai's demotion. He was demoted from the First Rank prince to Third Rank (''beile''). His father Mandahai was also demoted posthumously. He died in the 4th year of the Kangxi Emperor's reign (1665), and the court gave him the posthumous name Huaimin (懷愍). His princedom was inherited by his sixth son, Xingni. Family Parents: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandahai
Mandahai ( mnc, ᠮᠠᠨᡩᠠᡥᠠᡳ, ; 30 April 1622 – 15 March 1652), was an imperial prince of the Qing dynasty and one of Nurhaci's grandson. He was the seventh son of Daišan and in 1649 he inherited his father's princedom. He was posthumously honoured as Prince Xunjian of the First Rank (巽簡親王). Life Mandahai was born in the Aisin Gioro clan on 30 April 1622 as the seventh son of Daišan. His mother was Daišan's princess consort Lady Yehe Nara, who also bore the eighth son, Hūse. He would join his father and uncles in military campaigns. He accompanied his father to the siege of Jinzhou in 1640. In the following year, he was given the title of bulwark duke. He participated in the Battle of Shanhai Pass under Dorgon, which was a decisive battle leading to the beginning of Qing dynasty rule in China proper. Mandahai was promoted for his services to the rank of Prince of the Fourth Rank in 1644. In the next year, he joined his uncle, Ajige, in pursuit o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giyesu
Giyesu (; 1645–1697), formally known as Prince Kang, was a Manchu prince and general of the Qing dynasty. Born into the imperial Aisin Gioro clan, he was a distant cousin of the Kangxi Emperor and is best known for leading Qing forces to suppress a rebellion by Geng Jingzhong in southwestern China between 1674 and 1675 and repel an invasion by Taiwan warlord Zheng Jing in 1676–1677. Title inheritance Giyesu was born in the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan as a great-grandson of Nurhaci, the founder of the Qing dynasty. His grandfather, Daišan, was the founding title holder of the Prince Li peerage. His father, Hūse (祜塞; d. 1646), who was the eighth and youngest son of Daišan, held the title of a ''feng'en zhenguo gong'' or first-class imperial duke. After Hūse died, his title was inherited by his second son, Jinggi (精濟; 1644–1649), who, sometime before 1649, was promoted to a ''junwang'' (second-rank prince). Jinggi died in July 1649. Giyesu, who was then only four y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aisin Gioro
The House of Aisin-Gioro is a Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin dynasty (1616–1636), the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), and Manchukuo (1932–1945) in the history of China. Under the Ming dynasty, members of the Aisin Gioro clan served as chiefs of the Jianzhou Jurchens, one of the three major Jurchen tribes at this time. Qing bannermen passed through the gates of the Great Wall in 1644, and eventually conquered the short-lived Shun dynasty, Xi dynasty and Southern Ming dynasty. After gaining total control of China proper, the Qing dynasty later expanded into other adjacent regions, including Xinjiang, Tibet, Outer Mongolia, and Taiwan. The dynasty reached its zenith during the High Qing era and under the Qianlong Emperor, who reigned from 1735 to 1796. This reign was followed by a century of gradual decline. The house lost power in 1912 following the Xinhai Revolution. Puyi, the last Aisin-Gioro emperor, nominally maintained his imperial title in the Forbidden City un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorgon
Dorgon (17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650) was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, which was the predecessor of the Qing), Dorgon started his career in military campaigns against the Mongols, the Koreans, and the Ming dynasty during the reign of Hong Taiji (his eighth brother) who succeeded their father. After Hong Taiji's death in 1643, he was involved in a power struggle against Hong Taiji's eldest son, Hooge, over the succession to the throne. Both of them eventually came to a compromise by backing out and letting Hong Taiji's ninth son, Fulin, become the emperor; Fulin was installed on the throne as the Shunzhi Emperor. Dorgon served as Prince-Regent from 1643 to 1650, throughout the Shunzhi Emperor's early reign. In 1645, he was given the honorary title "Emperor's Uncle and Prince-Regent" (皇叔父攝政王); the title was changed to "Emperor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1643 Births
Events January–March * January 21 – Abel Tasman sights the island of Tonga. * February 6 **(17 Dhu al-Qadah 1052 AH) In India, the first ceremony at the nearly-complete Taj Mahal in Agra, the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan observes the 12th anniversary of the death of his wife, Mumtaz Mahal, and opens the structure to thousands of mourners. **Abel Tasman sights the Fiji Islands. * March 13 – First English Civil War: First Battle of Middlewich – Roundheads ( Parliamentarians) rout the Cavaliers (Royalist supporters of King Charles I) at Middlewich in Cheshire. * March 18 – Irish Confederate Wars: Battle of New Ross – English troops defeat those of Confederate Ireland. April–June * April 1 – Åmål, Sweden, is granted its city charter. * April 28 – Francisco de Lucena, former Portuguese Secretary of State, is beheaded after being convicted of treason. * May 14 – Louis XIV succeeds his father Louis XIII as Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty Imperial Princes
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty assembled the territorial base for modern China. The Qing controlled the most territory of any dynasty in Chinese history, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranks Of Imperial Consorts In China
The ranks of imperial consorts have varied over the course of Chinese history but remained important throughout owing to its prominence in the management of the inner court and in imperial succession, which ranked heirs according to the prominence of their mothers in addition to their birth order. Regardless of the age, however, it is common in English translation to simplify this hierarchy into the three ranks of empress, consorts, and concubines. It is also common to use the term "harem", an Arabic loan word used in recent times to refer to imperial women's forbidden quarters in many countries. In later Chinese dynasties, these quarters were known as the inner palace (內宮; ''nèigōng'') or the rear palace (後宮; ''hòugōng''). In Chinese, the system is called the "rear palace system" (後宮制度; ''hòugōng zhìdù''). No matter the dynasty, the empress (皇后; ''huánghòu'') held the highest rank and was the legal wife of the emperor, as well as the chief of the im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nara Clan
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an independent agency of the United States government within the executive branch, charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It is also tasked with increasing public access to those documents that make up the National Archives. NARA is officially responsible for maintaining and publishing the legally authentic and authoritative copies of acts of Congress, presidential directives, and federal regulations. NARA also transmits votes of the Electoral College to Congress. It also examines Electoral College and constitutional amendment ratification documents for prima facie legal sufficiency and an authenticating signature. The National Archives, and its publicly exhibited Charters of Freedom, which include the original United States Declaration of Independence, Constitution of the United States, United States Bill of Rights, Emancipation Proclamation (starting in 2026), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naimans
The Naiman (; ; Kazakh and , ), meaning The Eight, was a medieval tribe originating in the territory of modern Western Mongolia (possibly during the time of the Uyghur Khaganate), and is one of the 92 tribes of Uzbeks, modern Mongols and in the middle juz of the Kazakhs. History In ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', the Naiman subtribe the "Güchügüd" are mentioned. According to Russian Turkologist Nikolai Aristov's view, the Naiman Khanate's western border reached the Irtysh River and its eastern border reached the Mongolian Tamir River. The Altai Mountains and southern Altai Republic were part of the Naiman Khanate. They had diplomatic relations with the Kara-Khitans, and were subservient to them until 1175. In the Russian and Soviet historiography of Central Asia they were traditionally ranked among the Mongol-speaking tribes. For instance, such Russian orientalists as Vasily Bartold, Grigory Potanin, Boris Vladimirtsov, Ilya Petrushevsky, Nicholas Poppe, Lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 165420 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. He is considered one of China's greatest emperors. The third son of the Shunzhi Emperor, Kangxi was enthroned at the age of seven while actual power was held for six more years by the four regents nominated by his father. After assuming personal rule, Kangxi's attempt to revoke the fiefdoms of feudal princes sparked the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, which he suppressed. He also forced the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan and Mongols in the north and northwest to submit to Qing rule, and launched an expedition that incorporated Tibet into the empire. Domestically, he initially welcomed the Jesuits and the propagation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizu of Qing, personal name Fulin, was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper. Upon the death of his father Hong Taiji, a Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers, committee of Manchu princes chose the 5-year-old Fulin as successor. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon, the 14th son of Nurhaci, and Jirgalang, one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Qing imperial clan. In November 1644, the Shunzhi Emperor was enthroned as emperor of China in Beijing. From 1643 to 1650, political power lay mostly in the hands of the prince regent Dorgon. Under his leadership, the Qing conquered most of the territory of the fallen Ming dynasty, chased Southern Ming, Ming loyalist regimes deep into the southwestern provinces, and established the basis of Qing rule over China proper despite highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunzhi
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizu of Qing, personal name Fulin, was the second emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper. Upon the death of his father Hong Taiji, a committee of Manchu princes chose the 5-year-old Fulin as successor. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon, the 14th son of Nurhaci, and Jirgalang, one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Qing imperial clan. In November 1644, the Shunzhi Emperor was enthroned as emperor of China in Beijing. From 1643 to 1650, political power lay mostly in the hands of the prince regent Dorgon. Under his leadership, the Qing conquered most of the territory of the fallen Ming dynasty, chased Ming loyalist regimes deep into the southwestern provinces, and established the basis of Qing rule over China proper despite highly unpopular policies such as the "hair cutting command" of 1645, which forced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |