|
Campagnatico
Campagnatico is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Grosseto in the Italian region Tuscany, located about south of Florence and about northeast of Grosseto in the valley of the Ombrone River. History The town was founded as a fief of the San Salvatore Abbey of the Monte Amiata, which sold it to the Aldobrandeschi family, who are known to hold it in 973. After the death of Omberto Aldobrandeschi, it was acquired by the Republic of Siena. Later it was contended by the Visconti of Campiglia d'Orcia and the Tolomei of Siena. It belonged to the latter city until it was absorbed into the Grand Duchy of Tuscany in the mid-16th century. Government ''Frazioni'' The municipality is formed by the municipal seat of Campagnatico and the villages (''frazioni'') of Arcille, Marrucheti and Montorsaio. List of mayors Main sights *The Walls, built in the 12th and 13th centuries. They include the commanding Aldobrandeschi castle, founded in the 10th century. *Church of ''Sant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marrucheti
Marrucheti is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Campagnatico, province of Grosseto. At the time of the 2001 census its population amounted to 90. Istat Marrucheti is about 14 km from and 12 km from Campagnatico, and it is situated on the ancient road ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montorsaio
Montorsaio is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Campagnatico, province of Grosseto. At the time of the 2001 census its population amounted to 167. Montorsaio is about 20 km from and 11 km from Campagnatico, and it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcille
Arcille is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Campagnatico, province of Grosseto. At the time of the 2001 census its population amounted to 100. Arcille is about 14 km from Grosseto and 12 km from , and it is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omberto Aldobrandeschi
Omberto Aldobrandeschi (? - 1259; sometimes anglicized as Omberto Aldobrandesco), was a member of the Aldobrandeschi family The Aldobrandeschi were an Italian noble family from southern Tuscany. Overview Of probable Lombard origin, they appear in history as counts in the 9th century. The first known count was Hildebrand II (857). Their possession extended to wha ... and a Count of Santafiore in the Maremma of Siena. Counts of Santafiore were usually in wars against the city of Siena. In 1259, Omberto was killed in one of these battles, at the village of Campagnatico. Omberto is mentioned in Canto XI of Purgatorio of Divine Comedy by Dante, as an example of a sinner of pride. References Year of birth unknown 1259 deaths Date of death unknown Place of birth unknown Counts of Italy People from Siena {{Divine Comedy navbox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
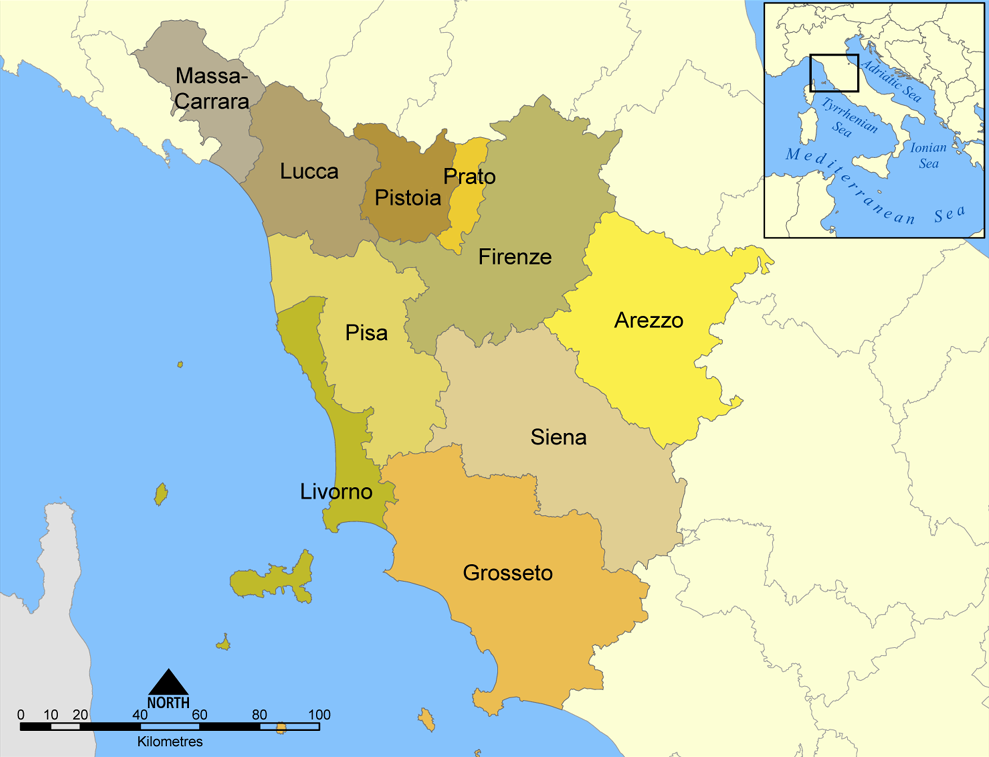
Province Of Grosseto
The province of Grosseto ( it, links=no, provincia di Grosseto) is a province in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Grosseto. As of 2013 the province had a total population of 225,098 people. Geography The Province of Grosseto completely occupies the southern end of Tuscany, and with a territorial area of , it is the most extensive in the region and one of the least dense in population in Italy. The province is bordered to the northwest by the Province of Livorno, to the north by the Province of Pisa, to the northeast by the Province of Siena, and to the southeast by the Province of Viterbo in Lazio. To the south is the Tyrrhenian Sea, which includes the southern islands of the Tuscan archipelago, including Isola del Giglio and the smaller Giannutri islands and Formiche di Grosseto and Formica di Burano. The Arcipelago Toscano National Park spans both the provinces of Grosseto and Livorno, and includes the seven main islands of the Tuscan Archipelago: Elba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciborium (architecture)
In ecclesiastical architecture, a ciborium ("ciborion": in Greek) is a canopy or covering supported by columns, freestanding in the sanctuary, that stands over and covers the altar in a basilica or other church. It may also be known by the more general term of baldachin, though ''ciborium'' is often considered more correct for examples in churches. Really a baldachin (originally an exotic type of silk from Baghdad) should have a textile covering, or at least, as at Saint Peter's in Rome, imitate one. There are exceptions; Bernini's structure in Saint Peter's, Rome is always called the baldachin. Early ciboria had curtains hanging from rods between the columns, so that the altar could be concealed from the congregation at points in the liturgy. Smaller examples may cover other objects in a church. In a very large church, a ciborium is an effective way of visually highlighting the altar, and emphasizing its importance. The altar and ciborium are often set upon a dais to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guido Di Graziano
Guido of Siena, was an Italian painter, active during the 13th-century in Siena, and painting in an Italo-Byzantine style. Biography The name Guido is known from the large panel in the church of San Domenico, Siena of th''Virgin and Child Enthroned'' The rhymed Latin inscription gives the painter's name as ''Guido de Senis'', with the date 1221. However, this date cannot relate to the painting of the panel, which is usually dated on the basis of style to the 1270s. The faces of the Virgin and Child were scraped and repainted in the early 14th century in the manner of Duccio and so are not representative of Guido's original. A dossal featuring the Virgin and Child with four saints (accession No. 7) in the Siena Pinacoteca has an identical inscription, but unfortunately the name before "de Senis" has been cut off. It is very often assumed that the missing name is Guido, and gives us some indication of the original appearance of the Madonna at San Domenico. Beyond this, little is k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frazione
A ''frazione'' (plural: ) is a type of subdivision of a ''comune'' (municipality) in Italy, often a small village or hamlet outside the main town. Most ''frazioni'' were created during the Fascist era (1922–1943) as a way to consolidate territorial subdivisions in the country. In the autonomous region of the Aosta Valley, a ''frazione'' is officially called an ''hameau'' in French. Description Typically the term ''frazioni'' applies to the villages surrounding the main town ('' capoluogo'') of a ''comune''. Subdivision of a ''comune'' is optional; some ''comuni'' have no ''frazioni'', but others have several dozen. The ''comune'' usually has the same name of the ''capoluogo'', but not always, in which case it is called a ''comune sparso''. In practice, most ''frazioni'' are small villages or hamlets, occasionally just a clump of houses. Not every hamlet is classified as a ''frazione''; those that are not are often referred to as '' località'', for example, in the telephone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Di Giorgio Martini
Francesco di Giorgio Martini (1439–1501) was an Italian architect, engineer, painter, sculptor, and writer. As a painter, he belonged to the Sienese School. He was considered a visionary architectural theorist—in Nikolaus Pevsner's terms: "one of the most interesting later Quattrocento architects". As a military engineer, he executed architectural designs and sculptural projects and built almost seventy fortifications for the Federico da Montefeltro, Count (later Duke) of Urbino, building city walls and early examples of star-shaped fortifications. Born in Siena, he apprenticed as a painter with Vecchietta. In panels painted for '' cassoni'' he departed from the traditional representations of joyful wedding processions in frieze-like formulas to express visions of ideal, symmetrical, vast and all but empty urban spaces rendered in perspective. He composed an architectural treatis''Trattato di architettura, ingegneria e arte militare'' the third of the Quattrocento, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbytery (architecture)
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building within the Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architectural traditions. Each half of a transept is known as a semitransept. Description The transept of a church separates the nave from the sanctuary, apse, choir, chevet, presbytery, or chancel. The transepts cross the nave at the crossing, which belongs equally to the main nave axis and to the transept. Upon its four piers, the crossing may support a spire (e.g., Salisbury Cathedral), a central tower (e.g., Gloucester Cathedral) or a crossing dome (e.g., St Paul's Cathedral). Since the altar is usually located at the east end of a church, a transept extends to the north and south. The north and south end walls often hold decorated windows of stained glass, such as rose wind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |