|
Camilo Sitte
Camillo Sitte (17 April 1843 – 16 November 1903) was an Austrian architect, painter and urban theorist whose work influenced urban planning and land use regulation. Today, Sitte is best remembered for his 1889 book, ''City Planning According to Artistic Principles'', in which he examined and documented the traditional, incremental approach to urbanism in Europe, with a close focus on public spaces in Italy and the Germanic countries. Career Camillo Sitte was born Vienna in 1843. As the son of architect Franz Sitte, he was able to work on his father's construction sites during his youth. Camillo Sitte is the father of the architect Siegfried Sitte. Sitte was an architect and cultural theoretician whose writings, according to Eliel Saarinen, were familiar to German-speaking architects of the late 19th century. He was educated and influenced by Rudolf von Eitelberger and Heinrich von Ferstel, and on the recommendation of Eitelberger Sitte became the head of the new State Trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camillo Sitte ZÖIAV 1903
Camillo is an Italian masculine given name, descended from Latin Camillus. Its Slavic cognate is Kamil. People *Camillo Agrippa, Italian Renaissance fencer, architect, engineer and mathematician *Camillo Almici (1714–1779), Italian priest, theologian and literary critic * Camillo Astalli (1616–1663), Italian cardinal *Camillo Benso, conte di Cavour (1810–1861), a leading figure in the movement toward Italian unification, founder of the original Italian Liberal Party and Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia *Camillo Berlinghieri (1590 or 1605–1635), Italian painter * Camillo Berneri (1897–1937), Italian professor of philosophy, anarchist militant, propagandist and theorist * Camillo Boccaccino (1546), Italian painter *Camillo Boito (1836–1914), Italian architect, engineer, art critic, art historian and novelist *Camillo Borghese (1550–1621), Pope Paul V, the Pope who persecuted Galileo Galilei * Camillo Borghese, 6th Prince of Sulmona (1775–1832), b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , ; ), was a Swiss-French architectural designer, painter, urban planner and writer, who was one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was born in Switzerland to French speaking Swiss parents, and acquired French nationality by naturalization on 19 September 1930. His career spanned five decades, in which he designed buildings in Europe, Japan, India, as well as North and South America. He considered that "the roots of modern architecture are to be found in Viollet-le-Duc." Dedicated to providing better living conditions for the residents of crowded cities, Le Corbusier was influential in urban planning, and was a founding member of the (CIAM). Le Corbusier prepared the master plan for the city of Chandigarh in India, and contributed specific designs for several buildings there, especially the government buildings. On 17 July 2016, seventeen projects by Le Corbusie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Theorists
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to: * Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas * Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities Urban may also refer to: General * Urban (name), a list of people with the given name or surname * ''Urban'' (newspaper), a Danish free daily newspaper * Urban contemporary music, a radio music format * Urban Dictionary * Urban Outfitters, an American multinational lifestyle retail corporation * Urban Records, a German record label owned by Universal Music Group Place names in the United States * Urban, South Dakota, a ghost town * Urban, Washington, an unincorporated community See also * New Urbanism, urban design movement promoting sustainable land use * Pope Urban (other), the name of several popes of the Catholic Church * Urban cluster (other) * Urban forest inequity, inequitable distribution of trees, with their associated benefits, across metropolitan areas * Urban forestry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian Urban Planners
Austrian may refer to: * Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent ** Someone who is considered an Austrian Austrian nationality law, citizen * Austrian German dialect * Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ** Austria-Hungary ** Austrian Airlines (AUA) ** Austrian cuisine ** Austrian Empire ** Austrian monarchy ** Austrian German (language/dialects) ** Austrian literature ** Austrian nationality law ** Austrian Service Abroad ** Music of Austria **Austrian School, Austrian School of Economics * Economists of the Austrian school of economic thought * The Pirc Defence, Austrian Attack, Austrian Attack variation of the Pirc Defence chess opening. See also * * * Austria (other) * Australian (other) * L'Autrichienne (other) {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Austrian Architects
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was Abolitionism, abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Christ, temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark and Gospel of Luke, Luke, before beginning his Ministry of Jesus, public ministry. Lent is usually observed in the Catholic Church, Catholic, Lutheranism, Lutheran, Moravian Church, Moravian, Anglican Communion, Anglican, United and uniting churches, United Protestant and Eastern Orthodoxy, Orthodox Christian traditions, among others. A number of Anabaptism, Anabaptist, Baptists, Baptist, Methodism, Methodist, Calvinism, Reformed (including certain Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continental Reformed, Presbyterianism, Presbyterian and Congregational church, Congregationalist churches), and Nondenominational Christianity, nondenominational Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix Pomatia
''Helix pomatia'', known as the Roman snail, Burgundy snail, or escargot, is a species of large, air-breathing stylommatophoran land Snails, snail native to Europe. It is characterized by a globular brown shell. It is an edible species which commonly occurs Synanthrope, synanthropically throughout its range. Distribution The present Species distribution, distribution of ''Helix pomatia'' is considerably affected by the dispersion by human and synanthropic occurrences. The northern limits of their natural distribution run presumably through central Germany and southern Poland with the eastern range limits running through western-most Ukraine and Moldova/Romania to Bulgaria. In the south, the species reaches northern Bulgaria, central Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnia and Hezegovina and Croatia. It occurs in northern Italy southwards to the Po (river), Po and the Ligurian Apennines. Westerly the native range extends to eastern France. Currently, ''H. pomatia'' is distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festina Lente
''Festina lente'' () or ''speûde bradéōs'' (, ) is a classical adage and oxymoron meaning "make haste slowly" (sometimes rendered in English as "more haste, less speed"). It has been adopted as a motto numerous times, particularly by the emperors Augustus and Titus, then later by the Medicis and the Onslows. During the 1960s the Cuban Revolution used this ancient phrase (apresúrate lentamente) in its message to the masses. The original form of the saying, ''speũde bradéōs'', is Classical Greek, of which ''festīnā lentē'' is the Latin translation. The words and ''festina'' are second-person-singular present active imperatives, meaning "make haste", while and ''lente'' are adverbs, meaning "slowly". History The Roman historian Suetonius, in '' De vita Caesarum'', tells that Augustus deplored rashness in a military commander, thus "" was one of his favourite sayings: Certain gold coins minted for Augustus bore images of a crab and a butterfly to attempt an emble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colophon (publishing)
In publishing, a colophon () is a brief statement containing information about the publication of a book such as an "imprint" (the place of publication, the publisher, and the date of publication). A colophon may include the device (logo) of a printer or publisher. Colophons are traditionally printed at the ends of books (see History below for the origin of the word), but sometimes the same information appears elsewhere (when it may still be referred to as colophon) and many modern (post-1800) books bear this information on the title page or on the verso of the title leaf, which is sometimes called a ''biblio page'' or (when bearing copyright data) the '' copyright page''. History The term ''colophon'' derives from the Late Latin ''colophōn'', from the Greek κολοφών (meaning "summit" or "finishing touch"). The term colophon was used in 1729 as the bibliographic explication at the end of the book by the English printer Samuel Palmer in his ''The General History of Prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
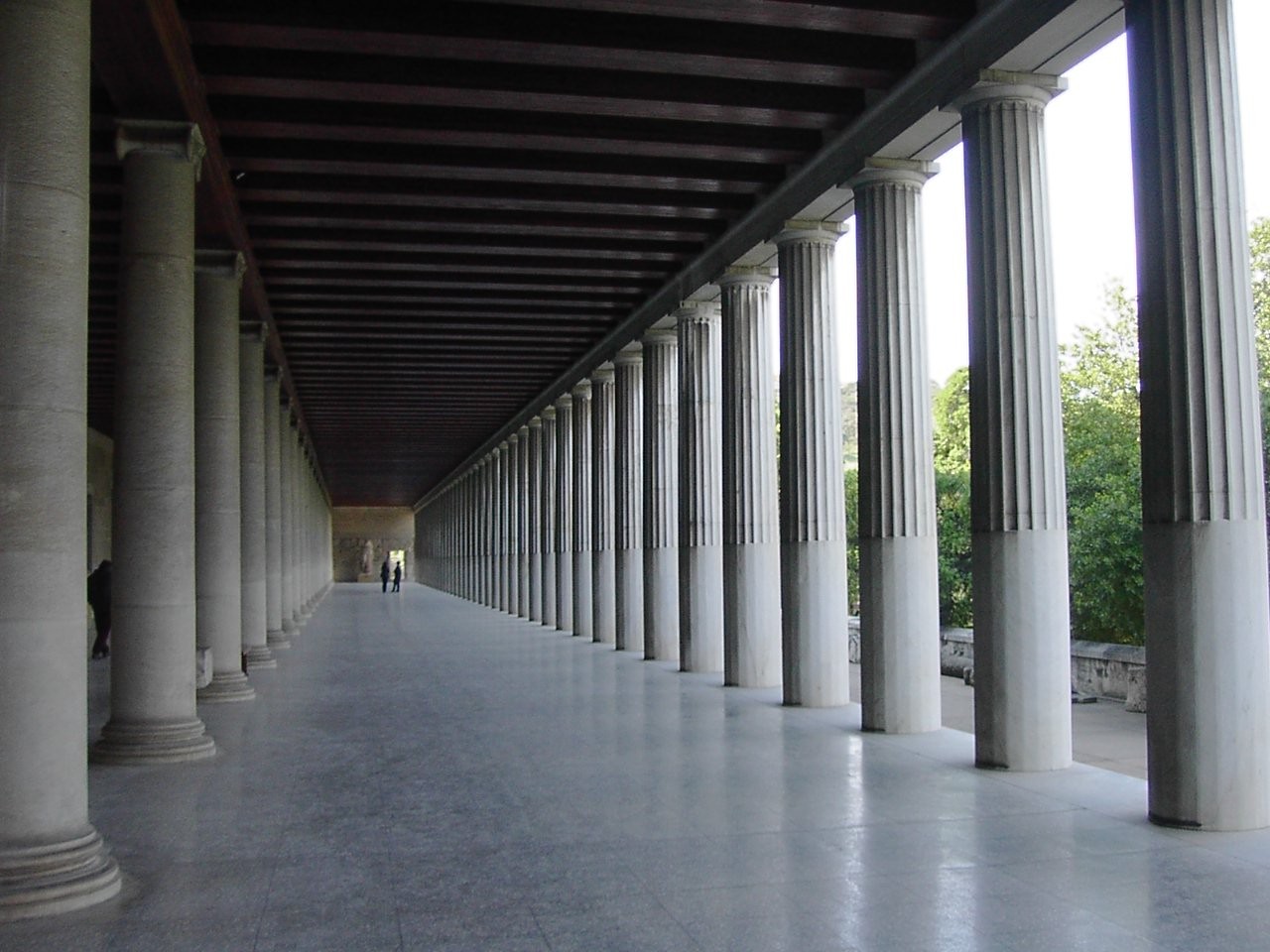
Forum (Roman)
A forum (Latin: ''forum'', "public place outdoors", : ''fora''; English : either ''fora'' or ''forums'') was a public square in a municipium, or any civitas, of Ancient Rome reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, along with the buildings used for shops and the stoas used for open stalls. But such fora functioned secondarily for multiple purposes, including as social meeting places for discussion. Many fora were constructed at remote locations along a road by the magistrate responsible for the road, in which case the forum was the only settlement at the site and had its own name, such as Forum Popili or Forum Livi. Functions In addition to its standard function as a marketplace, a forum was a gathering place of great social significance, and often the scene of diverse activities, including political discussions and debates, rendezvous, meetings, et cetera. In that case, it supplemented the function of a '' conciliabulum''. Every municipality () ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southernmost capital on the European mainland. With its urban area's population numbering over 3.6 million, it is the List of urban areas in the European Union, eighth-largest urban area in the European Union (EU). The Municipality of Athens (also City of Athens), which constitutes a small administrative unit of the entire urban area, had a population of 643,452 (2021) within its official limits, and a land area of . Athens is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years, and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BCE. According to Greek mythology the city was named after Athena, the ancient Greek goddess of wisdom, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agora
The agora (; , romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Ancient Greece, Greek polis, city-states. The literal meaning of the word "agora" is "gathering place" or "assembly". The agora was the center of the athletic, artistic, business, social, spiritual, and political life in the city. The Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example. Origins Early in Greek history (10th–4th centuries BC), free-born citizens would gather in the agora for military duty or to hear statements of the ruling king or council. Later, the agora also served as a marketplace, where merchants kept stalls or shops to sell their goods amid Arcade (architecture), arcades. This attracted artisans who built workshops nearby. From these twin functions of the agora as a political and a commercial spot came the two Greek verbs , ''agorázō'', "I shop", and , ''agoreúō'', "I speak in public". Ancient Agora of Athens The Ancient Agora of Athens was situat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |