|
Cambropachycopidae
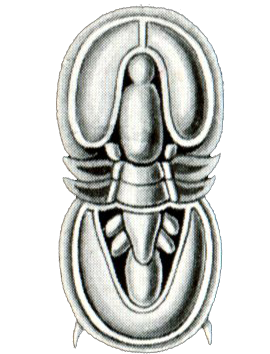
Cambropachycopidae is a family of Cambrian arthropods known from the Orsten The Orsten fauna are fossilized organisms preserved in the Orsten lagerstätte of Cambrian (Late Miaolingian to Furongian) rocks, notably at Kinnekulle and on the island of Öland, all in Sweden. The initial site, discovered in 1975 by Klaus M� ... of Sweden, united by their singular, large compound eye and heavily enlarged cephalic segment. Both species were roughly a millimeter long with similar body structures, however '' Goticaris'' is distinguished by two stalked blisters near its eye, as well as a longer body and smaller eye than ''Cambropachycope''. They are suggested to be stem-group mandibulates. References {{taxonbar, from1=Q125044245 Prehistoric arthropod families Pancrustacea Taxa described in 1990 Cambrian first appearances Fossils of Sweden Paleozoic Sweden Paleontology in Sweden Cambrian extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambropachycope
''Cambropachycope'' is an extinct genus of enigmatic Cambrian arthropod that includes the single species ''Cambropachycope clarksoni'', known from the Orsten lagerstätten in southern Sweden. It appears to have several apomorphic features, notably including a single large compound eye. Etymology The genus name ''Cambropachycope'' refers to the large unilobed eye, alongside it originating from the Cambrian period. The specific name ''clarksoni'' honours E. N. K. Clarkson. Description Cambropachycope diagrammatic reconstruction.png, Diagram of ''Cambropachycope'' Cambropachycopidae size comparison.svg, Size diagram, compared to '' Goticaris'' Originally, ''Cambropachycope'' was determined to be approximately long based on the specimens known up to that time, however, the discovery of new specimens helped infer the new size to be approximately long (3 mm head and abdomen, and 1 mm telson). The head of ''Cambropachycope'' has an unusual anterior projection that bears a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibulata
The clade Mandibulata constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda, alongside Chelicerata. Mandibulates include the crustaceans, myriapods (centipedes and millipedes, among others), and all true insects. The name "Mandibulata" refers to the mandibles, a modified pair of limbs used in food processing, the presence of which are characteristic of most members of the group. The mandibulates are divided between the extant groups Myriapoda (millipedes and centipedes, among others) and Pancrustacea (including crustaceans and hexapods, the latter group containing insects). Molecular phylogenetic studies suggest that the living arthropods are related as shown in the cladogram below. Crustaceans do not form a monophyletic In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria: # the grouping contains its own most recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goticaris
''Goticaris'' is an extinct genus of enigmatic Cambrian arthropod consisting of the single species ''Goticaris longispinosa'', known from the Orsten lagerstätten in southern Sweden. It appears to have several apomorphic features, notably including a large compound eye. Etymology The genus name ''Goticaris'' is in reference to the Gotes, a tribe which inhabited southern Sweden in the “Dark Ages”. The species name ''longispinosa'' refers to the long caudal spine. Description Originally, ''Goticaris'' was estimated to be approximately long, but new specimens helped infer the new size at long. The head of ''Goticaris'' has an unusual anterior projection of the head that bears a single large and what are possibly two smaller stalked compound eyes. There are four pairs of appendages on its head. The first pair of appendages are treated as antennae, and the other appendages on head are biramous. The mouth opens on the ventral surface in front of the second pair of appenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orsten
The Orsten fauna are fossilized organisms preserved in the Orsten lagerstätte of Cambrian (Late Miaolingian to Furongian) rocks, notably at Kinnekulle and on the island of Öland, all in Sweden. The initial site, discovered in 1975 by Klaus Müller and his assistants, exceptionally preserves soft-bodied organisms, and their larvae, who are preserved uncompacted in three dimensions. The fossils are phosphatized and silicified, thus the delicate chitinous cuticle and soft parts are not affected by acids, which act upon the limestone nodules within which the fossils have survived. Acids dissolve the limestone, revealing the microfossils in a recovery process called "acid etching". To recover the fossils, more than one and a half tons of Orsten limestone have been dissolved in acid, originally in a specifically designed laboratory in Bonn, more recently moved to Ulm. The insoluble residue is scanned by electron microscope. The phosphorus used to replace the fossils with calcium p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Arthropod Families
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancrustacea
Pancrustacea is the clade that comprises all crustaceans and all hexapods (insects and relatives). This grouping is contrary to the Atelocerata hypothesis, in which Hexapoda and Myriapoda are sister taxa, and Crustacea are only more distantly related. As of 2010, the Pancrustacea taxon was considered well accepted, with most studies recovering Hexapoda within Crustacea. The clade has also been called Tetraconata, referring to having a four-part cone in the ommatidium. The term "Tetraconata" is preferred by some scientists in order to avoid confusion with the use of "pan-" to indicate a clade that includes a crown group and all of its stem group representatives. Molecular studies A monophyletic Pancrustacea has been supported by several molecular studies, in most of which the subphylum Crustacea is paraphyletic with regard to hexapods (that is, that hexapods, including insects, are derived from crustacean ancestors). This means that within Pancrustacea, only some members are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Described In 1990
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian First Appearances
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Sweden
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic Sweden
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Greek ''palaiós'' (παλαιός, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (ζωή, "life") meaning "ancient lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology In Sweden
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796 in paleontology, 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822 in paleontology, 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |