|
Caldwell Objects
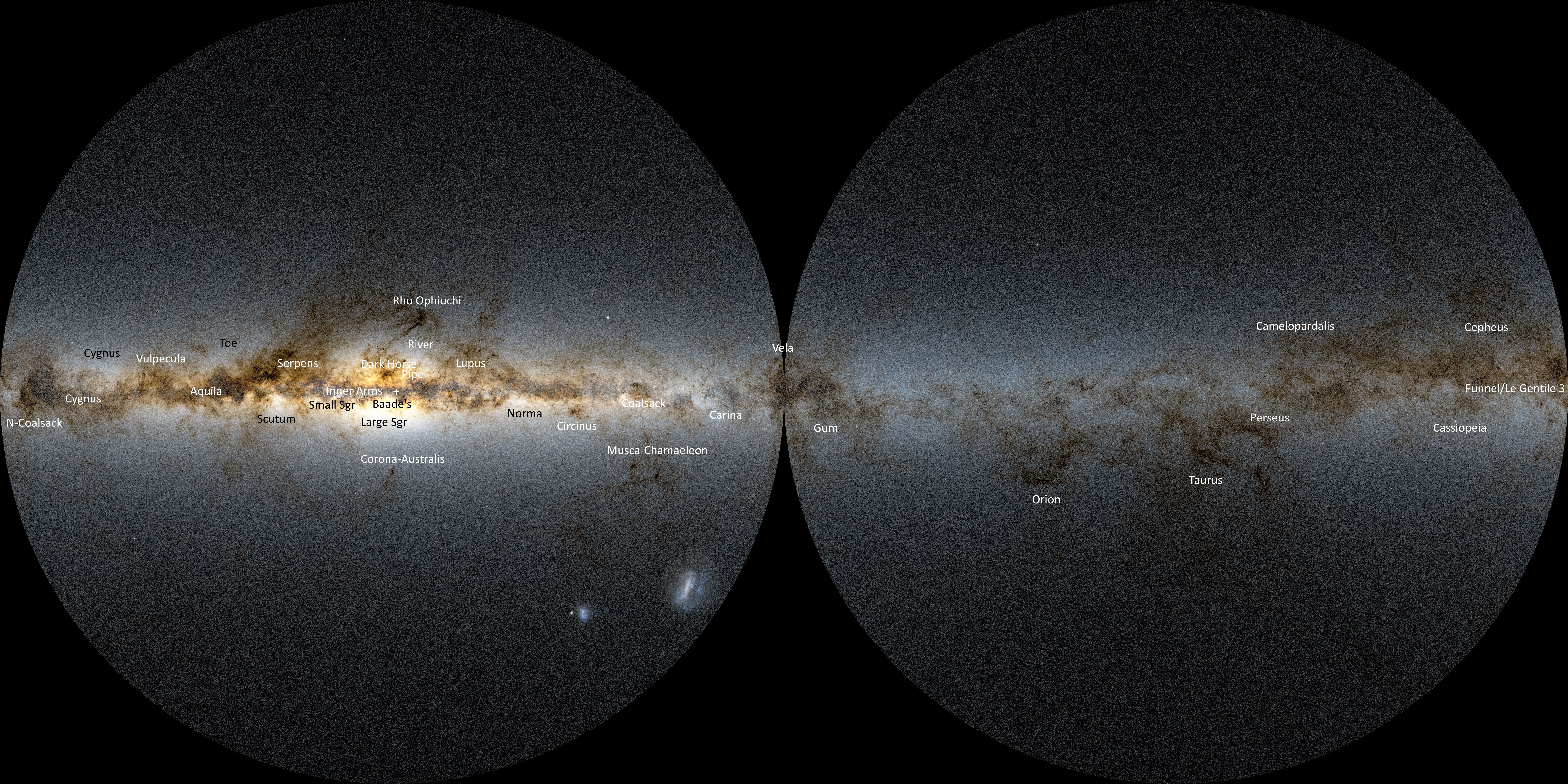
The Caldwell catalogue is an astronomical catalogue of 109 star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies for observation by amateur astronomers. The list was compiled by Patrick Moore as a complement to the Messier catalogue. While the Messier catalogue is used by amateur astronomers as a list of deep-sky objects for observation, Moore noted that Messier's list was not compiled for that purpose and excluded many of the sky's brightest deep-sky objects, such as the Hyades, the Double Cluster (NGC 869 and NGC 884), and the Sculptor Galaxy (NGC 253). The Messier catalogue was actually compiled as a list of known objects that might be confused with comets. Moore also observed that since Messier compiled his list from observations in Paris, it did not include bright deep-sky objects visible in the Southern Hemisphere, such as Omega Centauri, Centaurus A, the Jewel Box, and 47 Tucanae. Moore compiled a list of 109 objects to match the commonly accepted number of Messier objects (he excl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Catalogue
An astronomical catalogue is a list or tabulation of astronomical objects, typically grouped together because they share a common type, Galaxy morphological classification, morphology, origin, means of detection, or method of discovery. The oldest and largest are star catalogues. Hundreds have been published, including general ones and special ones for such objects as Infrared astronomy, infrared stars, variable stars, giant stars, multiple star systems, star clusters, and so forth. General catalogues for deep-sky objects or for objects other than stars are also large. Again, there are specialized ones for nebulas, galaxies, X-ray astronomy, X-ray sources, Astronomical radio source, radio sources, quasars and other classes. The same is true for asteroids, comets and other Small Solar System body, solar system bodies. Astronomical catalogues such as those for asteroids may be compiled from multiple sources, but most modern catalogues are the result of a particular astronomical su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewel Box (star Cluster)
The Jewel Box (also known as the Kappa Crucis cluster, NGC 4755, or Caldwell 94) is an open cluster in the constellation Crux, originally discovered by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1751–1752. This cluster was later named the Jewel Box by John Herschel when he described its telescopic appearance as "... a superb piece of fancy jewellery". It is easily visible to the naked eye as a hazy star some 1.0° southeast of the first-magnitude star Mimosa (Beta Crucis). This hazy star was given the Bayer star designation "Kappa Crucis", from which the cluster takes one of its common names. The modern designation Kappa Crucis has been assigned to one of the stars in the base of the A-shaped asterism of the cluster. This cluster is one of the youngest known, with an estimated age of 14 million years. It has a total integrated magnitude 4.2, is located 1.99 kpc, or 6497 light years from Earth, and contains just over 100 stars. Discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Nebulae
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the Visible spectrum, visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission nebula, emission or reflection nebula, reflection nebulae. The extinction (astronomy), extinction of the light is caused by cosmic dust, interstellar dust grains in the coldest, densest parts of molecular clouds. Clusters and large complexes of dark nebulae are associated with Giant Molecular Clouds. Isolated small dark nebulae are called Bok globules. Like other interstellar dust or material, the things it obscures are visible only using radio waves in radio astronomy or infrared in infrared astronomy. Dark clouds appear so because of sub-micrometre-sized dust particles, coated with frozen carbon monoxide and nitrogen, which effectively block the passage of light at visible wavelengths. Also present are molecular hydrogen, atomic helium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC 2944
IC 2944, also known as the Running Chicken Nebula, the Lambda Centauri Nebula or the λ Centauri Nebula, is an open cluster with an associated emission nebula found in the constellation Centaurus, near the star λ Centauri. It features Bok globules, which are frequently a site of active star formation. However, no evidence for star formation has been found in any of the globules in IC 2944. Other designations for IC 2944 include RCW 62, G40 and G42. The ESO Very Large Telescope image on the right is a close up of a set of Bok globules discovered in IC 2944 by astronomer A. David Thackeray in 1950. These globules are now known as Thackeray's Globules. In 2MASS images, 6 stars are visible within the largest globule. The region of nebulosity visible in modern images includes both IC 2944 and IC 2948, as well as the fainter IC 2872 nearby. IC 2948 is the brightest emission and reflection nebulae towards the southeast, while IC 2944 is the cluster of stars and surrounding nebulosity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
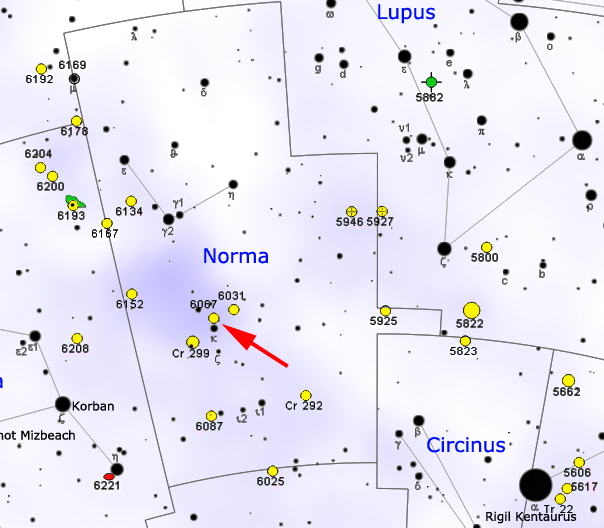
NGC 6067
NGC 6067 is an open star cluster, open cluster in the constellation Norma (constellation), Norma. It is located to the north of Kappa Normae, with an angular diameter of 12. Visible to the naked eye in dark skies, it is best observed with binoculars or a small telescope, and a 12-inch aperture telescope will reveal about 250 stars. Discovered by James Dunlop in 1826, it has been described by John Herschel as "a most superbly rich and large cluster" and by Stephen James O'Meara as "one of the sky's most stunning open star clusters". Its brightest stars have an apparent magnitude of around 8. There are 84 member stars with an apparent magnitude brighter than 12. NGC 6067 is located in the Norma Star Cloud in the Norma Arm of the Milky Way and is 15 to 20 times as rich as the Pleiades and about the same age. It is thought to be around 102 million years old, and contain 893 solar masses. Two Cepheid variables, QZ Normae and V340 Normae, have been identified as members of the cluster, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
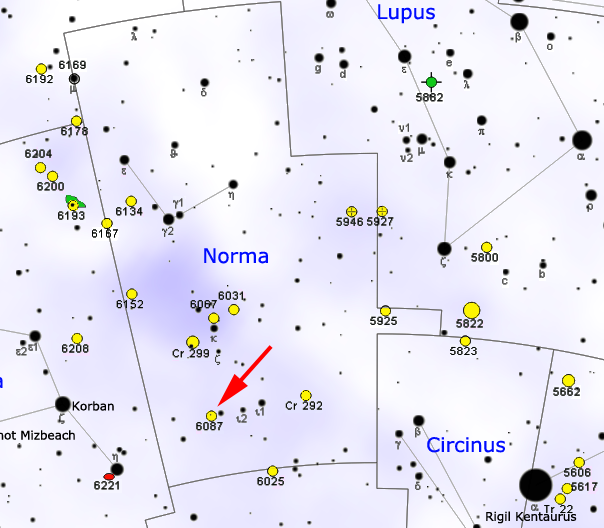
NGC 6087
NGC 6087 (also known as Caldwell 89 or the S Normae Cluster) is an open cluster of 40 or more Burnham's ''Celestial Handbook'' gives the number 40, though other studies go as high as 349; see Stephen James O'Meara, ''The Caldwell Objects'', Cambridge University Press, 2002, p. 351. stars centered on the Cepheid variable S Normae in the constellation Norma Norma may refer to: * Norma (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) ** Norma Lizbeth Ramos, a Mexican bullying victim Astronomy *Norma (constellation) * 555 Norma, a minor asteroid * Cygnus Arm or Norma Arm, a spiral .... At a distance of about 3500 ly and covering a field of almost one quarter of a degree, the stars range from seventh- to eleventh-magnitude, the brightest being 6.5 magnitude S Normae. The aggregate visual magnitude of the cluster is about 5.4. Spectral analysis of the radial motion of the stars confirm that S Normae is a member of the cluster, and the period/luminosity relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 4244
NGC 4244, also known as Caldwell 26, is an edge-on loose spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici, and is part of the M94 Group or Canes Venatici I Group, a galaxy group relatively close to the Local Group containing the Milky Way. In the sky, it is located near the yellow naked-eye star, Beta Canum Venaticorum, but also near the barred spiral galaxy NGC 4151 and irregular galaxy NGC 4214. With an apparent V-band magnitude of 10.18, NGC 4244 lies approximately 4.3 megaparsecs The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (AU), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and ... (14 million light years) away. A nuclear star cluster and halo is located near the centre of this galaxy. See also * IC 5052 - a similar edge-on galaxy Notes References * * External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 4244 Unbarred sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or south (negative) of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question. The root of the word ''declination'' (Latin, ''declinatio'') means "a bending away" or "a bending down". It comes from the same root as the words ''incline'' ("bend forward") and ''recline'' ("bend backward"). In some 18th and 19th century astronomical texts, declination is given as ''North Pole Distance'' (N.P.D.), which is equivalent to 90 – (declination). For instance an object marked as declination −5 would have an N.P.D. of 95, and a declination of −90 (the south celestial pole) would have an N.P.D. of 180. Explanation Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, projected onto the celestial sphere, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Publishing
Springer Publishing Company is an American publishing company of academic journals and books, focusing on the fields of nursing, gerontology, psychology, social work, counseling, public health, and rehabilitation (neuropsychology). It was established in 1951 by Bernhard Springer, a great-grandson of Julius Springer, and is based in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. History Springer Publishing Company was founded in 1950 by Bernhard Springer, the Berlin-born great-grandson of Julius Springer, who founded Springer Science+Business Media, Springer-Verlag (now Springer Science+Business Media). Springer Publishing's first landmark publications included ''Livestock Health Encyclopedia'' by R. Seiden and the 1952 ''Handbook of Cardiology for Nurses''. The company's books soon branched into other fields, including medicine and psychology. Nursing publications grew rapidly in number, as Modell's ''Drugs in Current Use'', a small annual paperback, sold over 150,000 copies over several edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-barrelled Name
A double-barrelled name is a type of compound surname, typically featuring two words (occasionally more), often joined by a hyphen. Notable people with double-barrelled names include Winnie Madikizela-Mandela, Julia Louis-Dreyfus, and Beyoncé Knowles-Carter. In the Western tradition of surnames, there are several types of double surname (or double-barrelled surname). If the two names are joined with a hyphen, it may also be called a hyphenated surname. The word "barrel" possibly refers to the barrel of a shotgun, as in " double-barreled shotgun" or " double-barreled rifle". In British tradition, a double surname is heritable, usually taken to preserve a family name that would have become extinct due to the absence of male descendants bearing the name, connected to the inheritance of a family estate. Examples include Harding-Rolls, Stopford-Sackville, and Spencer-Churchill. In Spanish tradition, double surnames are the norm and not an indication of social status. Peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sky & Telescope
''Sky & Telescope'' (''S&T'') is a monthly magazine covering all aspects of amateur and professional astronomy, including what to see in the sky tonight and new findings in astronomy. Other topics covered include: *observing guides for planets, galaxies, star clusters, and other objects visible in the night sky *reviews of telescopes and other astronomical equipment, books, and software *events in the amateur astronomy community * amateur telescope making * astrophotography The articles are intended for the informed lay reader and include detailed discussions of current discoveries, frequently by participating scientists. The magazine is illustrated in full color, with both amateur and professional photography of celestial sights, as well as tables and charts of upcoming celestial events. History ''Sky & Telescope'' was founded by Charles A. Federer and his wife Helen Spence Federer. The duo had formed the Sky Publishing Corporation in late 1939 to manage a magazine called '' T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |