|
Caetextia
Caetextia (from the Latin word ''caecus'', meaning "blind" and ''contextus'', meaning "context") is a term and concept first coined by psychologists Joe Griffin and Ivan Tyrrell to describe a chronic disorder that manifests as a context blindness in people on the autism spectrum. It was specifically used to designate the most dominant manifestation of autistic behaviour in higher-functioning individuals. Griffin and Tyrell also suggested that caetextia "is a more accurate and descriptive term for this inability to see how one variable influences another, particularly at the higher end of the spectrum, than the label of 'Asperger's syndrome. Caetextia presents itself as the inability to adjust behaviour appropriately to deal with interacting variables. People with caetextia may fail to consider the context surrounding the behaviour. This can result in people with caetextia experiencing elevated levels of frustration, anger, and anxiety when faced with a situation that requires giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Tyrrell
Ivan Tyrrell (; born 18 October 1943) is a British educator, writer, and artist. He lives with his wife Véronique in the Cotswolds, England. Artist Tyrrell left Wallington County Grammar School to study art as an apprentice at F.G. Marshal in 1959. In 1962 he began a fine arts course at Croydon Art College and was taught painting by Bridget Riley, Barry Fantoni and John Hoyland among others. He left college disillusioned with the art world and worked in London advertising studios before setting up a graphic design company in 1971 on the South Coast in Sussex. Two silk-screen posters produced with fellow artist Frederick Carver featured in ''Les Sixties'', a Paris exhibition of psychedelic art that then transferred to the Brighton Festival and... “the spectral, hallucinatory scenarios of J. G. Ballard, especially in his novel '' The Crystal World'' – bodied forth in Tyrrell’s apocalyptic poster design." In 1965 Tyrrell, whilst still a student, had met the writer, Idr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asperger's Syndrome
Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's, is a former neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with restricted and repetitive patterns of behaviour and interests. The syndrome is no longer recognised as a diagnosis in itself, having been merged with other disorders into autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It was considered to differ from other diagnoses that were merged into ASD by relatively unimpaired spoken language and intelligence. The syndrome was named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger, who, in 1944, described children in his care who struggled to form friendships, did not understand others' gestures or feelings, engaged in one-sided conversations about their favourite interests, and were clumsy. In 1994, the diagnosis of Asperger's was included in the fourth edition (DSM-IV) of the American ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders''; with the pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asperger Syndrome
Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's, is a former neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with restricted and repetitive patterns of behaviour and interests. The syndrome is no longer recognised as a diagnosis in itself, having been merged with other disorders into autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It was considered to differ from other diagnoses that were merged into ASD by relatively unimpaired spoken language and intelligence. The syndrome was named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger, who, in 1944, described children in his care who struggled to form friendships, did not understand others' gestures or feelings, engaged in one-sided conversations about their favourite interests, and were clumsy. In 1994, the diagnosis of Asperger's was included in the fourth edition (DSM-IV) of the American '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders''; with the pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism Spectrum Disorder
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a '' spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different from one's own states and include beliefs, desires, intentions, emotions, and thoughts. Possessing a functional theory of mind is considered crucial for success in everyday human social interactions. People use such a theory when analyzing, judging, and inferring others' behaviors. The discovery and development of theory of mind primarily came from studies done with animals and infants. Factors including drug and alcohol consumption, language development, cognitive delays, age, and culture can affect a person's capacity to display theory of mind. It has been proposed that deficits in theory of mind can occur in people with autism (although this is contentious), anorexia nervosa, schizophrenia, dysphoria, attention deficit hyperactiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Functions
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence (e.g., reasoning and problem-solving). Executive functions gradually develop and change across the lifespan of an individual and can be improved at any time over the course of a person's life. Similarly, these cognitive processes can be adversely affected by a variety of events which affect an individual. Both neuropsychological tests (e.g., the Stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Processing (psychology)
In psychology, parallel processing is the ability of the brain to simultaneously process incoming stimuli of differing quality. Parallel processing is associated with the visual system in that the brain divides what it sees into four components: color, motion, shape, and depth. These are individually analyzed and then compared to stored memories, which helps the brain identify what you are viewing. The brain then combines all of these into the field of view that then seen and comprehended. Parallel processing has been linked, by some experimental psychologists, to the stroop effect. This is a continual and seamless operation. For example, if one is standing between two different groups of people who are simultaneously carrying on two different conversations, one may be able to pick up only some information of both conversation at the same time. Background Parallel Distributed Processing Models are neurally inspired, emulating the organisational structure of nervous syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Empathy Problem
The double empathy problem is a psychological theory, coined in 2012 by autism researcher Damian Milton, which proposes that the social and communication difficulties present in autistic people when socializing with non-autistic people are actually due to a reciprocal lack of understanding and bidirectional differences in communication style, social-cognitive characteristics, and experiences between autistic people and non-autistic people, but not necessarily inherent deficiency, since most autistic people are able to socialize, communicate, and empathize well with most autistic people. The theory therefore fundamentally challenges both the common notion that social skills of autistic people are inherently impaired, and the theory, developed by Professor Simon Baron-Cohen, but since disputed, that empathy, and theory of mind (ToM) are generally impaired in autistic people, which is empirically questionable with many failed replications and mixed findings. In a podcast in December 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior that is inappropriate for a given situation. There may also be sleep problems, social withdrawal, lack of motivation, and difficulties carrying out daily activities. Psychosis can have serious adverse outcomes. As with many psychiatric phenomena, psychosis has several different causes. These include mental illness, such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, sensory deprivation and in rare cases, major depression ( psychotic depression). Other causes include: trauma, sleep deprivation, some medical conditions, certain medications, and drugs such as cannabis, hallucinogens, and stimulants. One type, known as postpartum psychosis, can occur after giving birth. The neurotransmitter dopamine is believed to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Eye Movement Sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly. The REM phase is also known as paradoxical sleep (PS) and sometimes desynchronized sleep or dreamy sleep, because of physiological similarities to waking states including rapid, low-voltage desynchronized brain waves. Electrical and chemical activity regulating this phase seems to originate in the brain stem, and is characterized most notably by an abundance of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, combined with a nearly complete absence of monoamine neurotransmitters histamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. Experiences of REM sleep are not transferred to permanent memory due to absence of norepinephrine. REM sleep is physiologically different from the other phases of sleep, which are collectively referred to as non-REM sleep (NRE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
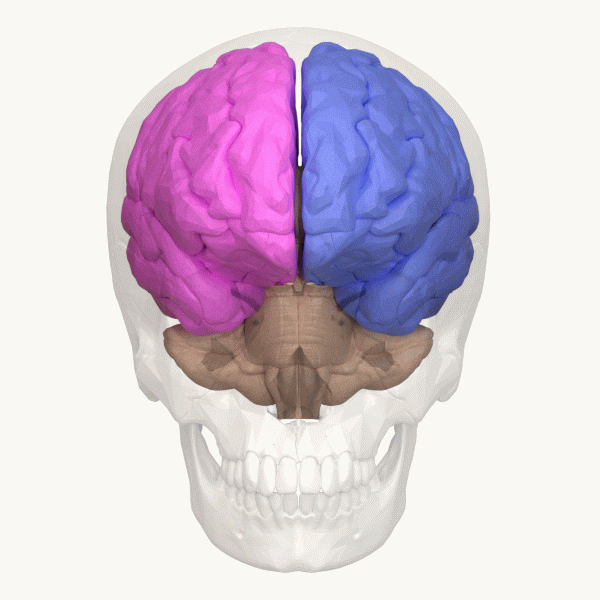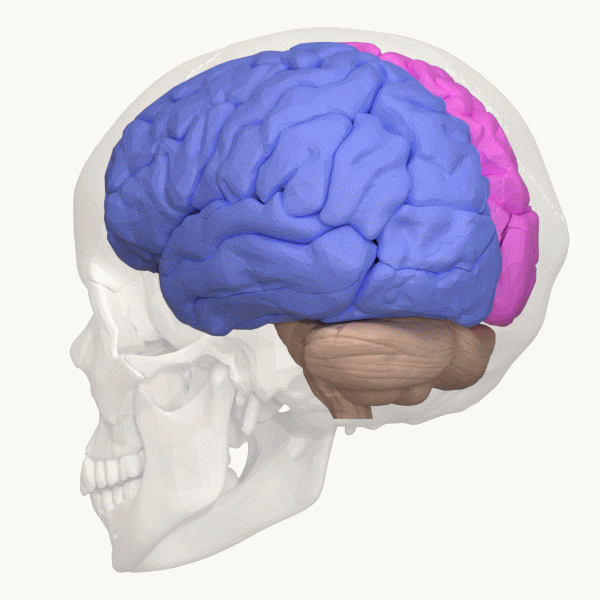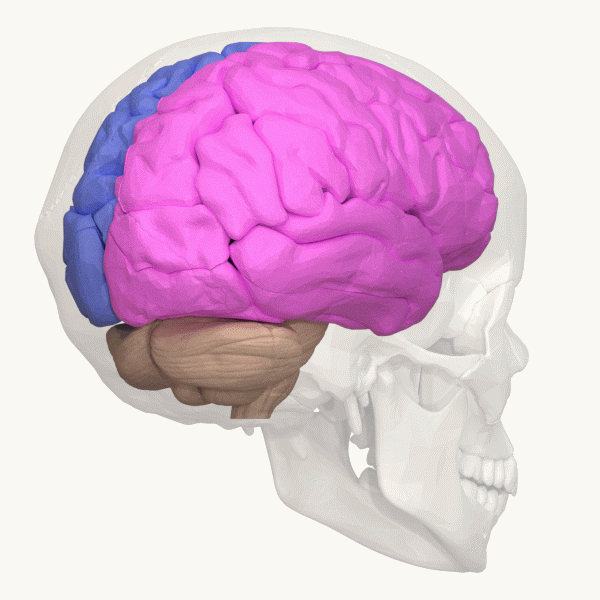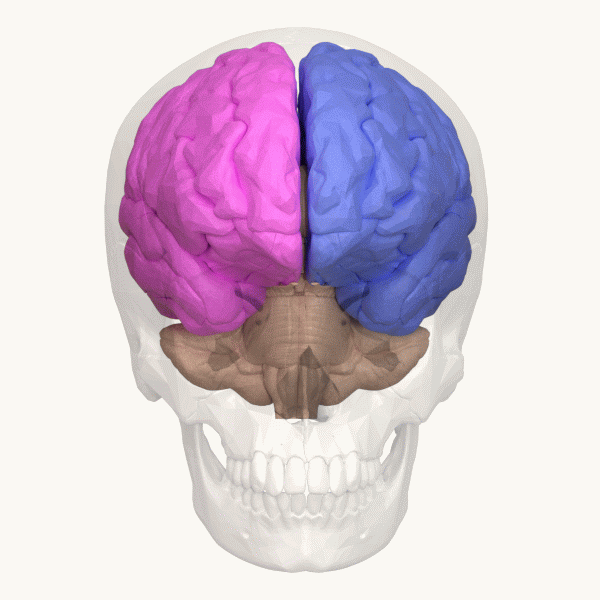
Hemispheric Lateralization
The lateralization of brain function is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. Although the macrostructure of the two hemispheres appears to be almost identical, different composition of neuronal networks allows for specialized function that is different in each hemisphere. Lateralization of brain structures is based on general trends expressed in healthy patients; however, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization. Each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger anthropological history. The best ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |