|
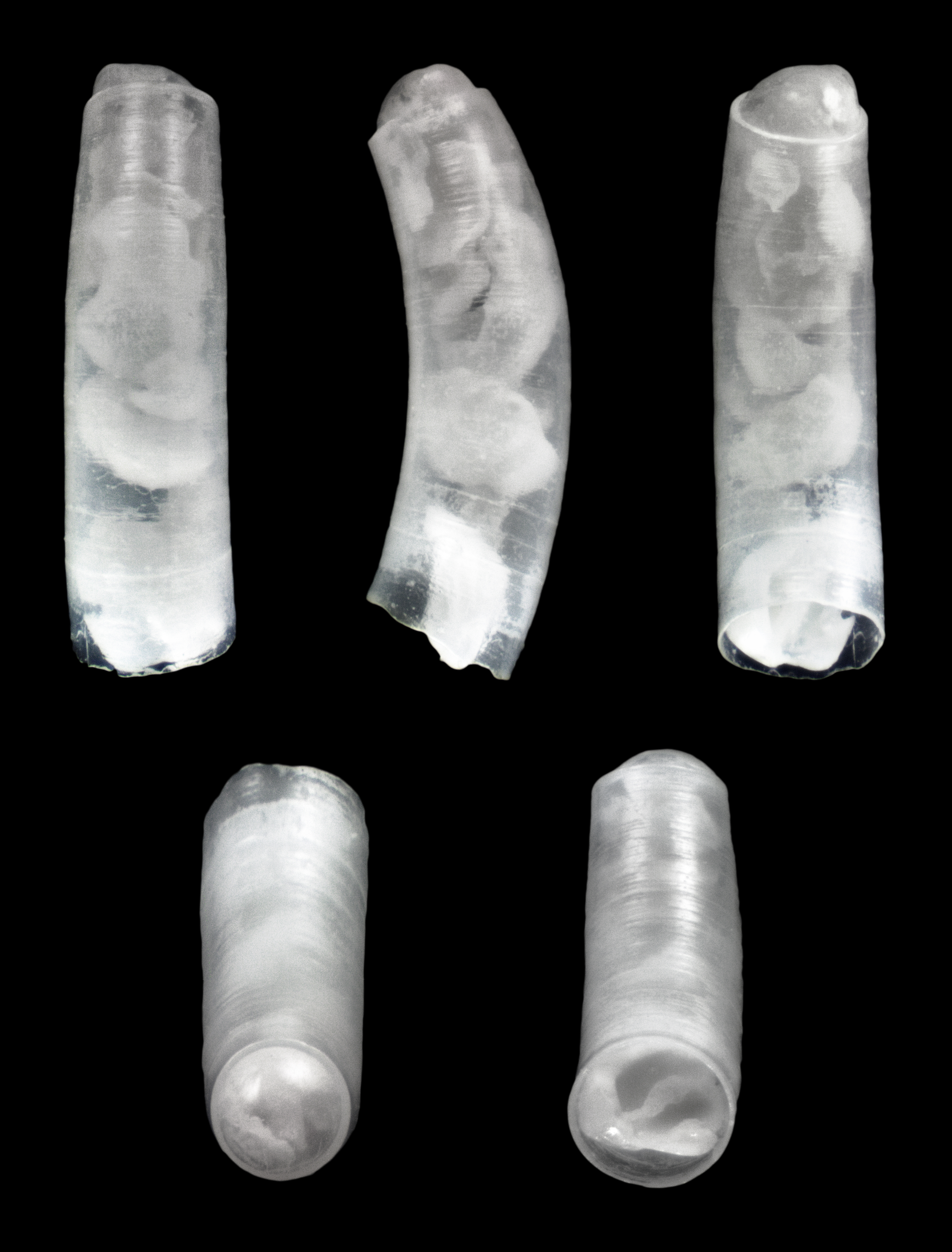
Caecidae
Caecidae is a taxonomic family of very small and minute sea snails or micromolluscs, marine gastropod molluscs in the order Littorinimorpha.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2013). Caecidae. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=126 on 2013-06-04 Habitat These minute tubular shells can be found living in marine sediment, or among algae or sponges, in warm and temperate seas. Shell description The shells in this family, are unusual in that the adult shell is a curving tube. In the subfamily Caecinae the protoconch is lost and the tube is sealed with a permanent calcareous plug at one end. In the subfamilies Ctiloceratinae and Strebloceratinae the protoconch is retained. At the other end the tube is sealed by a circular operculum. The spiral part is almost always lost when outgrowing the juvenile stage. The color of the shell is white to pale yellow. Taxonomy This family contains three subfamilies : * Caecinae Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecum (gastropod)
''Caecum'' is a genus of minute sea snails, marine gastropod micromolluscs or micromollusks in the family Caecidae or blind shells. Distribution This genus occurs worldwide in warm and temperate seas. Many species live in sponges, in sandy spots on reefs, or in grassy beds in shallow waters in bays and lagoons. Some species are very common and can be extremely numerous where they do occur, such as the "beautiful caecum"(''Caecum pulchellum''), but even they can be easily overlooked as they are so tiny. Many species are considered to be uncommon, but this assessment may be a result of lack of proper sampling. Shell description The shells in this genus, like the others in the family, are very small with a length between 2 mm and 6 mm. Their colour is white to yellowish white and some are almost translucent. They are unusual in that the teleoconch of the adult shell is a curving tube for most of its length. In the first stage of the shell it is spiral-shaped but soon be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meioceras
''Meioceras'' is a genus of minute sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks or micromollusks in the family Caecidae. Species Species within the genus ''Meioceras'' include: * ''Meioceras cornucopiae'' Carpenter, 1858 * ''Meioceras cubitatum'' Folin, 1868 * † ''Meioceras mateldae'' Selli, 1974 * ''Meioceras nitidum'' (Stimpson, 1851) * ''Meioceras tumidissimum'' de Folin, 1869 ; Species brought into synonymy: * ''Meioceras bermudezi'' Pilsbry & Aguayo, 1934: synonym of ''Meioceras cornucopiae'' Carpenter, 1859 * ''Meioceras bitumidum'' de Folin, 1869: synonym of ''Meioceras nitidum'' (Stimpson, 1851) * ''Meioceras boucheti'' Pizzini & Raines, 2011: synonym of ''Mauroceras boucheti'' (Pizzini & Raines, 2011) (original combination) * ''Meioceras carpenteri'' de Folin, 1869: synonym of ''Meioceras nitidum'' (Stimpson, 1851) * ''Meioceras cingulatum'' Dall, 1892: synonym of ''Meioceras nitidum'' (Stimpson, 1851) * ''Meioceras constrictum'' Pilsbry & Aguayo, 1933: synonym of ''Meio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauroceras
''Mauroceras'' is a genus of minute sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks or micromollusks in the family Caecidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Mauroceras Vannozzi, 2019. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1356167 on 2021-07-08 Species * ''Mauroceras amamiense'' (Habe, 1978) * ''Mauroceras boucheti'' (Pizzini & Raines, 2011) * ''Mauroceras kajiyamai'' (Habe, 1963) * ''Mauroceras legumen'' (Hedley, 1899) * ''Mauroceras maestratii'' (Pizzini, Raines & Vannozzi, 2013) * ''Mauroceras rhinoceros'' (Pizzini, Raines & Vannozzi, 2013) * ''Mauroceras sandwichense'' (de Folin, 1881) * ''Mauroceras serratum ''Mauroceras'' is a genus of minute sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks or micromollusks in the family Caecidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Mauroceras Vannozzi, 2019. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https: ...'' (Vannozzi, 2017) References * Vannozzi A. (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecum Glabrum
''Caecum glabrum'' is a species of minute sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Caecidae Caecidae is a taxonomic family of very small and minute sea snails or micromolluscs, marine gastropod molluscs in the order Littorinimorpha.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2013). Caecidae. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http: .... Description Distribution References External links Caecidae Gastropods described in 1803 {{Caecidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littorinimorpha
Littorinimorpha is a large order of snails, gastropods, consisting primarily of sea snails ( marine species), but also including some freshwater snails ( aquatic species) and land snails ( terrestrial species).Bouchet P. & Rocroi J.-P. (Ed.); Frýda J., Hausdorf B., Ponder W., Valdes A. & Warén A. 2005. ''Classification and nomenclator of gastropod families''. Malacologia: International Journal of Malacology, 47(1-2). ConchBooks: Hackenheim, Germany. . . 397 pp. http://www.vliz.be/Vmdcdata/imis2/ref.php?refid=78278 Previously, the Linnaean taxonomy used in the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Ponder & Lindberg (1997) ranked like this: subclass Orthogastropoda, superorder Caenogastropoda, order Sorbeoconcha, suborder Hypsogastropoda, infraorder Littorinimorpha. The order Littorinimorpha contains many gastropoda families that were formerly placed in the order Mesogastropoda, as introduced by J. Thiele in his work from 1921. Evidence for this group being monophyletic is scanty. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncatelloidea
Truncatelloidea is a superfamily of snails, gastropod mollusks in the clade Caenogastropoda.Bouchet, P. (2013). ''Truncatelloidea''. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=722756 on 2013-06-11 The families are marine, brackish, freshwater and terrestrial. Families * Amnicolidae Tryon, 1863 * Anabathridae Keen, 1971 * Assimineidae H. Adams & A. Adams, 1856 * Bithyniidae Gray, 1857 * Bythinellidae Locard, 1893 * Caecidae Gray, 1850 * Calopiidae Ponder, 1999 * Clenchiellidae D. W. Taylor, 1966 * Cochliopidae Tryon, 1866 * Elachisinidae Ponder, 1985 * Emmericiidae Brusina, 1870 * Epigridae Ponder, 1985 * Falsicingulidae Slavoshevskaya, 1975 * Helicostoidae Pruvot-Fol, 1937 * Hydrobiidae Stimpson, 1865 * Hydrococcidae Thiele, 1928 * Iravadiidae Thiele, 1928 * Lithoglyphidae Tryon, 1866 * Lithoglyphulidae Radoman, 1973 * Moitessieriidae Bourguignat, 1863 * Pomatiopsidae Stimpson, 1865 * Spirostylif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillip Pearsall Carpenter
Philip Pearsall Carpenter (4 November 1819 – 24 May 1877) was an English minister who emigrated to Canada, where his field work as a malacologist or conchologist is still well regarded today. A man of many talents, he wrote, published, taught, and was a volunteer explaining the growing study of shells in North America. Life Philip P. Carpenter was born in Bristol, England on 4 November 1819. His father was Lant Carpenter, a notable educator and Unitarian minister. His mother was Anna or Hannah Penn, daughter of John Penn and Mary. Anna was christened on 11 May 1787 in Bromsgrove, Worcester.Carpenters' Encyclopedia of Carpenters 2009, DVD format. The subject in RIN 25572. P. P. Carpenter, as he was called, was educated at Trinity Bristol College, and then Manchester College (then at York, now at Oxford), gaining a BA from the University of London in 1841, the year of his ordination as a minister. Carpenter was a vegetarian and joined the Vegetarian Society in 1851. Carp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micromollusc
A micromollusk is a shelled mollusk which is extremely small, even at full adult size. The word is usually, but not exclusively, applied to marine mollusks, although in addition, numerous species of land snails and freshwater mollusks also reach adult size at very small dimensions. These tiny mollusks or their tiny shells are easy to overlook, as many of them are not very noticeable to the naked eye, and thus many people are not aware that they even exist. Nonetheless there are large numbers of families and vast numbers of mollusk species, in particular marine gastropods or sea snails, which are minute enough to be considered micromollusks. Considerable numbers of marine gastropod species are only about 5 or 6 mm in adult size; many others are only about 2 or 3 mm in adult size; and a few have adult shells which are as small as one millimeter or even smaller still. Despite their tiny size, many of the shells have a good deal of elaborate sculpture. A fair numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenogastropoda
Caenogastropoda is a taxonomic clade, a large diverse group which are mostly sea snails and other marine gastropod mollusks, but also includes some freshwater snails and some land snails. The clade is the most diverse and ecologically successful of the gastropods. Caenogastropoda contains many families of shelled marine molluscs – including the periwinkles, cowries, wentletraps, moon snails, murexes, cone snails and turrids – and constitutes about 60% of all living gastropods. Biology The Caenogastropoda exhibit torsion, and thus are included in what was previously called the Streptoneura (meaning ''twisted nerves''), also known as Prosobranchia (meaning ''gills forward''). Specifically, they are characterized by having only a single auricle in the heart and a single pair of gill leaflets, and are equivalent to the Monotocardia or Pectinobranchia of older authors. Taxonomy The taxon Caenogastropoda was first established by Leslie Reginald Cox in 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropoda
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |