|
Cadmium Chloride
Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and the hemipentahydrate CdCl2•2.5H2O. Structure Anhydrous Anhydrous cadmium chloride forms a layered structure consisting of octahedral Cd2+ centers linked with chloride ligands. Cadmium iodide, CdI2, has a similar structure, but the iodide ions are arranged in a HCP lattice, whereas in CdCl2 the chloride ions are arranged in a CCP lattice.N. N. Greenwood, A. Earnshaw, ''Chemistry of the Elements'', 2nd ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, UK, 1997. Hydrates The anhydrous form absorbs moisture from the air to form various hydrates. Three of these hydrates have been examined by X-ray crystallography. Chemical properties Cadmium chloride di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption (chemistry), absorption or adsorption from the surrounding Natural environment, environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g. changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they dissolve in the water they absorb, forming an aqueous solution. Hygroscopy is essential for many plant and animal species' attainment of hydration, nutrition, reproduction and/or seed dispersal. Biological evolution created hygroscopic solutions for water harvesting, filament tensile strength, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Oxide
Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals.Lewis, Richard J. Sr., Hawley's condensed chemical dictionary, 13th ed., 1997, p. 189 Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor with a band gap of 2.18 eV (2.31 eV) at room temperature (298 K). Production and structure Since cadmium compounds are often found in association with zinc ores, cadmium oxide is a common by-product of zinc refining. It is produced by burning elemental cadmium in air. Pyrolysis of other cadmium compounds, such as the nitrate or the carbonate, also affords this oxide. When pure, it is red, but CdO is unusual in being available in many differing colours due to its tendency to form defect stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. Etymology Because it was produced from halite, rock salt according to the methods of Johann Rudolph Glauber, hydrochloric acid was historically called by European alchemists ''spirits of salt'' or ''acidum salis'' (salt acid). Both names are still used, especially in other languages, such as , , , , , , , , , , (''ensan''), zh, 盐酸 (''yánsuān''), and (''yeomsan''). Gaseous HCl was called ''marine acid air''. The name ''muriatic acid'' has the same origin (''muriatic'' means "pertaining to brine or salt", hence ''muriate'' means hydrochloride), and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
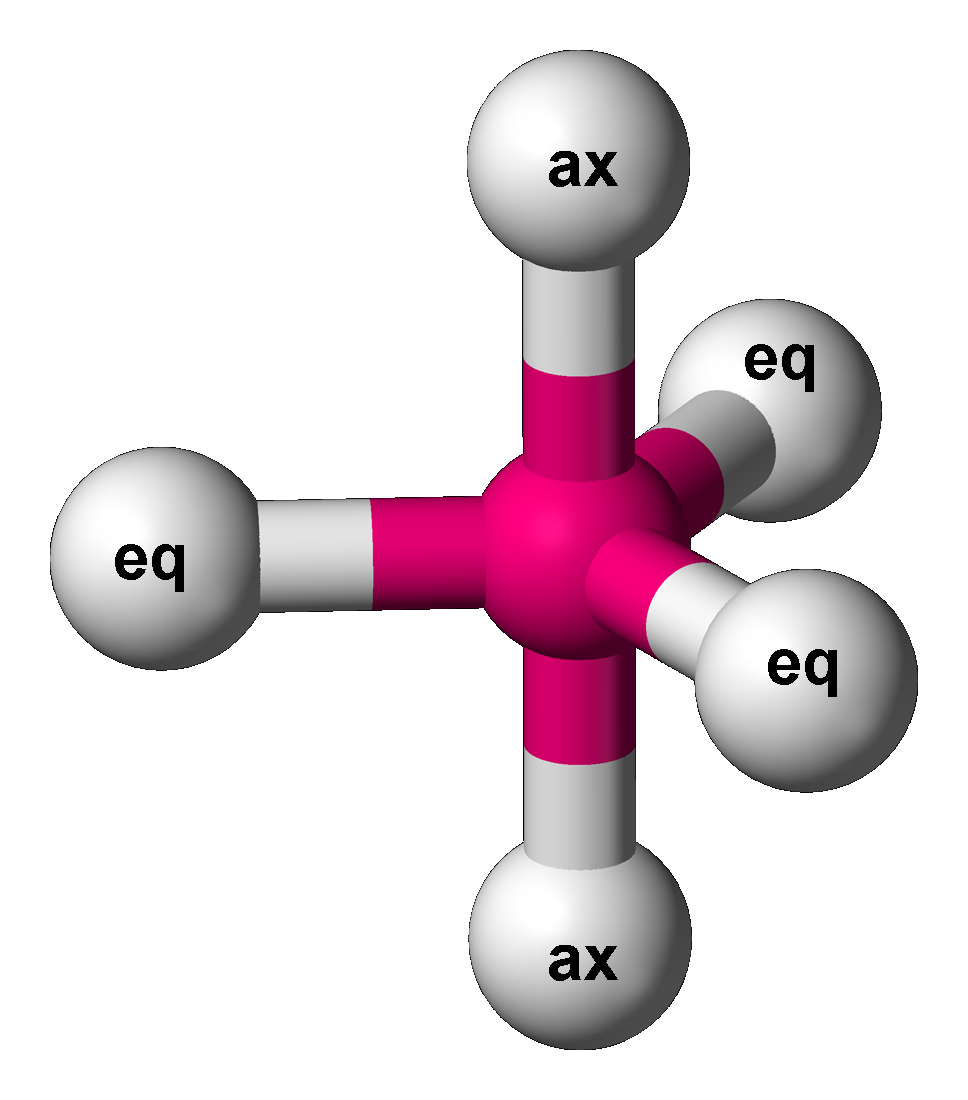
Trigonal Bipyramid Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramidal molecular geometry, pentagonal bipyramid), because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions. Examples of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride (), and phosphorus pentachloride () in the gas phase. Axial (or apical) and equatorial positions The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For phosphorus pentachloride as an example, the phosphorus atom shares a plane with three chlorine atoms at 120° angles to each other in ''equatorial'' positions, and two more chlorine atoms above and below the plane (''axial'' or ''apical'' positions). According to the VSEPR theory of molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane CH3)3Bis a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic Crystal System
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. The length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below organizes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic Crystal System
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendic .... Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Of Crystallization
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a chemical substance, substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the Crystal structure, crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt (chemistry), salt, which is not directly chemical bond, bonded to the metal cation. Upon crystallization from water, or water-containing solvents, many chemical compound, compounds incorporate water molecules in their crystalline frameworks. Water of crystallization can generally be removed by heating a sample but the crystalline properties are often lost. Compared to Inorganic compound, inorganic salts, proteins crystallize with large amounts of water i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close Packing
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement (or lattice). Carl Friedrich Gauss Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observatory and ... proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occupied by spheres – that can be achieved by a lattice packing is :\frac \approx 0.74048. The same packing density can also be achieved by alternate stackings of the same close-packed planes of spheres, including structures that are aperiodic in the stacking direction. The Kepler conjecture states that this is the highest density that can be achieved by any arrangement of spheres, either regular or irregular. This conjecture was proven by Thomas Callister Hales, Thomas Hales. The highest d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |