|
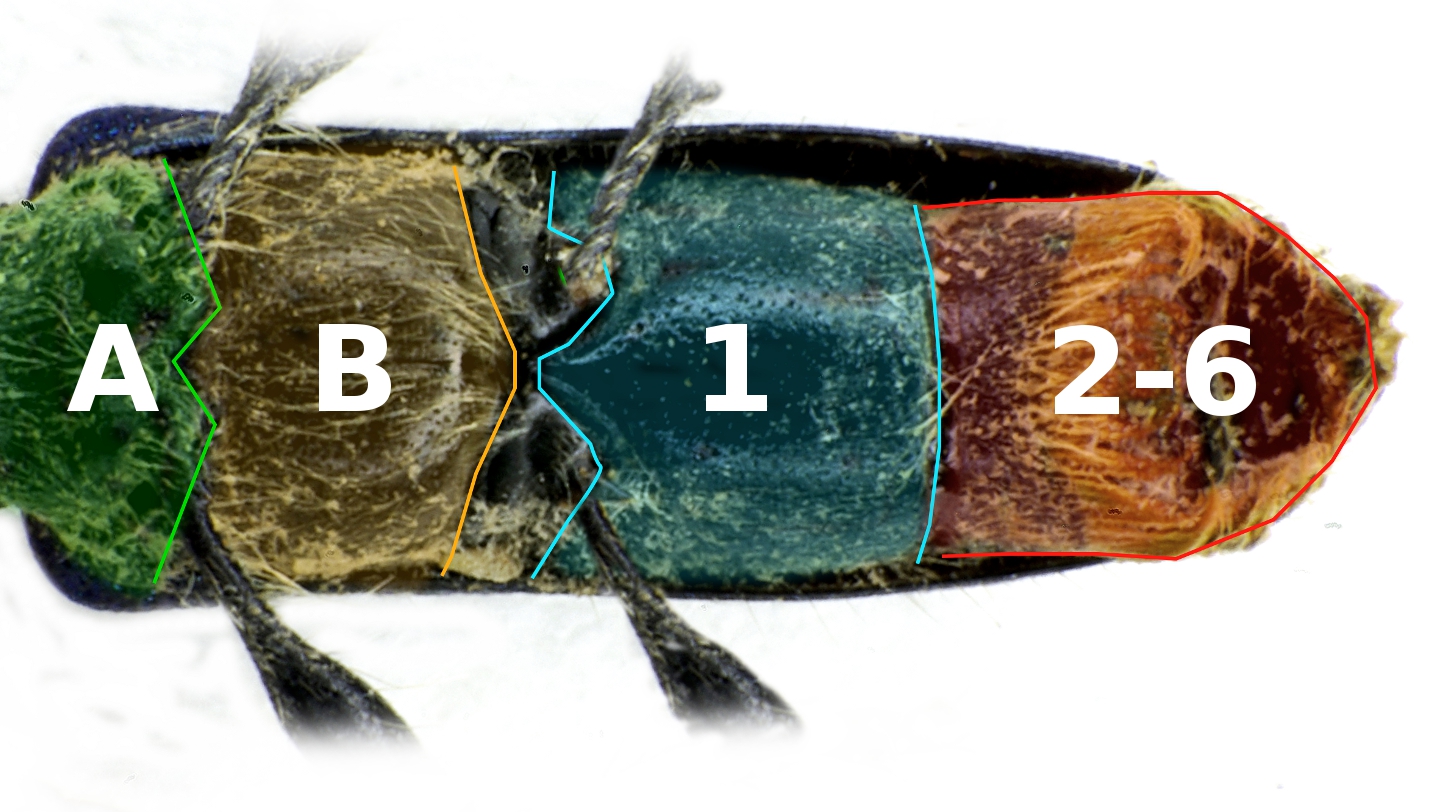
Caccothryptus Championi
''Caccothryptus championi'' is a species of Limnichidae, minute marsh-loving beetle in the subfamily Limnichinae. The species was described alongside five other ''Caccothryptus'' species by Natural History Museum entomologist Keita Matsumoto in 2021, using specimens gathered in 1953 by Harry George Champion in Haldwani, India alongside an earlier 1925 specimen collected nearby. Like the other ''Caccothryptus'' species described by Matsumoto, it was distinguished from its original classification of Caccothryptus ripicola, ''C. ripicola'' due to differences in the shape of its genitalia. Twenty-seven specimens from the British Natural History Museum collection were identified with ''C. championi,'' named after Champion. Taxonomy The Limnichidae (minute marsh-loving beetle) genus ''Caccothryptus'' was first described by David Sharp (entomologist), David Sharp in 1902. In 2014, the genus was divided into five species groups by Carles Hernando and Ignacio Ribera. A group of ''Caccoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnichidae
Limnichidae, commonly called minute marsh-loving beetles, is a family of beetles belonging to Byrrhoidea. There are at least 30 genera and 350 described species in Limnichidae. They are found worldwide, with the greatest diversity in tropical regions. Most species seem to be associated with water-adjacent habitats, such as riparian and coastal locations, though many species are likely fully terrestrial, with some species being associated with leaf litter and arboreal habitats. Species with known diets feed on moss or algae. The oldest fossils of the family are known from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber from Myanmar. Genera References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * Byrrhoidea Polyphaga families Limnichidae, {{Elateriformia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibia (arthropod Leg)
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, : ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (: ''femora''), ''tibia'' (: ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (: ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (: ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (: ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments articulates with the next segmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Journal Of Taxonomy
The ''European Journal of Taxonomy'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal for descriptive taxonomy of living and fossil eukaryotes, covering subjects in zoology, botany, and palaeontology. It is supported by the EJT Consortium, a group of European natural history institutes, which fully funds the publication. Therefore, the journal is free for both authors and readers (diamond open access). History The journal was initiated by a task force of people from the European Distributed Institute of Taxonomy network. The first article was published on 9 September 2011. In October 2015, the Consortium of European Taxonomic Facilities endorsed the journal. Several older journals have been merged into the ''European Journal of Taxonomy'': *''Journal of Afrotropical Zoology'' *''Bulletin de l'Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Entomologie'' *''Bulletin de l'Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Biologie'' *''Bulletin de l'Institut Royal des Sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typically its form is adapted to functions such as preparing a place for the egg, transmitting the egg, and then placing it properly. For most insects, the organ is used merely to attach the egg to some surface, but for many parasitic species (primarily in wasps and other Hymenoptera), it is a piercing organ as well. Some ovipositors only retract partly when not in use, and the basal part that sticks out is known as the scape, or more specifically oviscape, the word ''scape'' deriving from the Latin word , meaning "stalk" or "shaft". In insects Grasshoppers use their ovipositors to force a burrow into the earth to receive the eggs. Cicadas pierce the wood of twigs with their ovipositors to insert the eggs. Sawflies slit the tissues of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramere
Parameres ('side parts') are part of the external reproductive organs of male insects and the term was first used by Karl Wilhelm Verhoeff, Verhoeff in 1893 for the lateral genital lobes in Coleoptera. The primary phallic lobes which appear in the nymph or larval stages may become a pair of penes in the Ephemeroptera or a simple median penis in the Thysanura. In higher insect orders from Orthoptera to Hymenoptera, each of the primary lobes is divided into two secondary lobes or phallomeres, termed parameres and mesomeres (NB: this use of the term "mesomere" is not to be confused with the Somite, same term in Segmentation (biology), segmentation embryology.) In adult insects parameres may elongate and become genital claspers. These claspers may themselves occur in two segments, forming a Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, proximal basimere and a Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, distal telomere (insect morphology), telomere or harpago ('grappling hook' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Lobe
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of the center. Median income, for example, may be a better way to describe the center of the income distribution because increases in the largest incomes alone have no effect on the median. For this reason, the median is of central importance in robust statistics. Median is a 2-quantile; it is the value that partitions a set into two equal parts. Finite set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are listed in order from smallest to greatest. If the data set has an odd numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventrite
The sternum (: sterna) is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that ventrite numbers do not correspond to sternite numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustaceans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronotum
The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites (exoskeletal plates) are the pronotum (dorsal), the prosternum (ventral), and the propleuron (lateral) on each side. The prothorax never bears wings in extant insects (except in some cases of atavism), though some fossil groups possessed wing-like projections. All adult insects possess legs on the prothorax, though in a few groups (e.g., the butterfly family Nymphalidae) the forelegs are greatly reduced. In many groups of insects, the pronotum is reduced in size, but in a few it is hypertrophied, such as in all beetles (Coleoptera). In most treehoppers (family Membracidae, order Hemiptera), the pronotum is expanded into often fantastic shapes that enhance their camouflage or mimicry. Similarly, in the Tetrigidae, the pronotum is extended backward to cover the flight wings, supplanting the function of the tegmina. See also * Glossary of entom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsal Claws
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids. Links within the glossary are shown . Terms A * Abdomen or opisthosoma: One of the two main body parts ( tagmata), located towards the posterior end; see also Abdomen § Other animals * Accessory claw: Modified at the tip of the in web-building spiders; used with to grip strands of the web * Anal tubercle: A small protuberance (tubercule) above the through which the anus opens * Apodeme: see * Apophysis (plural apophyses): An outgrowth or process changing the general shape of a body part, particularly the appendages; often used in describing the male : see * Atrium (plural atria): An internal chamber at the entrance to the in female haplogyne spiders B * Bidentate: Having two * Book lungs: Respiratory organs on the ventral side (underside) of the , in front of the , opening through narrow slits; see also Book lungs * Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Tarsus
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, : ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (: ''femora''), ''tibia'' (: ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (: ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (: ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (: ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments articulates with the next segmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seta
In biology, setae (; seta ; ) are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms. Animal setae Protostomes Depending partly on their form and function, protostome setae may be called macrotrichia, chaetae, Scale (insect anatomy), scales, or Common name, informally, hairs. The setal membrane is not Cuticle, cuticularized, so movement is possible. Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. They allow earthworms and their relatives to attach to the surface and prevent backsliding during peristaltic motion. These hairs make it difficult to pull a worm straight from the ground. Setae in oligochaetes (the group including earthworms) are largely composed of chitin. They are classified according to the limb to which they are attached; for instance, notosetae are attached to notopodia; neurosetae to neuropodia. The setae on polychaete worms are referred to as chaeta due to their differing morphology. Crustaceans have mechano- and chemos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |