|
Cabras Island
Cabras Island was historically a low-lying finger of land off the coast of Piti, Guam that formed part of the northern protective arm of Apra Harbor. Shortly after the 1944 Battle of Guam it was connected by a causeway to the mainland and extended by the Glass Breakwater, and is now typically referred to simply as Cabras. Cabras houses both the Port of Guam and the primary Guam Power Authority generators supplying Guam. It lends its name to both a small vessel Cabras Marina, near the mainland, and the large vessel Cabras Channel, connecting the port to the deeper waters of the middle harbor. History A corruption of the CHamoru name for Cabras, ''apapa'', meaning "low", gives Apra Harbor its name. Before the twentieth century, Apra Harbor was protected by the Guam mainland to the east; Cabras Island, Luminao Reef, and Calalan Bank to the north; and Orote Peninsula to the south. After Spanish improvements to the harbor in the 1700s, Piti became the main port, with the only real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apra Harbor
Apra Harbor, also called Port Apra, is a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam. It is considered one of the best natural ports in the Pacific Ocean. The harbor is bounded by Cabras Island and the Glass Breakwater to the north and the Orote Peninsula in the south. Naval Base Guam and the Port of Guam are the two major users of the harbor. It is also a popular recreation area for boaters, surfers, scuba divers, and other recreationalists. Geography The geography of Apra Harbor has been extensively modified from its pre-historical state by humans. The entrance to the harbor is flanked by Point Udall (Guam), Point Udall, formerly Orote Point, to the south and Spanish Rocks at the tip of the Glass Breakwater. The Glass Breakwater, built on top of Calalan Bank and the fringing Luminao Reef, connects to Cabras Island, the location of the Port of Guam, which handles more than 90% of civilian cargo imported to Guam. Inland areas in the villages of Gua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Guam
Guam is a U.S. territory in the western Pacific Ocean, at the boundary of the Philippine Sea. It is the southernmost and largest member of the Mariana Islands archipelago, which is itself the northernmost group of islands in Micronesia. The closest political entity is the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), another U.S. territory. Guam shares maritime boundaries with CNMI to the north and the Federated States of Micronesia to the south. It is located approximately one quarter of the way from the Philippines to Hawaii. Its location and size make it strategically important. It is the only island with both a protected harbor and land for multiple airports between Asia and Hawaii, on an east–west axis, and between Papua New Guinea and Japan, on a north–south axis. The island is a result of the volcanic activity created by subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Philippine Sea Plate at the nearby Mariana Trench, which runs from the east of Guam to the southwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Karen
Typhoon Karen was the most powerful tropical cyclone to strike the island of Guam, and has been regarded as one of the most destructive events in the island's history. It was first identified as a tropical disturbance on November 6, 1962, well to the southeast of Truk. Over the following two days, the system tracked generally northward and quickly intensified. Karen became a tropical storm late on November 7, and within two days it explosively intensified into a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson scale. Turning westward, the typhoon maintained its intensity and struck Guam with winds of on November 11. Once clear of the island, it strengthened slightly and reached its peak intensity on November 13 with winds of and a barometric pressure of 894 mb (hPa; 26.40 inHg). The storm then gradually turned northward as it weakened, brushing the Ryukyu Islands on November 15, before moving east-northeastward over the ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guam Rehabilitation Act
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States, as measured from the geographic center of the U.S. In Oceania, Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia. As of 2022, its population was 168,801. Chamorros are its largest ethnic group, but a minority on the multiethnic island. The territory spans and has a population density of . Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamorro, who are related to the Austronesian peoples of the Malay Archipelago, the Philippines, Taiwan, and Polynesia. But unlike most of its neighbors, the Chamorro language is not classified as a Micronesian or Polynesian language. Rather, like Palauan, it possibly constitutes an independent branch of the Malayo-Polynesian la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Base Guam
Naval Base Guam is a strategic U.S. naval base located on Apra Harbor and occupying the Orote Peninsula. In 2009, it was combined with Andersen Air Force Base to form Joint Region Marianas, which is a Navy-controlled joint base. The Ship Repair Facility, Guam, was located next to Naval Base Guam, along Apra Harbor. It was closed in 1997, due to the recommendation of the 1995 Base Realignment and Closure Commission. Naval Base Guam is home to Commander Submarine Squadron 15, Coast Guard Sector Guam, and Naval Special Warfare Unit One, and supports 28 other tenant commands. It is the home base to dozens of Pacific Command, Pacific Fleet, Seventh Fleet, and Seabee units. is stationed in Guam to tend the submarines of the Seventh Fleet, and changed from Naval Support Facility Diego Garcia to Naval Base Guam to fulfill the same role. Coast Guard Sector Guam ships include and including , '' USCGC Oliver Henry'', '' USCGC Frederick Hatch'', and . History On July 21, 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander Naval Forces Marianas
The Commander Naval Forces Marianas, also known as COMNAVMARIANAS, is the Navy force shore commander responsible for United States Navy activities in Guam, Saipan, Tinian and the surrounding islands, and is an Rear Admiral. COMNAVMARIANAS is currently a shared position of Commander, Joint Region Marianas. From 1944 to 1949, an era of military government, the officers who served as COMNAVMARIANAS were respectively charged with such civil responsibilities as governor of the Marshalls-Gilberts; deputy military governor, Pacific Ocean Areas; and deputy military governor, Bonin-Volcano Islands. From 1944 until March 29, 1952, Naval Station served as a Naval Operations Base, providing a huge portion of every type of fleet service.Commander Joint Region MarianasHistory accessed August 2010 In September 1956, the Naval Base was disestablished and the Naval Station was reassigned to the military command of Commander, U.S. Naval Forces Marianas. The Navy and Air Force held a groundbreakin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Guam
The Capture of Guam was a bloodless engagement between the United States and Spain during the Spanish–American War. The U.S. Navy sent a single cruiser, , to capture the island of Guam, which was under Spanish control. The Spanish garrison on the island had no knowledge of the war and no real ability to resist the American forces. They surrendered without resistance, and the island passed into American control. The event was the only conflict of the Spanish–American War on Guam. Background Guam had been under Spanish control since 1668.Brief History of Guam /ref> By the time of the war, Guam had been neglected and there was only a small Spanish military presence. The last message the authorities on Guam had received from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Glass (admiral)
Henry Glass (January 7, 1844 – September 1, 1908) was a rear admiral in the United States Navy, best remembered for his role in the bloodless capture of Guam in the Spanish–American War. He was also a Union veteran of the American Civil War. Biography Glass was born in Hopkinsville, Kentucky, and entered the Naval Academy in 1860, graduating a year ahead of schedule with the rank of ensign on May 28, 1863. Civil War He saw considerable action during the Civil War while attached to the steam sloop . He took part in engagements with Confederate batteries at Charleston, South Carolina, between July and September 1863; in the Stono River in December 1863 and July 1864; and in the North Edisto River in February 1865. He also participated in the capture of Georgetown, South Carolina, in February 1865. 1865–1880 After the war, Glass was advanced to the rank of master on November 10, 1865; to lieutenant on November 10, 1866; and to lieutenant commander on March 12, 1868. Sea duty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
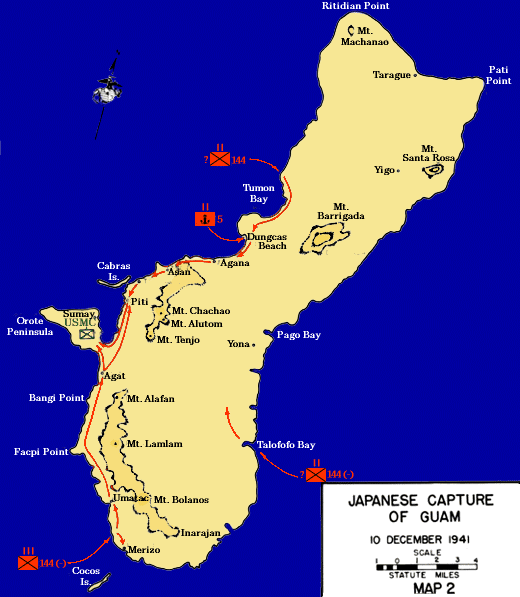
Battle Of Guam (1941)
The Battle of Guam was an engagement during the Pacific War in World War II that took place from 8 to 10 December 1941 on Guam in the Mariana Islands between Japan and the United States. The American garrison was defeated by Japanese forces on 10 December, which resulted in an occupation until the Second Battle of Guam in 1944. Background Guam is the southernmost part of the Mariana Islands in the Pacific Ocean. It is the largest of the islands, with an area of 225 square miles. Guam's interior is rugged, with heavy tropical forests in the north of the island and wooded hills in the south. Much of the island's coastline is edged with coral reefs and cliffs, though beaches suitable for landing troops exist in the center of the west coast. Guam has a tropical climate, though December forms part of the dry season. The United States captured Guam from the Kingdom of Spain on 21 June 1898 during the Spanish–American War. The next year Spain sold the other islands in the Maria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derrick
A derrick is a lifting device composed at minimum of one guyed mast, as in a gin pole, which may be articulated over a load by adjusting its Guy-wire, guys. Most derricks have at least two components, either a guyed mast or self-supporting tower, and a boom hinged at its base to provide articulation, as in a stiffleg derrick. The most basic type of derrick is controlled by three or four lines connected to the top of the mast, which allow it to both move laterally and cant up and down. To lift a load, a separate line runs up and over the mast with a hook on its free end, as with a Crane (machine), crane. Derricks are especially useful for high-rise rigging, jobs that cover a long period of time, or jobs when the impact to street or pedestrian traffic is a concern. Forms of derricks are commonly found aboard ships and at Dock (maritime), docking facilities. Large derricks mounted on dedicated Crane vessel, vessels are known as floating derricks and Sheerleg, shearlegs. The term de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakwater (structure)
A breakwater is a permanent structure constructed at a coastal area to protect against tides, currents, waves, and storm surges. Breakwaters have been built since antiquity to protect anchorage (maritime), anchorages, helping isolate vessels from marine hazards such as wind-driven waves. A breakwater, also known in some contexts as a jetty or a Mole_(architecture), mole, may be connected to land or freestanding, and may contain a walkway or road for vehicle access. Part of a coastal management system, breakwaters are installed parallel to the shore to minimize erosion. On beaches where longshore drift threatens the erosion of beach material, smaller structures on the beach may be installed, usually perpendicular to the water's edge. Their action on waves and current is intended to slow the longshore drift and discourage mobilisation of beach material. In this usage they are more usually referred to as groynes. Purposes Breakwaters reduce the intensity of wave action in ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |