|
Cabo De Rama Fort
Praça do Cabo de Rama, also known as Cabo de Rama Fort, is a medieval hillfort located in Khola village, on the coast of Canacona, Goa in India. History In the 1760s, the Portuguese gained control of Cabo de Rama after the Raja of Soonda surrendered his territory to them in return for protection against Hyder Ali of Mysore. Prior to that, the fort had regularly switched hands between Hindu and Muslim monarchs. The present structure with its walls, moats, ramparts turrets, chapel and cannons are remnants of the Portuguese era. The Portuguese equipped it with 21 guns and installed military barracks, a commander's quarter and a chapel. In 1799, the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War saw the defeat of the King of Mysore, thus bringing an end to the Portuguese's primary rival in the region. Over time, the purpose of the fort shifted from being a defensive structure, to a prison. This fort housed a government prison till 1955. Inside Cabo de Rama is the Capela de Santo António, a chapel whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canacona Taluka
Canacona is an administrative region in the district of South Goa district, South Goa, Goa state, India. Canacona is one of the six subdivisions (''Tehsil, talukas'') that constitute the South Goa district. It is bounded on the north by the taluka of Quepem taluk, Quepem, on the northeast by Sanguem, on the south by the state of Karnataka, and on the west by the Arabian Sea. The town of Chaudi is the administrative headquarters of the taluka of Canacona. The name Canacona is a corruption of the name Konkan. The area was one of the districts of the former Kingdom of Soonda, itself a remnant of the former Vijayanagara Empire. When Soonda was invaded and partially occupied by Hyder Ali of Mysore, the heirless Raja ceded the remaining parts to Portugal; and these were incorporated into Goa as the districts of Quepem, Sanguem, and Canacona. In the recent elections, Kishen Naikgaunkar got elected as the President of the Canacona, and Samba Naik Desai got elected as an Attorney. Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
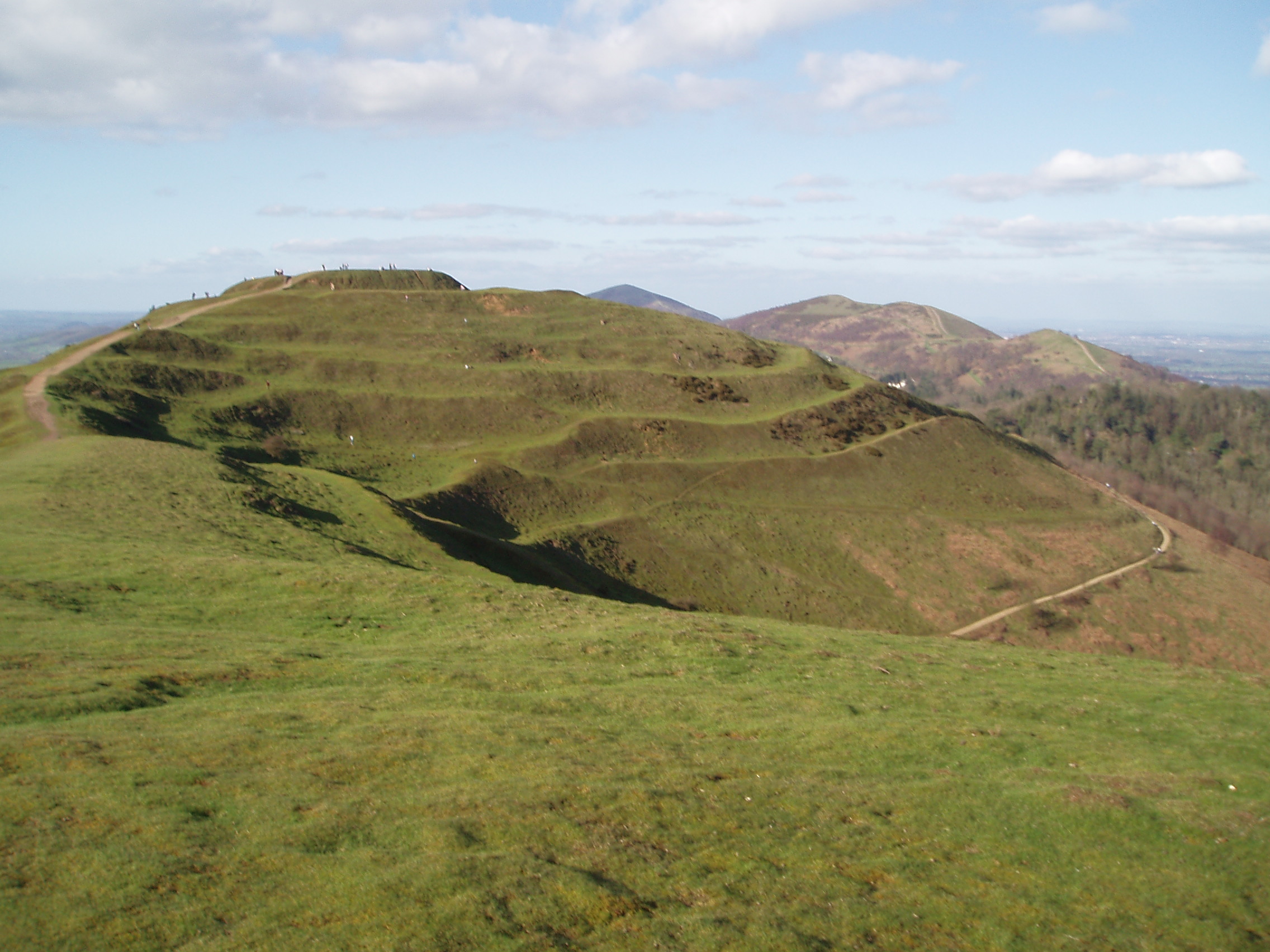
Hillfort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman Empire, Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of Earthworks (Archaeology), earthworks or stone Rampart (fortification), ramparts, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. If enemies were approaching, the inhabitants would spot them from a distance. Prehistoric Europe saw a growing population. It has been estimated that in about 5000 BC during the Neolithic between 2 million and 5 million lived in Europe; in the Late Iron Age it had an estimated population of around 15 to 30 million. Outside Greece and Italy, which were more densely populated, the vast majority of settlements in the Iron Age were small, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khola, Goa
Khola is a village located in Canacona, Goa, India. "Cola" is the variation of the same name. Location Located in the northernmost part of Canacona taluk, South Goa, the historic fort of Cabo de Rama Fort is located in this village. Notability Cultivated uniquely on Khola village's hilly slopes, the Khola chilli stands out with its striking red hue and elongated shape, boasting moderate pungency and an enticing aroma that defines its distinctive flavor. Khola Chilli was awarded the Geographical Indication (GI) status tag from the Geographical Indications Registry under the Union Government of India The Government of India (ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of 36 states and union territo ... on 28 August 2019 (valid until 5 August 2028). Tourist Attractions Khola (Cola) beach is located at this village. References Vil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali (''Haidar'alī''; ; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers. Rising to the post of Dalavayi ( commander-in-chief) to Krishnaraja Wodeyar II, he came to dominate the titular monarch and the Mysore government. He became the ''de facto'' ruler, King of Mysore as Sarvadhikari (Chief Minister) by 1761. During intermittent conflicts against the East India Company during the First and Second Anglo–Mysore Wars, Hyder Ali was the military leader. Though illiterate, Hyder Ali concluded an alliance with the French, and used the services of French workmen in raising his artillery and arsenal. His rule of Mysore was characterised by frequent warfare with his neighbours and rebellion within his territories. This was not unusual for the time as much of the Indian subcontinent was then in turmoil. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a geopolitical realm in southern India founded in around 1399 in the vicinity of the modern-day city of Mysore and prevailed until 1950. The territorial boundaries and the form of government transmuted substantially throughout the kingdom's lifetime. While originally a feudal vassal under the Vijayanagara Empire, it became a princely state in British Raj from 1799 to 1947, marked in-between by major political changes. The kingdom, which was founded and ruled for the most part by the Wadiyars, initially served as a feudal vassal under the Vijayanagara Empire. With the gradual decline of the Empire, the 16th-century Timmaraja Wodeyar II declared independence from it. The 17th century saw a steady expansion of its territory and, during the rules of Narasaraja Wodeyar I and Devaraja Wodeyar II, the kingdom annexed large expanses of what is now southern Karnataka and parts of Tamil Nadu, becoming a formidable power in the Deccan. During a brief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Conquests In The Indian Subcontinent
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place between the 13th and the 18th centuries, establishing the Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Indo-Muslim period. Early Muslim conquests, Earlier Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent include the invasions which started in the Northwest India (pre-1947), northwestern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Pakistan), especially the Umayyad campaigns in India, Umayyad campaigns during the 8th century. Mahmud of Ghazni, sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, preserved an ideological link to the suzerainty of the Abbasid caliph, Abbasid Caliphate and invaded vast parts of Punjab and Gujarat during the 11th century. After the capture of Siege of Lahore (1186), Lahore and the end of the Ghaznavids, the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor laid the foundation of Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim rule in India in 1192. In 1202, Bakhtiyar Khalji led the Muslim conquest of Bengal, marking the easternmost expansion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water defences, including natural or artificial lakes, dams and sluices. In older fortifications, such as hillforts, they are usually referred to simply as ditches, although the function is similar. In later periods, moats or water defences may be largely ornamental. They could also act as a sewer. Historical use Ancient Some of the earliest evidence of moats has been uncovered around ancient Egyptian fortresses. One example is at Buhen, a settlement excavated in Nubia. Other evidence of ancient moats is found in the ruins of Babylon, and in reliefs from ancient Egypt, Assyria, and other cultures in the region. Evidence of early moats around settlements has been discovered in many archaeological sites throughout Southeast Asia, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rampart (fortification)
In fortification architecture, a rampart is a length of Embankment (earthworks), embankment or wall forming part of the defensive boundary of a castle, hillfort, Human settlement, settlement or other fortified site. It is usually broad-topped and made of excavated earth and/or masonry.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 241. Darvill, Timothy (2008). ''Oxford Concise Dictionary of Archaeology'', 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York, p. 376. . Types The composition and design of ramparts varied from the simple mounds of earth and stone, known as dump ramparts, to more complex earth and timber defences (box ramparts and timberlaced ramparts), as well as ramparts with stone revetments. One particular type, common in Central Europe, used earth, stone and timber posts to form a ''Pfostenschlitzmauer'' or "post-slot wall". Vitrified ramparts were composed of stone that was subsequently fired, possibly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turret (architecture)
In architecture, a turret is a small circular tower, usually notably smaller than the main structure, that projects outwards from a wall or corner of that structure. Turret also refers to the small towers built atop larger tower structures. Etymology The word ''turret'' originated in around the year 1300 from ''touret'' which meant "small tower rising from a city wall, castle, or other larger building." ''Touret'' came from the Old French term ''torete'' which is the diminutive form of ''tour'', meaning “tower.” ''Tour'' dates back to the Latin word ''turris'' which also means “tower.” There is a record from 1862 of ''turret'' being used to mean "low, flat gun tower on a warship." Around this time, the word split into two separate definitions, with this definition being the one that goes on to describe gun turrets, a separate idea from the architectural element. Uses Turrets initially arose on castles out of a defensive need for greater visibility. Since they proje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Anglo-Mysore War
The Fourth Anglo-Mysore War was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore against the British East India Company and the Hyderabad Deccan in 1798–99. This was the last of the four Anglo-Mysore Wars. The British captured the capital of Mysore. The ruler Tipu Sultan was killed in the battle. Britain took indirect control of Mysore, restoring the Wadiyar dynasty to the Mysore throne (with a British commissioner to advise him on all issues). Tipu Sultan's young heir, Fateh Ali, was sent into exile. The Kingdom of Mysore became a princely state in a subsidiary alliance with British India covering parts of present Kerala–Karnataka and ceded Coimbatore, Dakshina Kannada and Uttara Kannada to the British. Background Napoleon Bonaparte's landing in Ottoman Egypt in 1798 was intended to further the capture of the British possessions in India, and the Kingdom of Mysore was a key to that next step, as the ruler of Mysore, Tipu Sultan, sought France as an ally and his lett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (, , ''Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu''; 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799) commonly referred to as Sher-e-Mysore or "Tiger of Mysore", was a ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery. He expanded the iron-cased Mysorean rockets and commissioned the military manual ''Fathul Mujahidin''. The economy of Mysore reached a zenith during his reign. He deployed rockets against advances of British forces and their allies during the Anglo-Mysore Wars, including the Battle of Pollilur (1780), Battle of Pollilur and Siege of Srirangapatna (1799), Siege of Srirangapatna. Tipu Sultan and his father Hyder Ali used their French-trained army in alliance with the French in their struggle with the British, and in Mysore's struggles with other surrounding powers: against the Maratha Empire, Marathas, Sira, India, Sira, and rulers of Malabar (Northern Kerala), Malabar, Kodagu district, Kodagu, Keladi Nayaka Kingdom, Bednore, Carnatic regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colva
Colva () is a coastal village situated in the Salcete ''taluka'', in South Goa district, of Goa state on the west coast of the Indian subcontinent. Colva Beach () spans about along a sandy coastline of approximately extending from Bogmalo in the north to Cabo de Rama in the south. The village had significant importance to the Portuguese, local (Gancars) noble chardó (Kshatriya) Feudal Lords and was the retreat for Goa's high, elite and aristocratic society, who would come to Colvá for their (change of air), to enjoy the private beach of the then Roiz family. Today the Portuguese area is dotted with the past elite houses and modern villas, including many ruins from more than 300 years. On weekends, huge crowds of tourists, visitors from around the world as well as local Indians, enjoy the sunset and various activities. The beach is particularly busy in October, when hordes of religious pilgrims come and visit Colvá Church, called (Church of Our Lady of Mercy), tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |