|
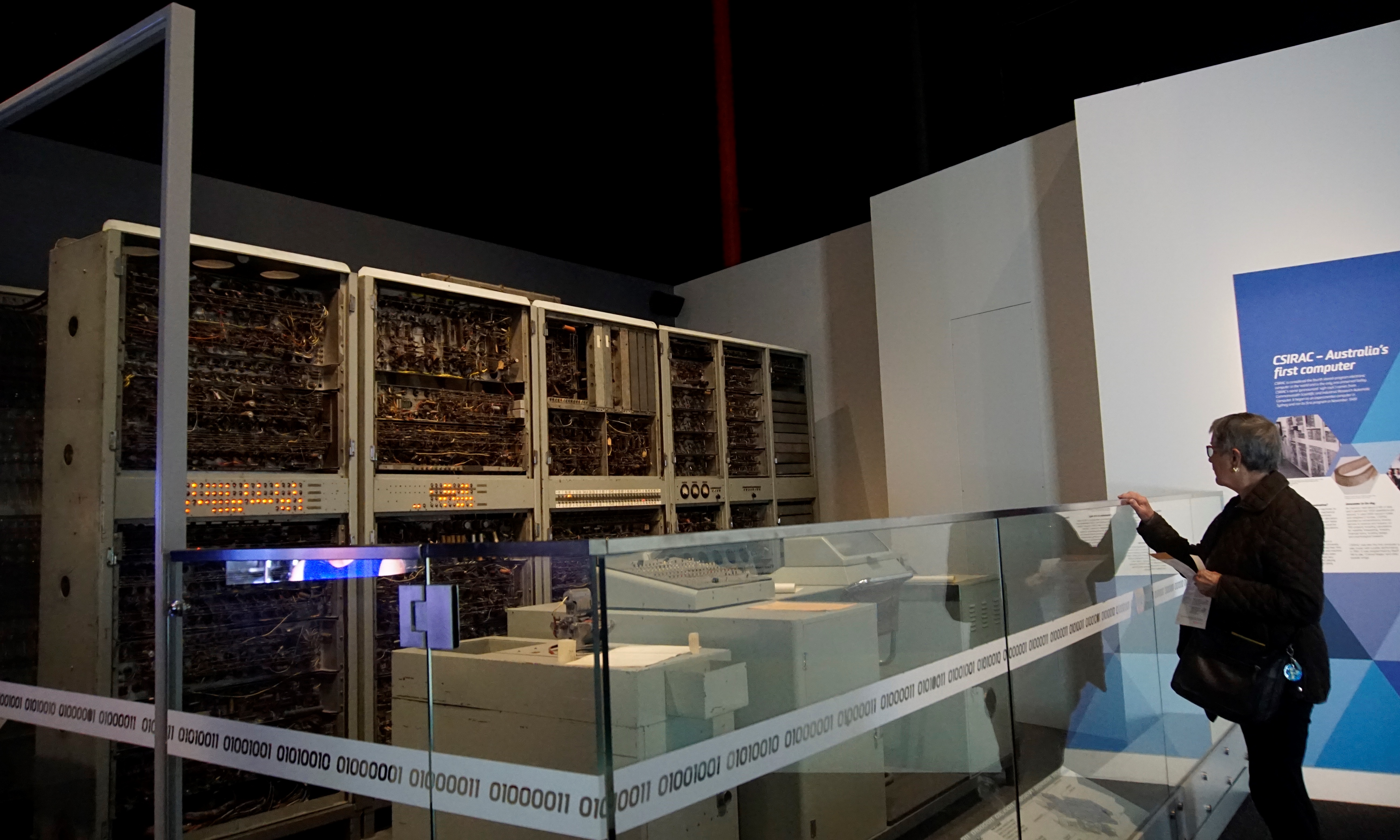
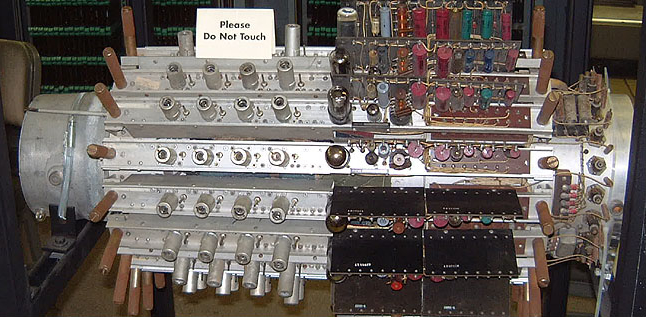
CSIR Mk 1
CSIRAC (; ''Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer''), originally known as CSIR Mk 1, was Australia's first digital computer, and the fifth stored program computer in the world. It is the oldest surviving first-generation electronic computer (the Zuse Z4 at the Deutsches Museum is older, but was electro-mechanical, not electronic), and was the first in the world to play digital music. After being exhibited at Melbourne Museum for many years, it was relocated to Scienceworks in 2018 and is now on permanent display in the Think Ahead gallery. A comprehensive source of information about the CSIRA collection, its contributors and related topics is available from Museums Victoria on their Collections website. History The CSIRAC was constructed by a team led by Trevor Pearcey and Maston Beard, working in large part independently of similar efforts across Europe and the United States, and ran its first test program (multiplication of numbers) so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melbourne Museum
The Melbourne Museum is a natural and cultural history museum located in the Carlton Gardens in Melbourne, Australia. Located adjacent to the Royal Exhibition Building, the museum was opened in 2000 as a project of the Government of Victoria, on behalf of Museums Victoria which administers the venue. The museum won Best Tourist Attraction at the Australian Tourism Awards in 2011. In addition to its galleries, the museum features spaces such as ''Curious?'', which is a place to meet staff and find answers relating to the collections, research, and behind-the-scenes work of Museums Victoria; as well as a cafe and a gift shop. The back-of-house area houses some of the Victoria's State Collections, which holds over 17 million items, including objects relating to Indigenous Australian and Pacific Islander cultures, geology, historical studies, palaeontology, technology and society, and zoology, as well as a library collection that holds 18th and 19th century scientific monographs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor Pearcey
Trevor Pearcey (5 March 1919 – 27 January 1998) was a British-born Australian scientist, who created CSIRAC, one of the first stored-program electronic computers in the world. Born in Woolwich, London, he graduated from Imperial College in 1940 with first class honours in physics and mathematics. He emigrated to Australia in 1945. In a 1948 paper, published in the ''Australian Journal of Science'', he envisaged using a digital electronic computer for providing information over a national telecommunications network: He bet that he could make an electronic device that would be 1000 times faster than the best electronic device of the time. One of his calculators filled a small room, weighing 7 tons. He was awarded a D.Sc. by the University of Melbourne in 1971. In his later years he lived on the Mornington Peninsula near Melbourne. The Pearcey Foundation and the Pearcey Award for outstanding achievement by an Australian in the ICT ICT may refer to: Sciences and tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KT66
KT66 is the designator for a beam power tube introduced by Marconi-Osram Valve Co. Ltd. (M-OV) of Britain in 1937 and marketed for application as a power amplifier for audio frequencies and driver for radio frequencies.Editors "The New Valves" ''Wireless World'', August 20th 1937, p. 178General Electric Co., Ltd."Osram Valves" ''Television and Short-Wave World'', Sept. 1939, p. 524 The KT66 is a beam tetrode that utilizes partially collimated electron beams to form a low potential space charge region between the anode and screen grid to return anode secondary emission electrons to the anode and offers significant performance improvements over comparable power pentodes.Dreyer, J. F. Jr."The Beam Power Output Tube" ''Electronics'', Vol. 9, No. 4, April 1936, pp. 18 - 21, 35 In the 21st century, the KT66 is manufactured and used in some high fidelity audio amplifiers and musical instrument amplifiers. Overview Although the RCA 6L6 of 1936 (the result of a license agreement between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6SN7
6SN7 is a dual triode vacuum tube with an eight-pin octal base. It provides a medium gain (20 dB). The 6SN7 is basically two 6J5 triodes in one envelope. History Originally released in 1939 it was officially registered in 1941 by RCA and Sylvania as the glass-cased 6SN7GT, originally listed on page 235 of RCA's 1940 RC-14 Receiving Tube Manual, in the Recently Added section, as: 6SN7-GT. Although the 6S-series tubes are often metal-cased, there was never a ''metal-envelope'' 6SN7 (there being no pin available to connect the metal shield); there were, however, a few glass-envelope tubes with a metal band, such as the 6SN7A developed during World War II - slightly improved in some respects but the metal band was prone to splitting. Numerous variations on the 6SN7 type have been offered over the years, including: * 7N7 (Sylvania 1940, short-lived loktal-base version), * 1633 (RCA 1941, also for 26-V radios), * 12SX7 (RCA 1946, intended for use in 12-volt aircraft electronics), * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Communication
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels. Serial communication is used for all long-haul communication and most computer networks, where the cost of cable and synchronization difficulties make parallel communication impractical. Serial computer buses are becoming more common even at shorter distances, as improved signal integrity and transmission speeds in newer serial technologies have begun to outweigh the parallel bus's advantage of simplicity (no need for serializer and deserializer, or SerDes) and to outstrip its disadvantages ( clock skew, interconnect density). The migration from PCI to PCI Express is an example. Cables Many serial communication systems were originally designed to transfer data over relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Bus
In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin ''omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components (wire, optical fiber, etc.) and software, including communication protocols. Early computer buses were parallel electrical wires with multiple hardware connections, but the term is now used for any physical arrangement that provides the same logical function as a parallel electrical busbar. Modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop (electrical parallel) or daisy chain topology, or connected by switched hubs, as in the case of Universal Serial Bus (USB). Background and nomenclature Computer systems generally consist of three main parts: * The central processing unit (CPU) that processes data, * The memory that holds the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Unit
The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor. A CU typically uses a binary decoder to convert coded instructions into timing and control signals that direct the operation of the other units (memory, arithmetic logic unit and input and output devices, etc.). Most computer resources are managed by the CU. It directs the flow of data between the CPU and the other devices. John von Neumann included the control unit as part of the von Neumann architecture. In modern computer designs, the control unit is typically an internal part of the CPU with its overall role and operation unchanged since its introduction. Multicycle control units The simplest computers use a multicycle microarchitecture. These were the earliest designs. They are still popular in the very smallest computers, such as the embedded systems that operate machinery. In a multicycle computer, the control unit often steps through the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
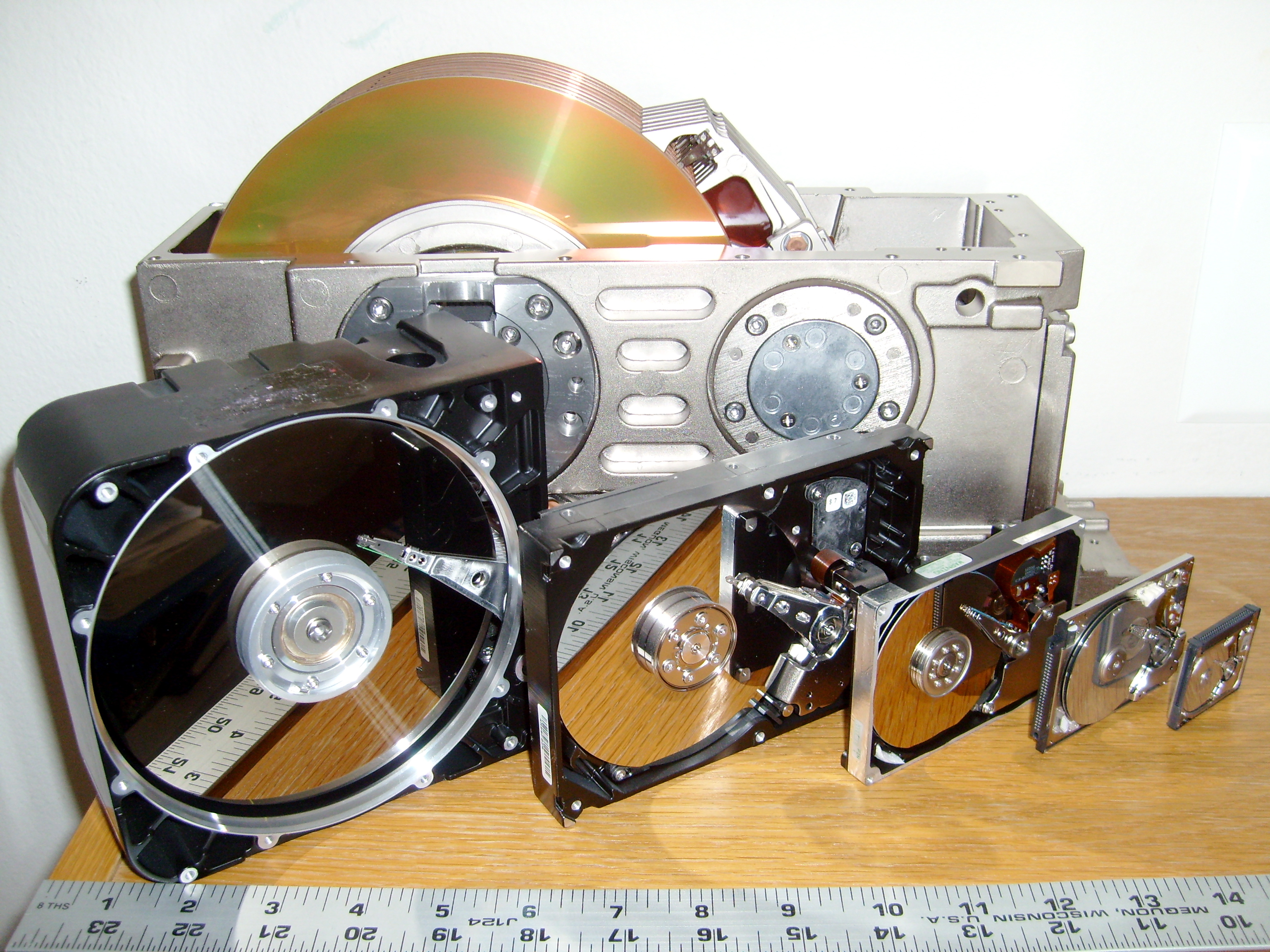
Disk Storage
Disk storage (also sometimes called drive storage) is a general category of storage mechanisms where data is recorded by various electronic, magnetic, optical, or mechanical changes to a surface layer of one or more rotating disks. A disk drive is a device implementing such a storage mechanism. Notable types are the hard disk drive (HDD) containing a non-removable disk, the floppy disk drive (FDD) and its removable floppy disk, and various optical disc drives (ODD) and associated optical disc media. (The spelling ''disk'' and ''disc'' are used interchangeably except where trademarks preclude one usage, e.g. the Compact Disc logo. The choice of a particular form is frequently historical, as in IBM's usage of the ''disk'' form beginning in 1956 with the " IBM 350 disk storage unit".) Background Audio information was originally recorded by analog methods (see Sound recording and reproduction). Similarly the first video disc used an analog recording method. In the music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delay-line Memory
Delay-line memory is a form of computer memory, now obsolete, that was used on some of the earliest digital computers. Like many modern forms of electronic computer memory, delay-line memory was a refreshable memory, but as opposed to modern random-access memory, delay-line memory was sequential-access. Analog delay line technology had been used since the 1920s to delay the propagation of analog signals. When a delay line is used as a memory device, an amplifier and a pulse shaper are connected between the output of the delay line and the input. These devices recirculate the signals from the output back into the input, creating a loop that maintains the signal as long as power is applied. The shaper ensures the pulses remain well-formed, removing any degradation due to losses in the medium. The memory capacity is determined by dividing the time taken to transmit one bit into the time it takes for data to circulate through the delay line. Early delay-line memory systems had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum ( ) from the Greek words, ''hydor'' (water) and ''argyros'' (silver). A heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar ( mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Mercury is used in thermometers, barometers, manometers, sphygmomanometers, float valves, mercury switches, mercury relays, fluorescent lamps and other devices, though concerns about the element's toxicity have led to mercury thermometers and sphygmomanometers being largely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |