|
CLE Peptide
CLE peptides (CLAVATA3/Embryo Surrounding Region-Related) are a group of peptides found in plants that are involved with cell signaling. Production is controlled by the CLE genes. Upon binding to a CLE peptide receptor in another cell, a chain reaction of events occurs, which can lead to various physiological and developmental processes. This signaling pathway is conserved in diverse land plants. Background Plants and animals alike both use small polypeptides for signaling in cell-to-cell communication. CLAVATA3/Embryo Surrounding Region-Related, also known as a plant peptide hormone, signaling is important for cell to cell signaling but also long distance communication. These two actions are especially important for plant cells because they are stationary and must perform cell expansion. In multicellular organisms cell-to-cell communication has been found to be very crucial for many growth processes that occur inside the organism. The 12 or 13 amino acid polypeptides are the matu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
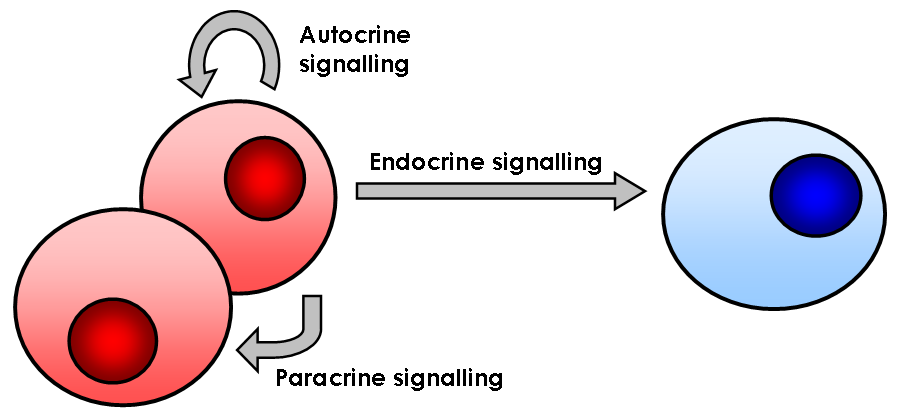
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biology), cellular life in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Typically, the signaling process involves three components: the signal, the receptor, and the effector. In biology, signals are mostly chemical in nature, but can also be physical cues such as pressure, Membrane potential, voltage, temperature, or light. Chemical signals are molecules with the ability to bind and activate a specific Receptor (biochemistry), receptor. These molecules, also referred to as Ligand (biochemistry), ligands, are chemically diverse, including ions (e.g. Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.), lipids (e.g. steroid, prostaglandin), peptides (e.g. insulin, ACTH), carbohydrates, glycosylated proteins (proteoglycans), nucleic acids, etc. Peptide and lipid ligands are particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato Cyst Nematode
Potato root nematodes or potato cyst nematodes (PCN) are 1-mm long roundworms belonging to the genus ''Globodera'', which comprises around 12 species. They live on the roots of plants of the family Solanaceae, such as potatoes and tomatoes. PCN cause growth retardation and, at very high population densities, damage to the roots and early senescence of plants. The nematode is not indigenous to Europe but originates from the Andes. Fields are free from PCN until an introduction occurs, after which the typical patches, or hotspots, occur on the farmland. These patches can become full field infestations when unchecked. Yield reductions can average up to 60% at high population densities. Biology and life cycle The eggs hatch in the presence of Solanoeclepine A, a substance secreted by the roots of host plants otherwise known as root exudates. The nematodes hatch when they grow into a second-stage juvenile (J2). At this stage, the J2 nematodes find host cells to feed off of. The potat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean Cyst Nematode
The soybean cyst nematode (SCN), ''Heterodera glycines'', is the most devastating pest to soybean crop yields in the U.S., targeting the roots of soybean and other legume plants. When infection is severe SCNs cause stunting, yellowing, impaired canopy development, and yield loss. The symptoms caused by SCNs can go easily unrecognized by farmers—in some cases there are no warning symptoms before a loss of 40% of the yield.“You can literally have 40% yield loss with no symptoms,” says Greg Tylka, Iowa State University (ISU) Extension nematologist. Due to the slight stunting and yellowing, many farmers may mistake these symptoms as environmental problems when in fact they are SCNs. Another symptom of SCNs that may affect farmers' yields is stunted roots with fewer nitrogen-fixing nodules. Due to the fact that soybean cyst nematodes can only move a few centimeters in the soil by themselves, they mostly are spread via tillage or plant transplants. This area of infection will look ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise Marchantiophyta, liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaf, leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a plant stem, stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing sporangium, spores. They are typically tall, though some species ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicot
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, that the seed has two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. There are around 200,000 species within this group. The other group of flowering plants were called monocotyledons (or monocots), typically each having one cotyledon. Historically, these two groups formed the two divisions of the flowering plants. Largely from the 1990s onwards, molecular phylogenetic research confirmed what had already been suspected: that dicotyledons are not a group made up of all the descendants of a common ancestor (i.e., they are not a monophyletic group). Rather, a number of lineages, such as the magnoliids and groups now collectively known as the basal angiosperms, diverged earlier than the monocots did; in other words, monocots evolved from within the dico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants whose seeds contain only one Embryo#Plant embryos, embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. A monocot taxon has been in use for several decades, but with various ranks and under several different names. The APG IV system recognises its monophyly but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank, and instead uses the term "monocots" to refer to the group. Monocotyledons are contrasted with the Dicotyledon, dicotyledons, which have two cotyledons. Unlike the monocots however, the dicots are not Monophyly, monophyletic and the two cotyledons are instead the ancestral characteristic of all flowering plants. Botanists now classify dicots into the eudicots ("true dicots") and several Basal (phylogenetics), basal lineages from which the monocots emerged. The monocots are extremely important economically, culturally, and ecologically, and make up a majority of plant biomass used in agriculture. Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meristematic Cells
In cell biology, the meristem is a structure composed of specialized biological tissue, tissue found in plants, consisting of Stem cell, stem cells, known as meristematic cells, which are undifferentiated cells capable of continuous cell division, cellular division. These meristematic cells play a fundamental role in plant growth, Regeneration (biology), regeneration, and acclimatization, as they serve as the source of all Cellular differentiation, differentiated plant tissues and Plant organ, organs. They contribute to the formation of structures such as fruits, leaves, and seeds, as well as supportive tissues like stems and roots. Meristematic cells are totipotent, meaning they have the ability to differentiate into any plant cell type. As they divide, they generate new cells, some of which remain meristematic cells while others differentiate into specialized cells that typically lose the ability to divide or produce new cell types. Due to their active division and undifferent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Meristems In Crassula Ovata
Apical means "pertaining to an apex". It may refer to: *Apical ancestor, refers to the last common ancestor of an entire group, such as a species (biology) or a clan (anthropology) *Apical (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features located opposite the base of an organism or structure *Apical (chemistry), a position in certain molecular geometries in chemistry *Apical (dentistry), direction towards the root tip of a tooth *Apical consonant, a consonant produced with the tip of the tongue *Apical dendrite, a type of dendrite found on pyramidal neurons *Apical dominance, the phenomenon whereby the main, central stem of a plant is dominant over other side stems *Apical membrane, in cell biology the surface of a plasma membrane that faces inward to the lumen *Apical meristem, or apex, on a flower See also *Apex (other) The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to: Arts and media Fictional entities * Apex (comics), a teenaged super villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biology), cellular life in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Typically, the signaling process involves three components: the signal, the receptor, and the effector. In biology, signals are mostly chemical in nature, but can also be physical cues such as pressure, Membrane potential, voltage, temperature, or light. Chemical signals are molecules with the ability to bind and activate a specific Receptor (biochemistry), receptor. These molecules, also referred to as Ligand (biochemistry), ligands, are chemically diverse, including ions (e.g. Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.), lipids (e.g. steroid, prostaglandin), peptides (e.g. insulin, ACTH), carbohydrates, glycosylated proteins (proteoglycans), nucleic acids, etc. Peptide and lipid ligands are particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |