|
CH3Cl
Chloromethane, also called methyl chloride, Refrigerant-40, R-40 or HCC 40, is an organic compound with the chemical formula . One of the haloalkanes, it is a colorless, sweet-smelling, flammable gas. Methyl chloride is a crucial reagent in industrial chemistry, although it is rarely present in consumer products, and was formerly utilized as a refrigerant. Most chloromethane is biogenic. Occurrence Chloromethane is an abundant organohalogen, anthropogenic or natural, in the atmosphere. Natural sources produce an estimated 4,100,000,000 kg/yr. Marine Laboratory cultures of marine phytoplankton (''Phaeodactylum tricornutum'', ''Phaeocystis'' sp., ''Thalassiosira weissflogii'', ''Chaetoceros calcitrans'', ''Isochrysis'' sp., ''Porphyridium'' sp., ''Synechococcus'' sp., ''Tetraselmis'' sp., ''Prorocentrum'' sp., and ''Emiliana huxleyi'') produce CH3Cl, but in relatively insignificant amounts. An extensive study of 30 species of polar macroalgae revealed the release of significant am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocladia Muricata
''Endocladia muricata'', commonly known as nailbrush seaweed or turfweed, is a marine alga that is widely distributed along the shores of the North Pacific Ocean, from Alaska to Punto Santo Tomas, Baja California. ''E. muricata'' is common north of Point Conception, and is one of the most common algae in the high intertidal zone of the central California, coast. It commonly forms the top-most conspicuous band of seaweed along that coast. ''E. muricata'' often grows with '' Pelvetiopsis limitata'' (dwarf rockweed) and '' Mastocarpus papillatus'' (Turkish washcloth), on rocks in the high intertidal. at SeaNet, Hopkins Marine Lab ''E. muricatas is 4–8 cm tall, short & bushy; bran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, Volatility (chemistry), volatile, colorless and flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odor similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol), but is more acutely toxic than the latter. Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced through destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl ''tert''-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène-Melchior Péligot
Eugène-Melchior Péligot (24 March 1811 – 15 April 1890), also known as Eugène Péligot, was a French chemist who isolated the first sample of uranium metal in 1841. Péligot proved that the black powder of Martin Heinrich Klaproth was not a pure metal (it was an oxide of uranium, known in chemistry as UO2). He then succeeded in producing pure uranium metal by reducing uranium tetrachloride (UCl4) with potassium metal in 1841.Celestial Bodies Today better methods have been found. Péligot was a of analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Dumas
Jean Baptiste André Dumas (; 14 July 180010 April 1884) was a French chemist, best known for his works on organic analysis and synthesis, as well as the determination of atomic weights (relative atomic masses) and molecular weights by measuring vapor densities. He also developed a method for the analysis of nitrogen in compounds. Biography Dumas was born in Alès (Gard), and became an apprentice to an apothecary in his native town. In 1816, he moved to Geneva, where he attended lectures by M. A. Pictet in physics, C. G. de la Rive in chemistry, and A. P. de Candolle in botany, and before he had reached his majority, he was engaged with Pierre Prévost in original work on problems of physiological chemistry and embryology. In 1822, he moved to Paris, acting on the advice of Alexander von Humboldt, where he became professor of chemistry, initially at the Lyceum, later (1835) at the École polytechnique. He was one of the founders of the École centrale des arts et manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organochlorine Chemistry
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–chlorine bonds. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted by chlorine) includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious. Organochlorides such as trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, dichloromethane and chloroform are commonly used as solvents and are referred to as "chlorinated solvents". Physical and chemical properties Chlorination modifies the physical properties of hydrocarbons in several ways. These compounds are typically denser than water due to the higher atomic weight of chlorine versus hydrogen. They have higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylene (compound)
Methylene (IUPAC name: methylidene, also called carbene or methene) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (also written and not to be confused with compressed hydrogen, which is also denoted ). It is a colourless gas that fluoresces in the mid-infrared range, and only persists in dilution, or as an adduct. Methylene is the simplest carbene.Roald Hoffman (2005), ''Molecular Orbitals of Transition Metal Complexes''. Oxford. . It is usually detected only at very low temperatures or as a short-lived intermediate in chemical reactions.W. B. DeMore and S. W. Benson (1964), Preparation, properties, and reactivity of methylene'. In ''Advances in Photochemistry'', John Wiley & Sons, 453 pages. Nomenclature The trivial name ''carbene'' is the preferred IUPAC name. The systematic names ''methylidene'' and ''dihydridocarbon'', valid IUPAC names, are constructed according to the substitutive and additive nomenclatures, respectively. ''Methylidene'' is viewed as methane with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALMA And Rosetta Detect Freon-40 In Space
Alma or ALMA may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Alma'' (film), a 2009 Spanish short animated film * ''Alma'', an upcoming film by Sally Potter * ''Alma'' (Oswald de Andrade novel), 1922 * ''Alma'' (Le Clézio novel), 2017 * ''Alma'' (play), a 1996 drama by Joshua Sobol about Alma Mahler-Werfel * ''Alma'' (Carminho album), 2012 * Alma (Nicki Nicole album), 2023 * "Alma" (song), by Fonseca, 2008 * "Alma", a song by Tom Lehrer from the 1965 album ''That Was the Year That Was'' * ALMA Award, or American Latino Media Arts Award Businesses * Alma (restaurant), an Asian fusion restaurant located in Toronto, Ontario * Alma Books, a British publishing house * Alma Media, a Finnish digital service business * ALMA de México, a low-cost airline Military * Battle of the Alma, an 1854 Crimean War battle * ''Alma''-class ironclad, French Navy corvettes built in the 1860s ** French ironclad ''Alma'' People and fictional characters * Alma (given name), including a list of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Forming Region
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
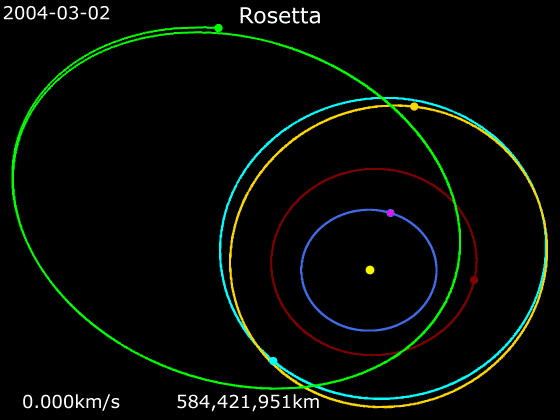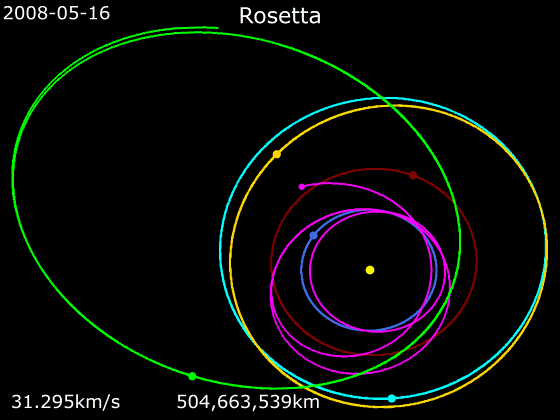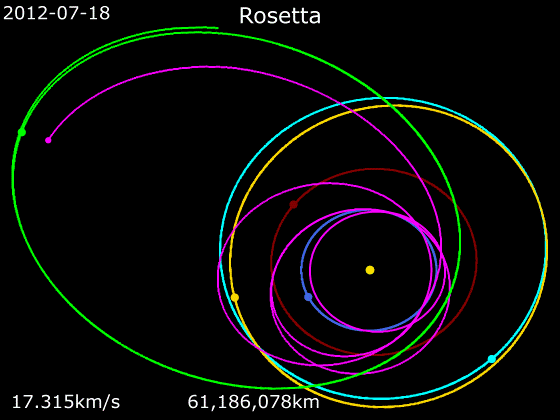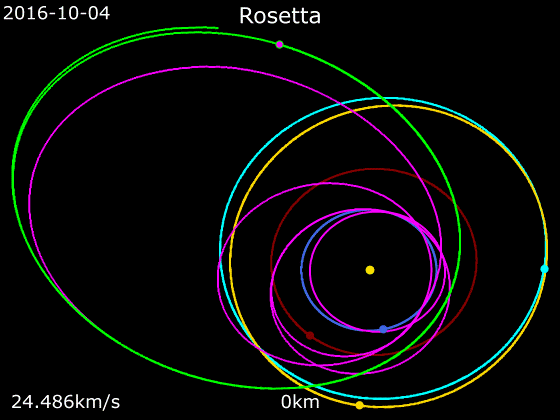
Rosetta (spacecraft)
''Rosetta'' was a space probe built by the European Space Agency that launched on 2 March 2004. Along with ''Philae'', its lander module, ''Rosetta'' performed a detailed study of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P). During its journey to the comet, the spacecraft performed flybys of Earth, Mars, and the asteroids 21 Lutetia and 2867 Šteins. It was launched as the third cornerstone mission of the ESA's Horizon 2000 programme, after ''SOHO' Cluster'' and '' XMM-Newton''. On 6 August 2014, the spacecraft reached the comet and performed a series of manoeuvers to eventually orbit the comet at distances of . On 12 November, its lander module ''Philae'' performed the first successful landing on a comet, though its battery power ran out two days later. Communications with ''Philae'' were briefly restored in June and July 2015, but due to diminishing solar power, ''Rosetta'' communications module with the lander was turned off on 27 July 2016. On 30 September 2016, the ''Rosett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko
67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (abbreviated as 67P or 67P/C–G) is a Jupiter-family comet. It is originally from the Kuiper belt and has an orbital period of 6.45 years as of 2012, a rotation period of approximately 12.4 hours, and a maximum velocity of . Churyumov–Gerasimenko is approximately at its longest and widest dimensions. It was first observed on photographic plates in 1969 by Soviet astronomers Klim Churyumov, Klim Ivanovych Churyumov and Svetlana Gerasimenko, Svetlana Ivanovna Gerasimenko, after whom it is Naming of comets, named. It most recently came to Perihelion and aphelion, perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) on 2 November 2021, and will next come to perihelion on 9 April 2028. Churyumov–Gerasimenko was the destination of the European Space Agency's Rosetta (spacecraft), ''Rosetta'' mission, launched on 2 March 2004. ''Rosetta'' space rendezvous, rendezvoused with Churyumov–Gerasimenko on 6 August 2014 and entered orbit on 10 September 2014. ''Rosetta' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atacama Large Millimeter Array
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) is an astronomical interferometer of 66 radio telescopes in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile, which observe electromagnetic radiation at millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths. The array has been constructed on the elevation Chajnantor plateau – near the Llano de Chajnantor Observatory and the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment. This location was chosen for its high elevation and low humidity, factors which are crucial to reduce noise and decrease signal attenuation due to Earth's atmosphere. ALMA provides insight on star birth during the early Stelliferous era and detailed imaging of local star and planet formation. ALMA is an international partnership amongst Europe, the United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Chile. Costing about US$1.4 billion, it is the most expensive ground-based telescope in operation. ALMA began scientific observations in the second half of 2011 and the first images were rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |