|
CDC 924
The CDC 1604 is a 48-bit computing, 48-bit computer designed and manufactured by Seymour Cray and his team at the Control Data Corporation (CDC). The 1604 is known as one of the first commercially successful transistor computer, transistorized computers. (The IBM 7090 was delivered earlier, in November 1959.) Legend has it that the 1604 designation was chosen by adding CDC's first street address (501 Park Avenue) to Cray's former project, the ERA-UNIVAC 1103. A cut-down 24-bit version, designated the #The 924, CDC 924, was shortly thereafter produced, and delivered to NASA. The first 1604 was delivered to the United States Navy, U.S. Navy Post Graduate School in January 1960 for JOVIAL applications supporting major Fleet Operations Control Centers primarily for weather prediction in Hawaii, London, and Norfolk, Virginia. By 1964, over 50 systems were built. The CDC 3000 series#Upper 3000 series, CDC 3600, which added five op codes, succeeded the 1604, and "was largely compatible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Data Corporation
Control Data Corporation (CDC) was a mainframe and supercomputer company that in the 1960s was one of the nine major U.S. computer companies, which group included IBM, the Burroughs Corporation, and the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC), the NCR Corporation (NCR), General Electric, Honeywell, RCA, and UNIVAC. For most of the 1960s, the strength of CDC was the work of the electrical engineer Seymour Cray who developed a series of fast computers, then considered the fastest computing machines in the world; in the 1970s, Cray left the Control Data Corporation and founded Cray Research (CRI) to design and make supercomputers. In 1988, after much financial loss, the Control Data Corporation began withdrawing from making computers and sold the affiliated companies of CDC; in 1992, CDC established Control Data Systems, Inc. The remaining affiliate companies of CDC currently do business as the software company Dayforce. Background: World War II – 1957 During World War II the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a type of general-purpose computer mostly developed from the mid-1960s, built significantly smaller and sold at a much lower price than mainframe computers . By 21st century-standards however, a mini is an exceptionally large machine. Minicomputers in the traditional technical sense covered here are only small relative to generally even earlier and much bigger machines. The class formed a distinct group with its own software architectures and operating systems. Minis were designed for control, instrumentation, human interaction, and communication switching, as distinct from calculation and record keeping. Many were sold indirectly to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) for final end-use application. During the two-decade lifetime of the minicomputer class (1965–1985), almost 100 minicomputer vendor companies formed. Only a half-dozen remained by the mid-1980s. When single-chip CPU microprocessors appeared in the 1970s, the defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bytes Per Inch
Magnetic-tape data storage is a system for storing digital information on magnetic tape using digital recording. Tape was an important medium for primary data storage in early computers, typically using large open reels of 7-track, later 9-track tape. Modern magnetic tape is most commonly packaged in cartridges and cassettes, such as the widely supported Linear Tape-Open (LTO) and IBM 3592 series. The device that performs the writing or reading of data is called a tape drive. Autoloaders and tape libraries are often used to automate cartridge handling and exchange. Compatibility was important to enable transferring data. Tape data storage is now used more for system backup, data archive and data exchange. The low cost of tape has kept it viable for long-term storage and archive. Open reels Initially, magnetic tape for data storage was wound on reels. This standard for large computer systems persisted through the late 1980s, with steadily increasing capacity due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
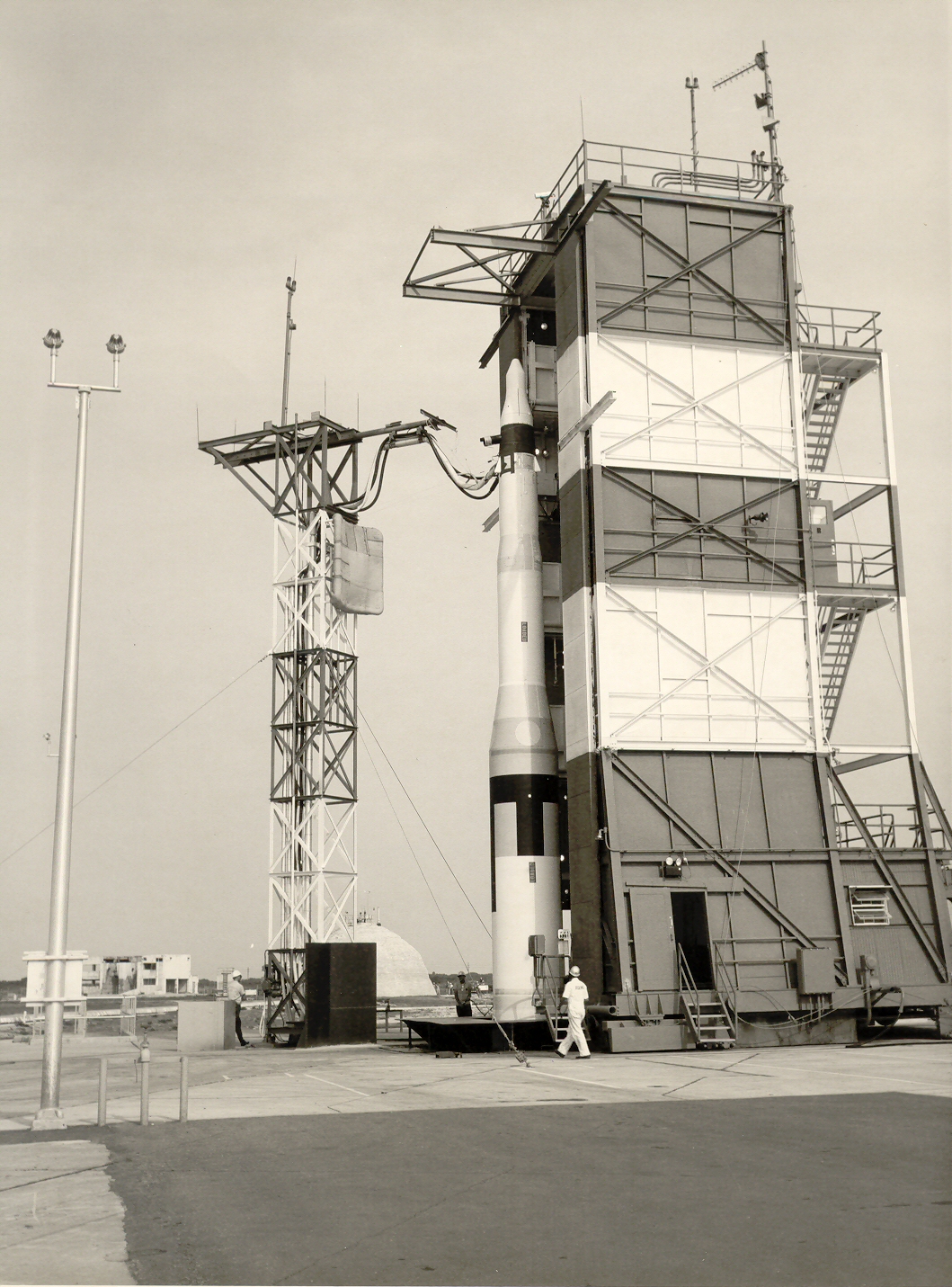
LGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G (Version 3) is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and represents the land leg of the U.S. nuclear triad, along with the Trident II submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) and nuclear weapons carried by long-range strategic bombers. Development of the Minuteman began in the mid-1950s when basic research indicated that a solid-fuel rocket motor could stand ready to launch for long periods of time, in contrast to liquid-fueled rockets that required fueling before launch and so might be destroyed in a surprise attack. The missile was named for the colonial minutemen of the American Revolutionary War, who could be ready to fight on short notice. The Minuteman entered service in 1962 as a deterrence weapon that could hit Soviet cities with a second strike and countervalue counterattack if the U.S. wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oahu
Oahu (, , sometimes written Oahu) is the third-largest and most populated island of the Hawaiian Islands and of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. The island of Oahu and the uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu. In 2021, Oahu had a population of 995,638, up from 953,207 in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the Hawaiian Islands, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Oahu is long and across. Its shoreline is long. Including small associated islands such as Ford Island plus those in Kāneohe Bay and off the eastern (windward and leeward, windward) coast, its area is , making it the List of islands of the United States by area, 20th-largest island in the United States. Well-known features of Oahu include Waikīkī, Pearl Harbor, Diamond Head, Hawaii, Diamond Head, Hanauma Bay, Kān ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
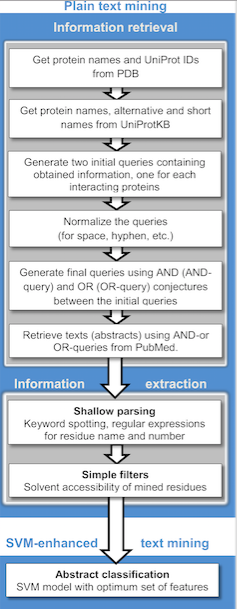
Text-mining
Text mining, text data mining (TDM) or text analytics is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. It involves "the discovery by computer of new, previously unknown information, by automatically extracting information from different written resources." Written resources may include websites, books, emails, reviews, and articles. High-quality information is typically obtained by devising patterns and trends by means such as statistical pattern learning. According to Hotho et al. (2005), there are three perspectives of text mining: information extraction, data mining, and knowledge discovery in databases (KDD). Text mining usually involves the process of structuring the input text (usually parsing, along with the addition of some derived linguistic features and the removal of others, and subsequent insertion into a database), deriving patterns within the structured data, and finally evaluation and interpretation of the output. 'High quality' in text mining usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Findlay, Ohio
Findlay ( ) is a city in Hancock County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. The second-largest city in Northwest Ohio, Findlay lies about 40 miles (64 km) south of Toledo, Ohio, Toledo. Its population was 40,313 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The principal city of the Micropolitan statistical area, Findlay micropolitan area, it is home to the University of Findlay and the headquarters of Fortune 100, ''Fortune'' 100 company Marathon Petroleum. History In the War of 1812, Colonel James Findlay (Cincinnati mayor), James Findlay of Cincinnati built a road and a stockade to transport and shelter troops in the Great Black Swamp region. This stockade was named Fort Findlay in his honor. At the conclusion of the war, the community of Findlay was born. The first town lots were laid out in 1821 by future Ohio Governor Joseph Vance (Ohio politician), Joseph Vance and Elnathan Corry. Before the American Civil War, Civil War, Findlay was a stop for Slavery in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathon Oil
Marathon Oil Corporation was an American company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration. In November 2024, it was acquired by ConocoPhillips and absorbed into the company. Marathon was founded in Lima, Ohio, as the Ohio Oil Company. In 1899, the company was acquired by the Standard Oil Company (New Jersey). After the antitrust case against Jersey Standard in 1911 and subsequent breakup of its holdings, Ohio Oil once again became an independent company. In 1930, Ohio Oil acquired the Transcontinental Oil Company, which operated the "Marathon" brand of retail fuel stations. Ohio Oil continued to use the Marathon brand, and in 1962, Ohio changed its name to the Marathon Oil Company. In January 1982, Marathon was acquired by U.S. Steel. After the acquisition, the USX Corporation was created to act as the parent of U.S. Steel and Marathon Oil, which operated as divisions. In 2001, USX spun off Marathon under the name Marathon Oil Corporation. In 2011, Marathon Oil spun off its dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital-to-analog Converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function. DACs are commonly used in music players to convert digital data streams into analog audio signals. They are also used in televisions and mobile phones to convert digital video data into analog video signals. These two applications use DACs at opposite ends of the frequency/resolution trade-off. The audio DAC is a low-frequency, high-resolution type while the video DAC is a high-frequency low- to medium-resolution type. There are several DAC architectures; the suitability of a DAC for a particular application is determined by figures of merit including: resolution, maximum sampling frequency and others. Digital-to-analog conversion can degrade a signal, so a DAC should be specified that has insignificant errors in terms of the application. Due to the complexity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ones' Complement
The ones' complement of a binary number is the value obtained by inverting (flipping) all the bits in the Binary number, binary representation of the number. The name "ones' complement" refers to the fact that such an inverted value, if added to the original, would always produce an "all ones" number (the term "Method of complements, complement" refers to such pairs of mutually additive inverse numbers, here in respect to a non-0 base number). This mathematical operation is primarily of interest in computer science, where it has varying effects depending on how a specific computer represents numbers. A ones' complement system or ones' complement arithmetic is a system in which negative numbers are represented by the inverse of the binary representations of their corresponding positive numbers. In such a system, a number is negated (converted from positive to negative or vice versa) by computing its ones' complement. An N-bit ones' complement numeral system can only represent int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Memory
Core or cores may refer to: Science and technology * Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages * Core (laboratory), a highly specialized shared research resource * Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding * Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber * Core, the central part of a fruit * Hydrophobic core, the interior zone of a protein * Nuclear reactor core, a portion containing the fuel components * Pit (nuclear weapon) or core, the fissile material in a nuclear weapon * Semiconductor intellectual property core (IP core), is a unit of design in ASIC/FPGA electronics and IC manufacturing * Atomic core, an atom with no valence electrons * Lithic core, in archaeology, a stone artifact left over from toolmaking Geology and astrophysics * Core sample, in Earth science, a sample obtained by coring ** Ice core * Core, the central part of a galaxy; see Mass deficit * Core (anticline), the central part of an anticline or syncline * Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |