|
CD195
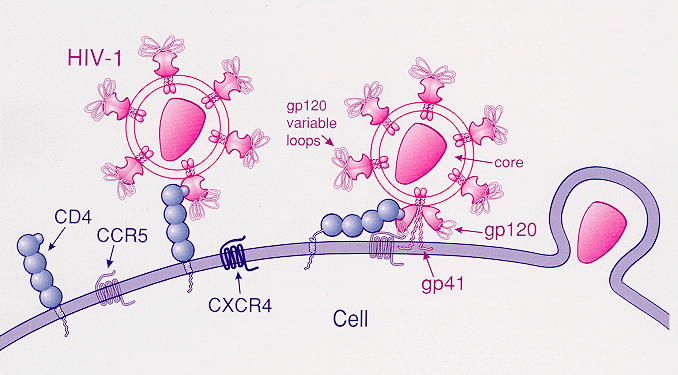
C-C chemokine receptor type 5, also known as CCR5 or CD195, is a protein on the surface of white blood cells that is involved in the immune system as it acts as a receptor for chemokines. In humans, the ''CCR5'' gene that encodes the CCR5 protein is located on the short (p) arm at position 21 on chromosome 3. Certain populations have inherited the ''Delta 32'' mutation, resulting in the genetic deletion of a portion of the CCR5 gene. Homozygous carriers of this mutation are resistant to M-tropic strains of HIV-1 infection. Function The CCR5 protein belongs to the beta chemokine receptors family of integral membrane proteins. It is a G protein–coupled receptor which functions as a chemokine receptor in the CC chemokine group. CCR5's cognate ligands include CCL3, CCL4 (also known as MIP 1''α'' and 1''β'', respectively), and CCL3L1. CCR5 furthermore interacts with CCL5 (a chemotactic cytokine protein also known as RANTES). CCR5 is predominantly expressed on T cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCR5 Primary Protein Sequence
C-C chemokine receptor type 5, also known as CCR5 or CD195, is a protein on the surface of white blood cells that is involved in the immune system as it acts as a receptor (biology), receptor for chemokines. In humans, the ''CCR5'' gene that encodes the CCR5 protein is Locus (genetics), located on the short (p) arm at position 21 on Chromosome 3 (human), chromosome 3. Certain populations have inherited the ''Delta 32'' mutation, resulting in the genetic deletion of a portion of the CCR5 gene. Homozygous carriers of this mutation are resistant to HIV tropism, M-tropic strains of HIV-1 infection. Function The CCR5 protein belongs to the beta chemokine receptors family of integral membrane proteins. It is a G protein–coupled receptor which functions as a chemokine receptor in the CC chemokine receptors, CC chemokine group. CCR5's cognate ligand (biochemistry), ligands include CCL3, CCL4 (also known as MIP 1''α'' and 1''β'', respectively), and CCL3L1. CCR5 furthermore intera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simian Immunodeficiency Virus
''Simian immunodeficiency virus'' (''SIV'') is a species of retrovirus that cause persistent infections in at least 45 species of non-human primates. Based on analysis of strains found in four species of monkeys from Bioko Island, which was isolated from the mainland by rising sea levels about 11,000 years ago, it has been concluded that SIV has been present in monkeys and apes for at least 32,000 years, and probably much longer. Virus strains from three of these primate species, SIVsmm in sooty mangabeys, SIVgor in gorillas and SIVcpz in chimpanzees, are believed to have crossed the species barrier into humans, resulting in HIV-2 and HIV-1 respectively, the two HIV viruses. The most likely route of transmission of HIV-1 to humans involves contact with the blood of chimps and gorillas that are often hunted for bushmeat in Africa. Four subtypes of HIV-1 (M, N, O, and P) likely arose through four separate transmissions of SIV to humans, and the resulting HIV-1 group M s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS. Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenance—they are constantly scavenging the CNS for plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents. Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS. This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular potassium. Recent evidence shows that microglia are also key players in the sustainment of normal brain functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophils
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells (WBCs) and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. They form about 2 to 3% of WBCs. These cells are eosinophilic or " acid-loving" due to their large acidophilic cytoplasmic granules, which show their affinity for acids by their affinity to coal tar dyes: Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining with eosin, a red dye, using the Romanowsky method. The staining is concentrated in small granules within the cellular cytoplasm, which contain many chemical mediators, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbe A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...s, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life— eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + '' taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cell A somatic cell (from Ancient Greek σῶμα ''sôma'', meaning "body"), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Such cells compo ...s, bacteria, and other single-cell organism, single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function and health (e.g., migration of White blood cell, leukocytes d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCL5
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 (also CCL5) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CCL5'' gene. The gene has been discovered in 1990 by ''in situ'' hybridisation and it is localised on 17q11.2-q12 chromosome. It is also known as RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted). RANTES was first described by Dr. Tom Schall who named the protein, the original source of the name Rantes was from the Argentine movie '' Man Facing Southeast'' about an alien who shows up in a mental ward who was named Rantés, the rather clunky acronym was only made to fit the name. Function CCL5 belongs to the CC subfamily of chemokines, due to its adjacent cysteines near N terminus. It is an 8kDa protein acting as a classical chemotactic cytokine or chemokine. It consists of 68 amino acids. CCL5 is proinflammatory chemokine, recruiting leukocytes to the site of inflammation. It is chemotactic for T cells, eosinophils, and basophils, but also for monocytes, natural-k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)