|
CD-RW
CD-RW (Compact Disc-Rewritable) is a digital optical disc storage format introduced in 1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-RWs) can be written, read, erased, and re-written. CD-RWs, as opposed to CDs, require specialized readers that have sensitive laser optics. Consequently, CD-RWs cannot be read in many CD readers built prior to the introduction of CD-RW. CD-ROM drives with a "MultiRead" certification are compatible. CD-RWs must be erased or blanked before reuse. Erasure methods include full blanking where the entire surface of the disc is erased and fast blanking where only metadata areas, such as PMA, TOC and pregap, are cleared. Fast blanking is quicker and usually sufficient to allow rewriting the disc. Full blanking removes all traces of the previous data, and is often used for confidentiality purposes. CD-RWs can sustain fewer re-writes compared to other storage media (ca. 1,000 compared up to 100,000). Ideal use is for test discs (e.g. for CD authoring), temporary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMA (CD)
CD-RW (Compact Disc-Rewritable) is a digital optical disc storage format introduced in 1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-RWs) can be written, read, erased, and re-written. CD-RWs, as opposed to CDs, require specialized readers that have sensitive laser optics. Consequently, CD-RWs cannot be read in many CD readers built prior to the introduction of CD-RW. CD-ROM drives with a "MultiRead" certification are compatible. CD-RWs must be erased or blanked before reuse. Erasure methods include full blanking where the entire surface of the disc is erased and fast blanking where only metadata areas, such as PMA, TOC and pregap, are cleared. Fast blanking is quicker and usually sufficient to allow rewriting the disc. Full blanking removes all traces of the previous data, and is often used for confidentiality purposes. CD-RWs can sustain fewer re-writes compared to other storage media (ca. 1,000 compared up to 100,000). Ideal use is for test discs (e.g. for CD authoring), temporary ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
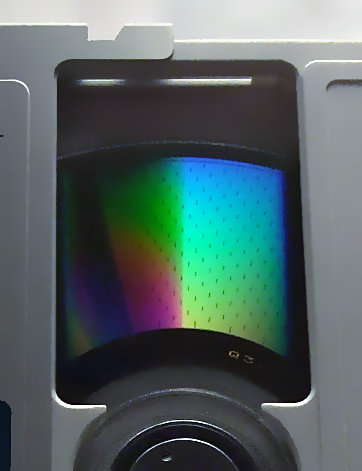
CD-R
CD-R (Compact disc-recordable) is a digital optical disc storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can be written once and read arbitrarily many times. CD-R discs (CD-Rs) are readable by most CD readers manufactured prior to the introduction of CD-R, unlike CD-RW discs. History Originally named CD Write-Once (WO), the CD-R specification was first published in 1988 by Philips and Sony in the Orange Book, which consists of several parts that provide details of the CD-WO, CD-MO (Magneto-Optic), and later CD-RW (ReWritable). The latest editions have abandoned the use of the term "CD-WO" in favor of "CD-R", while " CD-MO" was rarely used. Written CD-Rs and CD-RWs are, in the aspect of low-level encoding and data format, fully compatible with the audio CD (''Red Book'' CD-DA) and data CD (''Yellow Book'' CD-ROM) standards. The Yellow Book standard for CD-ROM only specifies a high-level data format and refers to the Red Book for all physical format and low-level code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Disc
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was co-developed by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. In August 1982, the first compact disc was manufactured. It was then released in October 1982 in Japan and branded as '' Digital Audio Compact Disc''. The format was later adapted (as CD-ROM) for general-purpose data storage. Several other formats were further derived, including write-once audio and data storage ( CD-R), rewritable media ( CD-RW), Video CD (VCD), Super Video CD (SVCD), Photo CD, Picture CD, Compact Disc-Interactive (CD-i) and Enhanced Music CD. Standard CDs have a diameter of and are designed to hold up to 74 minutes of uncompressed stereo digital audio or about 650 MiB of data. Capacity is routinely extended to 80 minutes and 700 MiB by arranging data more closely on the same sized disc. The Mini CD has various diameters ranging from ; they are sometimes used for CD singles, storing up to 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Disc
In computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc (OD) is a flat, usually circular disc that encodes binary data (bits) in the form of pits and lands on a special material, often aluminum, on one of its flat surfaces. Its main uses are physical offline data distribution and long-term archival. Changes from pit to land or from land to pit correspond to a binary value of 1; while no change, regardless of whether in a land or a pit area, corresponds to a binary value of 0. Non-circular optical discs exist for fashion purposes; see shaped compact disc. Design and technology The encoding material sits atop a thicker substrate (usually polycarbonate) that makes up the bulk of the disc and forms a dust defocusing layer. The encoding pattern follows a continuous, spiral path covering the entire disc surface and extending from the innermost track to the outermost track. The data are stored on the disc with a laser or stamping machine, and can be accessed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Books
The Rainbow Books are a collection of CD format specifications. ''Red Book'' (1980) * CD-DA (''Digital Audio'') – standardized as IEC 60908 ** CD-Text—a 1996 extension to CD-DA ** CD-MIDI—part of the original red-book standard ** CD+G (''plus Graphics'') – karaoke *** CD+EG / CD+XG (''plus Extended Graphics'') – an extension of CD+G ''Yellow Book'' (1983) * CD-ROM (''Read-Only Memory'') – standardized as ISO/IEC 10149 in 1988 and ECMA-130 in 1989 ** CD-ROM XA (''eXtended Architecture'') – a 1991 extension of CD-ROM ''Green Book'' (1986) *CD-i (''Interactive'') ''Orange Book'' (1990) Orange is a reference to the fact that red and yellow mix to orange. This correlates with the fact that CD-R and CD-RW are capable of audio ("Red") and data ("Yellow"); although other colors (other CD standards) that do not mix are capable of being burned onto the physical medium. ''Orange Book'' also introduced the standard for multisession writing. * CD-MO (''Magneto-Opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOC (CD)
Optical disc authoring, including DVD and Blu-ray Disc authoring, is the process of assembling source material—video, audio or other data—into the proper logical volume format to then be recorded ("burned") onto an optical disc (typically a compact disc or DVD). Process To burn an optical disc, one usually first creates an optical disc image with a full file system, of a type designed for the optical disc, in temporary storage such as a file in another file system on a disk drive. One may test the image on target devices using rewriteable media such as CD-RW, DVD±RW and BD-RE. Then, one copies the image to the disc (usually write-once media for hard distribution). Most optical disc authoring utilities create a disc image and copy it to the disc in one bundled operation, so that end-users often do not know the distinction between creating and burning. However, it is useful to know because creating the disc image is a time-consuming process, while copying the im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.Anderson, Don L.; "Chemical Composition of the Mantle" in ''Theory of the Earth'', pp. 147-175 Tellurium-bearing compounds were first discovered in 1782 in a gold mine in Kleinschlatten, Transylvania (now Zlatna, Romania) by Austrian mineralogist Franz-Joseph Müller von Reichenstein, although it was Martin Heinrich Klaproth who named the new element in 1798 after the Latin 'earth'. Gold telluride minera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD Authoring
Optical disc authoring, including DVD and Blu-ray Disc authoring, is the process of assembling source material—video, audio or other data—into the proper logical volume format to then be recorded ("burned") onto an optical disc (typically a compact disc or DVD). Process To burn an optical disc, one usually first creates an optical disc image with a full file system, of a type designed for the optical disc, in temporary storage such as a file in another file system on a disk drive. One may test the image on target devices using rewriteable media such as CD-RW, DVD±RW and BD-RE. Then, one copies the image to the disc (usually write-once media for hard distribution). Most optical disc authoring utilities create a disc image and copy it to the disc in one bundled operation, so that end-users often do not know the distinction between creating and burning. However, it is useful to know because creating the disc image is a time-consuming process, while copying the ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curie Point
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (''T''C), or Curie point, is the temperature above which certain materials lose their permanent magnetic properties, which can (in most cases) be replaced by induced magnetism. The Curie temperature is named after Pierre Curie, who showed that magnetism was lost at a critical temperature. The force of magnetism is determined by the magnetic moment, a dipole moment within an atom which originates from the angular momentum and spin of electrons. Materials have different structures of intrinsic magnetic moments that depend on temperature; the Curie temperature is the critical point at which a material's intrinsic magnetic moments change direction. Permanent magnetism is caused by the alignment of magnetic moments and induced magnetism is created when disordered magnetic moments are forced to align in an applied magnetic field. For example, the ordered magnetic moments (ferromagnetic, Figure 1) change and become disorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
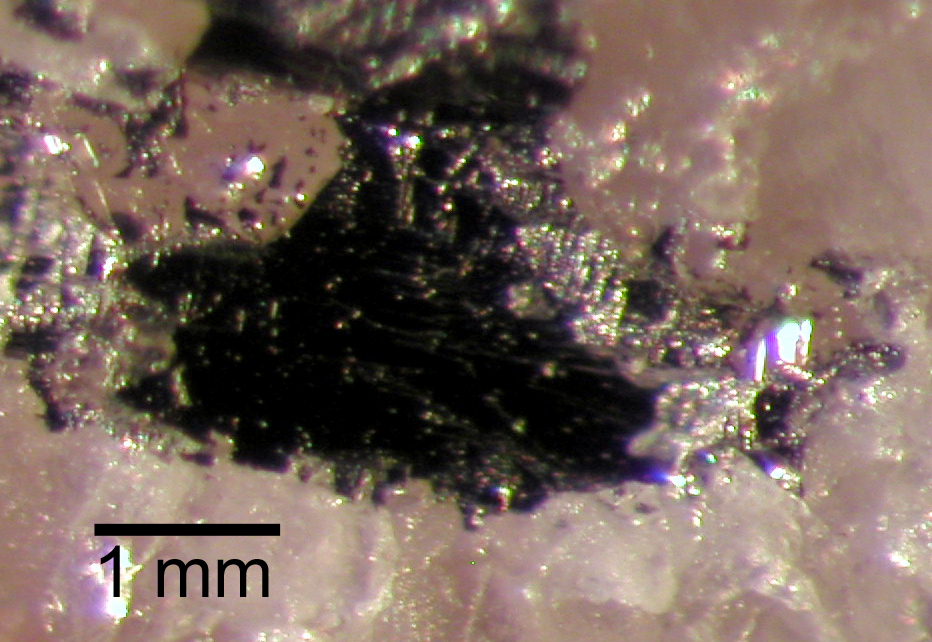
AgInSbTe
AgInSbTe, or silver-indium-antimony-tellurium, is a phase change material from the group of chalcogenide glasses, used in rewritable optical discs (such as rewritable CDs) and phase-change memory applications. It is a quaternary compound of silver, indium, antimony, and tellurium. During writing, the material is first erased, initialized into its crystalline state, with long, lower-intensity laser irradiation. The material heats up to its crystallization temperature, but not up to its melting point, and crystallizes in a metastable face-centered cubic structure. Then the information is written on the crystalline phase, by heating spots of it with short (<10 ns), high-intensity laser pulses; the material locally melts and is quickly cooled, remaining in the amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (o ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magneto-optical
A magneto-optical drive is a kind of optical disc drive capable of writing and rewriting data upon a magneto-optical disc. Both 130 mm (5.25 in) and 90 mm (3.5 in) form factors exist. In 1983, just a year after the introduction of the Compact Disc, Kees Schouhamer Immink and Joseph Braat presented the first experiments with erasable magneto-optical Compact Discs during the 73rd AES Convention in Eindhoven. The technology was introduced commercially in 1985. Although optical, they normally appear as hard disk drives to an operating system and can be formatted with any file system. Magneto-optical drives were common in some countries, such as Japan, but have fallen into disuse. Overview Early drives are 130 mm and have the size of full-height 130 mm hard-drives (like in the IBM PC XT). 130 mm media looks similar to a CD-ROM enclosed in an old-style caddy, while 90 mm media is about the size of a regular 3-inch floppy disk, but twice the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |