|
CCIR System C
CCIR System C (originally known as the Belgian 625-line system) is an analog broadcast television system used between 1953 and 1978 in Belgium, Italy, Netherlands and Luxembourg. Used on VHF only. Specifications Some of the important specifications for System C are listed below: * Frame rate: 25 Hz * Interlace: 2/1 * Field rate: 50 Hz * Lines/frame: 625 * Line rate: 15.625 kHz * Visual bandwidth: 5 MHz * Vision modulation: Positive * Preemphasis: 50 μs * Sound modulation: AM * Sound offset: +5.5 MHz * Channel bandwidth: 7 MHz * Assumed display device gamma: 2.0 Television channels were arranged as follows: See also * CCIR System B * CCIR System L * Broadcast television systems * Television transmitter * Transposer In broadcasting, a transposer or translator is a device in or beyond the service area of a radio or television station transmitter that rebroadcasts signals to receivers which can’t properly receive the signals of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is responsible for radio communications. Its role is to manage the international radio-frequency spectrum and satellite orbit resources and to develop standards for radiocommunication systems with the objective of ensuring the effective use of the spectrum. ITU is required, according to its constitution, to allocate spectrum and register frequency allocation, orbital positions and other parameters of satellites, "in order to avoid harmful interference between radio stations of different countries". The international spectrum management system is therefore based on regulatory procedures for frequency coordination, notification and registration. ITU-R has a permanent secretariat, the Radiocommunication Bureau, based at the ITU HQ in Geneva, Switzerland. The elected Director of the Bureau is Mario Maniewicz; he was first elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a :wikt:one-to-many, one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio, which came into popular use around 1920 with the spread of vacuum tube radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. Before this, most implementations of electronic communication (early radio, telephone, and telegraph) were wikt:one-to-one, one-to-one, with the message intended for a single recipient. The term ''broadcasting'' evolved from its use as the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about. It was later adopted for describing the widespread distribution of information by printed materials or by telegraph. Examples applying it to "one-to-many" radio transmissions of an individual station to multiple listeners appeared as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
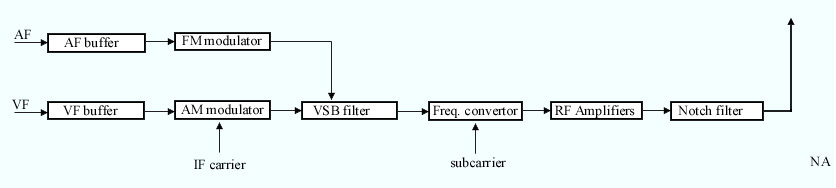
Video Formats
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems, which, in turn, were replaced by flat-panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities, and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcasts, magnetic tape, optical discs, computer files, and network streaming. Etymology The word ''video'' comes from the Latin verb ''video,'' meaning to see or ''videre''. And as a noun, "that which is displayed on a (television) screen," History Analog video Video developed from facsimile systems developed in the mid-19th century. Early mechanical video scanners, such as the Nipkow disk, were patented as early as 1884, however, it took several decade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Technology
The technology of television has evolved since its early days using a mechanical system invented by Paul Gottlieb Nipkow in 1884. Every television system works on the scanning principle first implemented in the rotating disk scanner of Nipkow. This turns a two-dimensional image into a time series of signals that represent the brightness and color of each resolvable element of the picture. By repeating a two-dimensional image quickly enough, the impression of motion can be transmitted as well. For the receiving apparatus to reconstruct the image, synchronization information is included in the signal to allow proper placement of each line within the image and to identify when a complete image has been transmitted and a new image is to follow. While mechanically scanned systems were experimentally used, television as a mass medium was made practical by the development of electronic camera tubes and displays. By the turn of the 21st century, it was technically feasible to replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-R Recommendations
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is responsible for radio communications. Its role is to manage the international radio-frequency spectrum and satellite orbit resources and to develop standards for radiocommunication systems with the objective of ensuring the effective use of the spectrum. ITU is required, according to its constitution, to allocate spectrum and register frequency allocation, orbital positions and other parameters of satellites, "in order to avoid harmful interference between radio stations of different countries". The international spectrum management system is therefore based on regulatory procedures for frequency coordination, notification and registration. ITU-R has a permanent secretariat, the Radiocommunication Bureau, based at the ITU HQ in Geneva, Switzerland. The elected Director of the Bureau is Mario Maniewicz; he was first elected by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposer
In broadcasting, a transposer or translator is a device in or beyond the service area of a radio or television station transmitter that rebroadcasts signals to receivers which can’t properly receive the signals of the transmitter because of a physical obstruction (like a hill). A translator receives the signals of the transmitter and rebroadcasts the signals to the area of poor reception. Sometimes the translator is also called a ''relay transmitter'', ''rebroadcast transmitter'' or ''transposer.'' Since translators are used to cover a small shadowed area, their output powers are usually lower than that of the radio or television station transmitters feeding them. Physical obstruction Reception of RF signals is sensitive to the size of obstruction in the path between the transmitter and the receiver. Generally speaking, if the size exceeds the wavelength the reception is interrupted. Since the wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency, it follows than that the higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Transmitter
A television transmitter is a transmitter that is used for terrestrial television, terrestrial (over-the-air) television broadcasting. It is an electronic device that radiates radio waves that carry a video signal representing moving images, along with a synchronized audio signal, audio channel, which is received by television receivers ('televisions' or 'TVs') belonging to a public audience, which display the image on a screen. A television transmitter, together with the Television studio, broadcast studio which originates the content, is called a television station. Television transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to a certain frequency channel and power level. They transmit on frequency television channel frequencies, channels in the very high frequency, VHF and ultrahigh frequency, UHF bands. Since radio waves of these frequencies travel by line-of-sight propagation, line of sight, they are limited by the horizon to reception distances of 40–60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCIR System L
ITU-R#CCIR, CCIR System L is an Analog signal, analog Broadcast television systems, broadcast television system used in France, Luxembourg, Monaco and Chausey. It was the last system to use positive video modulation and AM sound. Initially adopted in the 1970s and associated with the SECAM color system (SECAM-L), it was discontinued in 2011, when France transitioned to DVB, Digital Video Broadcasting. Specifications The main System L specifications are listed below: * Frame rate: 25 Hz * Interlaced video, Interlace: 2/1 * Refresh rate, Field rate: 50 Hz * Film frame#Video frames, Lines/frame: 625 * Scan line, Line rate: 15.625 kHz * Bandwidth (signal processing), Visual bandwidth: 6 MHz * Modulation, Vision modulation: Positive * Preemphasis: 50 μs * Sound modulation: AM * Sound offset: -6.5 MHz * Broadcasting, Channel bandwidth: 8 MHz Television channels were arranged as follows: See also * Broadcast television systems * Television tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCIR System B
CCIR System B (originally known as the "Gerber Standard") was the 625-line VHF analog broadcast television system which at its peak was adopted by more than one hundred countries, either with PAL or SECAM colour. It is usually associated with CCIR System G for UHF broadcasts. System B was the first internationally accepted 625-line broadcasting standard in the world. A first 625-line system with a 8 MHz channel bandwidth was proposed at the CCIR Conference in Stockholm in July 1948 (based on 1946-48 studies in the Soviet Union by Mark KrivosheevOn the beginning of broadcast in 625-lines 60 year s ago, ''625'' magazine (in Russian). ). At a CCIR Geneva meeting in July 1950 Dr. Gerber (a Swiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a Nonlinearity, nonlinear operation used to encode and decode Relative luminance, luminance or CIE 1931 color space#Tristimulus values, tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following Power law, power-law expression: : V_\text = A V_\text^\gamma, where the non-negative real input value V_\text is raised to the power \gamma and multiplied by the constant ''A'' to get the output value V_\text. In the common case of , inputs and outputs are typically in the range 0–1. A gamma value \gamma 1 is called a ''decoding gamma'', and the application of the expansive power-law nonlinearity is called gamma expansion. Explanation Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. The human perception of brightness (lightness), un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |