|
CCBE1
Collagen and calcium-binding EGF domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCBE1'' gene. Function CCBE1 is a regulator of the development and growth of the lymphatic system. CCBE1 is necessary for the proteolytic activation of VEGF-C by ADAMTS3, which is the main growth factor for the lymphatic system. Clinical significance Hennekam syndrome Hennekam syndrome also known as intestinal lymphagiectasia–lymphedema–mental retardation syndrome, is an autosomal recessive disorder consisting of intestinal lymphangiectasia, facial anomalies, peripheral lymphedema, and mild to moderate le ... type I (a generalized lymphatic dysplasia in humans) is associated with mutations in the CCBE1 gene, and the molecular etiology of the disease has been elucidated. References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-18-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADAMTS3
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ADAMTS3'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is the major procollagen II N-propeptidase. Structure This gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family. Members of the family share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The protein encoded by this gene is the major procollagen II N-propeptidase. Function Because of the high similarity to ADAMTS2, the major substrate of ADAMTS3 had been erroneously assumed to be procollagen II. However, ADAMTS3 appears largely irrelevant for collagen maturation but instead is required for the activation of the lymphangiogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VEGF-C
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a protein that is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor / vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. It is encoded in humans by the ''VEGFC'' gene, which is located on chromosome 4q34. Functions The main function of VEGF-C is to promote the growth of lymphatic vessels ( lymphangiogenesis). It acts on lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) primarily via its receptor VEGFR-3 promoting survival, growth and migration. It was discovered in 1996 as a ligand for the orphan receptor VEGFR-3. Soon thereafter, it was shown to be a specific growth factor for lymphatic vessels in a variety of models. However, in addition to its effect on lymphatic vessels, it can also promote the growth of blood vessels and regulate their permeability. The effect on blood vessels can be mediated via its primary receptor VEGFR-3 or its secondary receptor VEGFR-2. Apart from vascular targets, VEGF-C is also important for neural development and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
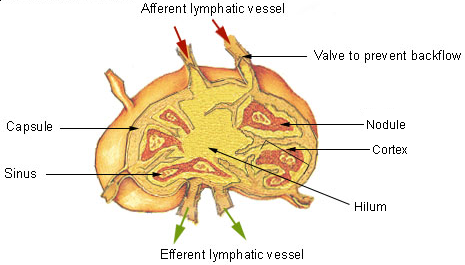
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, " Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |