|
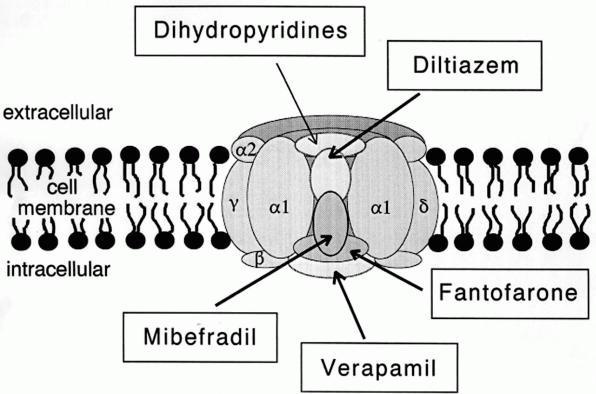
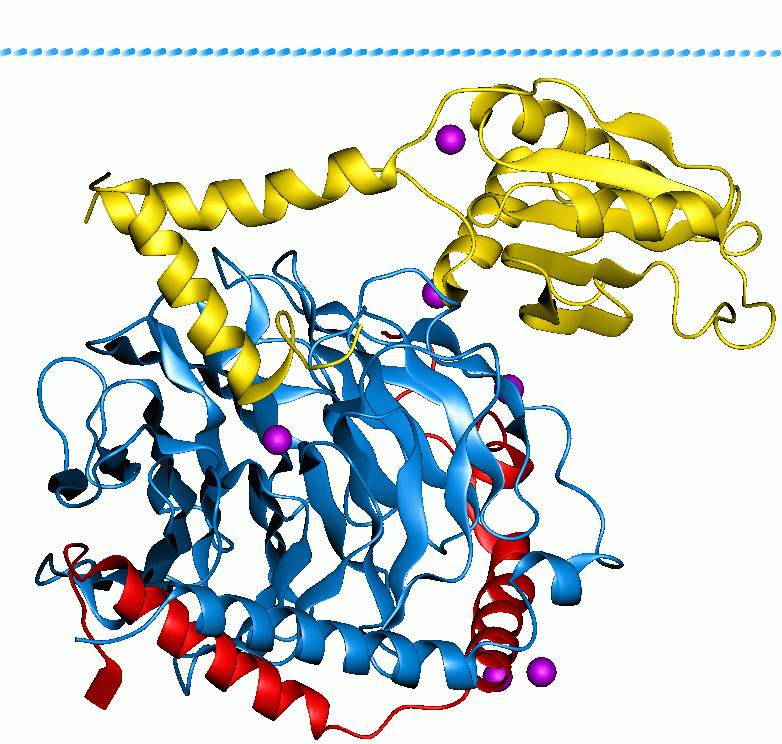
CACNB4
Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CACNB4'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the beta subunit family, a protein in the voltage-dependent calcium channel complex. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization and consist of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta, beta, and gamma subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. Various versions of each of these subunits exist, either expressed from similar genes or the result of alternative splicing. The protein described in this record plays an important role in calcium channel function by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the alpha-1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. Clinical significance Certain mutations in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), also known as Janz syndrome or impulsive petit mal, is a form of hereditary, idiopathic generalized epilepsy, representing 5–10% of all epilepsy cases. Typically it first presents between the ages of 12 and 18 with myoclonic seizures (brief, involuntary, single or multiple episodes of muscle contractions caused by abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain). These events typically occur after awakening from sleep, during the evening or when sleep-deprived. JME is also characterized by generalized tonic–clonic seizures, and a minority of patients have absence seizures. It was first described by Théodore Herpin in 1857. Understanding of the genetics of JME has been rapidly evolving since the 1990s, and over 20 chromosomal loci and multiple genes have been identified. Given the genetic and clinical heterogeneity of JME some authors have suggested that it should be thought of as a spectrum disorder. Epidemiology The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-dependent Calcium Channel
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'' muscle, glial cells, neurons) with a permeability to the calcium ion Ca2+. These channels are slightly permeable to sodium ions, so they are also called Ca2+–Na+ channels, but their permeability to calcium is about 1000-fold greater than to sodium under normal physiological conditions. At physiologic or resting membrane potential, VGCCs are normally closed. They are activated (''i.e.'': opened) at depolarized membrane potentials and this is the source of the "voltage-gated" epithet. The concentration of calcium (Ca2+ ions) is normally several thousand times higher outside the cell than inside. Activation of particular VGCCs allows a Ca2+ influx into the cell, which, depending on the cell type, results in activation of calcium-sensitive potassium channels, muscular contraction, excit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) is a group of epileptic disorders that are believed to have a strong underlying genetic basis. IGE is considered a subgroup of Genetic Generalized Epilepsy (GGE). Patients with an IGE subtype are typically otherwise normal and have no structural brain abnormalities. People also often have a family history of epilepsy and seem to have a genetically predisposed risk of seizures. IGE tends to manifest itself between early childhood and adolescence although it can be eventually diagnosed later. The genetic cause of some IGE types is known, though inheritance does not always follow a simple monogenic mechanism. Types Benign myoclonic epilepsy in infancy This form of epilepsy is very rare, representing less than 1% of cases, and is twice as prevalent in boys compared to girls. Age of seizure onset is between 5 months and 5 years of age. Children with this disorder often present with head drops and brief arm jerks. Although there is believed to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, which are a type of calcium channel regulated by changes in membrane potential. Some calcium channels are regulated by the binding of a ligand.Striggow F, Ehrlich BE (August 1996). "Ligand-gated calcium channels inside and out". ''Current Opinion in Cell Biology''. 8 (4): 490–495. Doi (identifier), doi:doi:10.1016/S0955-0674(96)80025-1, 10.1016/S0955-0674(96)80025-1. PMID (identifier), PMID]8791458 Other calcium channels can also be regulated by both voltage and ligands to provide precise control over ion flow. Some cation channels allow calcium as well as other cations to pass through the membrane. Calcium channels can participate in the creation of Action potential, action potentials across cell membranes. Calcium channels can also be used to release calcium ions as Second messenger system, second messengers within the cell, affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a Protein family, family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell (biology), cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein protein complex, complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''G alpha subunit, alpha'' (Gα), ''beta'' (Gβ) and ''gamma'' (Gγ) protein subunit, subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable Protein dimer, dimeric complex re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |