|
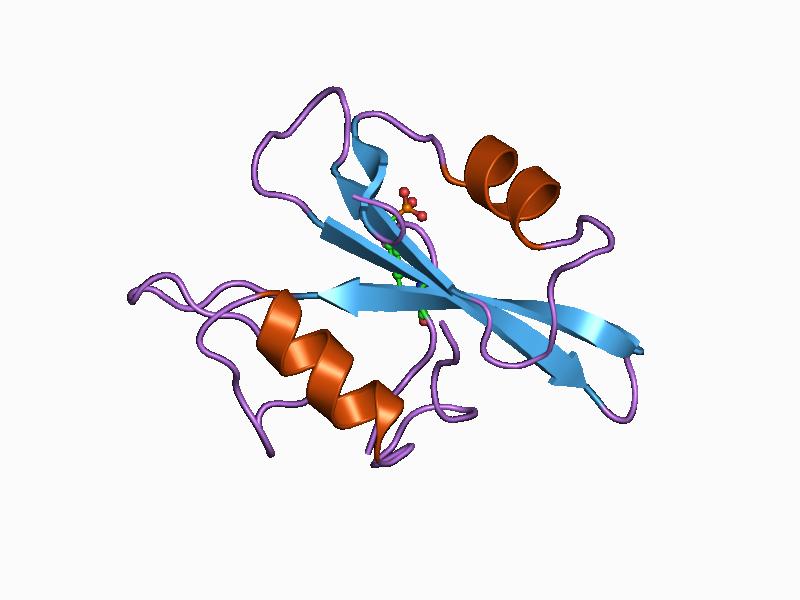
C13orf42
C13orf42 is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the gene chromosome 13 open reading frame 42 (C13orf42). RNA sequencing data shows low expression of the C13orf42 gene in a variety of tissues. The C13orf42 protein is predicted to be localized in the mitochondria, nucleus, and cytosol. Tertiary structure predictions for C13orf42 indicate multiple alpha helices. Gene Summary C13orf42 is a protein encoding gene containing 4 exons. C13orf42 is also known by aliases LINC00371 and LINC00372. RNA sequencing shows the gene's expression at low levels in various tissues. Location C13orf42 is located on the minus strand of chromosome 13 at 13q14.3 in humans. C13orf42 is located from 51.08 Mb to 51.20 Mb on chromosome 13 and spans 118 kilobases. Neighborhood The genomic neighborhood of C13orf42 consists of several pseudogenes along with ribonuclease H2 subunit B (RNASEH2B), uncharacterized LOC107984554, and family with sequence similarity 124 member A (FAM124A). Exons The C13orf42 g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla ( hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Of C13orf42 Evolution Compared To Cytochrome C And Fibrinogen Alpha
Graph may refer to: Mathematics *Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges **Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties *Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discrete mathematics *Graph of a function *Graph of a relation *Graph paper *Chart, a means of representing data (also called a graph) Computing *Graph (abstract data type), an abstract data type representing relations or connections *graph (Unix), Unix command-line utility *Conceptual graph, a model for knowledge representation and reasoning Other uses * HMS ''Graph'', a submarine of the UK Royal Navy See also * Complex network *Graf * Graff (other) * Graph database *Grapheme, in linguistics * Graphemics * Graphic (other) *-graphy (suffix from the Greek for "describe," "write" or "draw") *List of information graphics software *Statistical graphics Statistical graphics, also known as statistical graphical techniques, are gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-GlcNAc
''O''-GlcNAc (short for ''O''-linked GlcNAc or ''O''-linked β-''N''-acetylglucosamine) is a reversible enzymatic post-translational modification that is found on serine and threonine residues of nucleocytoplasmic proteins. The modification is characterized by a β-glycosidic bond between the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine side chains and ''N''-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). ''O''-GlcNAc differs from other forms of protein glycosylation: (i) ''O''-GlcNAc is not elongated or modified to form more complex glycan structures, (ii) ''O''-GlcNAc is almost exclusively found on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins rather than membrane proteins and secretory proteins, and (iii) ''O''-GlcNAc is a highly dynamic modification that turns over more rapidly than the proteins which it modifies. ''O''-GlcNAc is conserved across metazoans. Due to the dynamic nature of ''O''-GlcNAc and its presence on serine and threonine residues, ''O''-GlcNAcylation is similar to protein phosphorylation in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades. In biochemistry, the PKC family consists of fifteen isozymes in humans. They are divided into three subfamilies, based on their second messenger requirements: conventional (or classical), novel, and atypical. Conventional (c)PKCs contain the isoforms α, βI, βII, and γ. These require Ca2+, DAG, and a phospholipid such as phosphatidylserine for activation. Novel (n)PKCs include the δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms, and require DAG, but do not require Ca2+ f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at various locations in the interior of the cell. Adenylate cyclase is ''activated'' by a range of signaling molecules through the activation of adenylate cyclase stimulatory G ( Gs)-protein-coupled receptors. Adenylate cyclase is ''inhibited'' by agonists of adenylate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine Phosphorylation
Tyrosine phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to the amino acid tyrosine on a protein. It is one of the main types of protein phosphorylation. This transfer is made possible through enzymes called tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine phosphorylation is a key step in signal transduction and the regulation of enzymatic activity. History In the summer of 1979, studies of polyomavirus middle T and v-Src associated kinase activities led to the discovery of tyrosine phosphorylation as a new type of protein modification. Following the 1979 discovery that Src is a tyrosine kinase, the number of known distinct tyrosine kinases grew rapidly, accelerated by the advent of rapid DNA sequencing technology and PCR. About one year later, researchers discovered an important role for tyrosine phosphorylation in growth factor signaling and proliferation, and by extension in oncogenesis through hijacking of growth factor tyrosine phosphorylation signaling pathways. In 1990 receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casein Kinase 2
Casein kinase 2 ()(CK2/CSNK2) is a serine/threonine-selective protein kinase that has been implicated in cell cycle control, DNA repair, regulation of the circadian rhythm, and other cellular processes. De-regulation of CK2 has been linked to tumorigenesis as a potential protection mechanism for mutated cells. Proper CK2 function is necessary for survival of cells as no knockout models have been successfully generated. Structure CK2 typically appears as a tetramer of two α subunits; α being 42 kDa and α’ being 38 kDa, and two β subunits, each weighing in at 28 kDa. The β regulatory domain only has one isoform and therefore within the tetramer will have two β subunits. The catalytic α domains appear as an α or α’ variant and can either be formed in a homodimer (α & α, or α’ & α’) formation or heterodimer formation (α & α’). It is worth noting that other β isoforms have been found in other organisms but not in humans. The α subunits do not require the β ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human C13orf42 Predicted Post Translational Modification Illustration
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy. History The nucleolus was identified by bright-field microscopy during the 1830s. Little was known about the function of the nucleolus until 1964, when a study of nucleoli by John Gurdon and Donald Brown in the African clawed frog '' Xenopus laevis'' generated increasing interest in the function and detailed structure of the nucleolus. They found that 25% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)