|
C-Band All Sky Survey
The C-Band All Sky Survey (C-BASS) is a radio astronomy project that aims to map the entire sky in the C band (IEEE), C Band (5 GHz). It has been conducted on two radio telescopes, one operating in the Karoo in South Africa, the other at Owens Valley Radio Observatory in California. Project description The survey is a collaboration between the University of Oxford, University of Manchester, the California Institute of Technology, the Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory (HartRAO), and the King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology. The initial observations were made with two telescopes; one based at the Owens Valley Radio Observatory (OVRO) in California, United States, and the other near the Meerkat National Park in Klerefontein in the Karoo desert, South Africa.Square Kilometer Array Media Release , So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies Astronomical object, celestial objects using radio waves. It started in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxy, galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as Radio galaxy, radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and Astrophysical maser, masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang, Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy. Radio astronomy is conducted using large Antenna (radio), radio antennas referred to as ''radio telescopes'', that are either used alone, or with multiple linked telescopes utilizing the techniques of Astronomical interferometer, radio interferometry and aperture synthesis. The use of interferometry allows radio astronomy to achieve high angular resolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
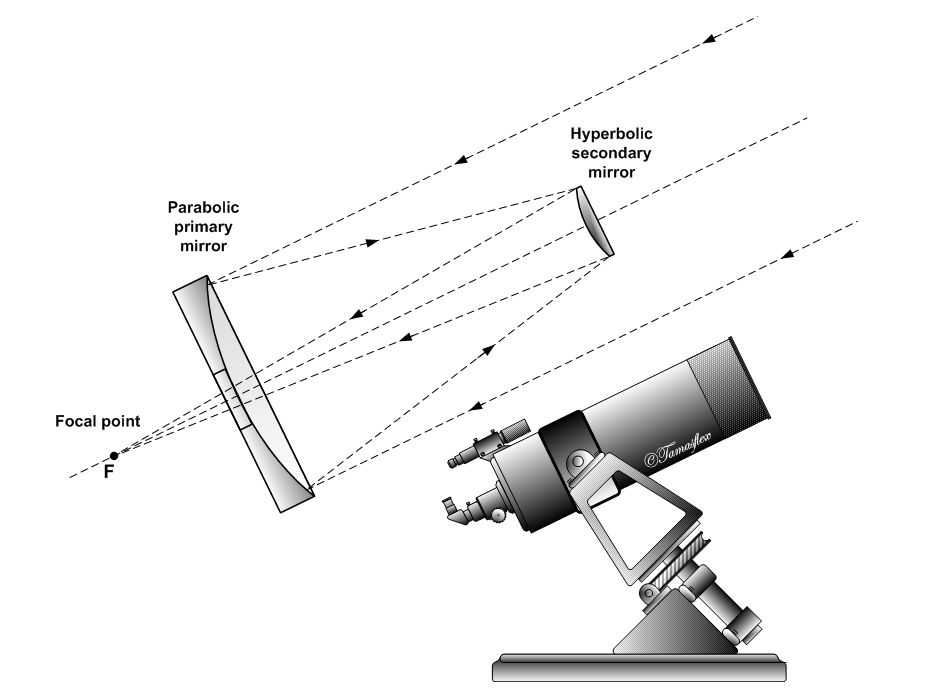
Cassegrain Telescope
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Waves
In fluid dynamics, gravity waves are waves in a fluid medium or at the interface between two media when the force of gravity or buoyancy tries to restore equilibrium. An example of such an interface is that between the atmosphere and the ocean, which gives rise to wind waves. A gravity wave results when fluid is displaced from a position of equilibrium. The restoration of the fluid to equilibrium will produce a movement of the fluid back and forth, called a ''wave orbit''. Gravity waves on an air–sea interface of the ocean are called surface gravity waves (a type of surface wave), while gravity waves that are the body of the water (such as between parts of different densities) are called '' internal waves''. Wind-generated waves on the water surface are examples of gravity waves, as are tsunamis, ocean tides, and the wakes of surface vessels. The period of wind-generated gravity waves on the free surface of the Earth's ponds, lakes, seas and oceans are predominantly b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation Theory
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the very early universe. Following the inflationary period, the universe continued to expand, but at a slower rate. The re-acceleration of this slowing expansion due to dark energy began after the universe was already over 7.7 billion years old (5.4 billion years ago). Inflation theory was developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s, with notable contributions by several theoretical physicists, including Alexei Starobinsky at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Alan Guth at Cornell University, and Andrei Linde at Lebedev Physical Institute. Starobinsky, Guth, and Linde won the 2014 Kavli Prize "for pioneering the theory of cosmic inflation". It was developed further in the early 1980s. It explains the origin of the large-scale structure of the cosmos. Quantum fluctuations in the microscopic inflationary region, magnified to cos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreground Radiation
Foreground and background or background and foreground may refer to: *Background, foreground, sideground and postground intellectual property, distinct forms of intellectual property assets *Background subtraction, a technique in image processing and computer vision by which an image's foreground is extracted for further processing *Figure–ground (perception), a humans' ability to separate foreground from background in visual images *Foreground-background, a scheduling algorithm that is used to control execution of multiple processes on a single processor *Foreground-background segmentation, a method for studying change blindness using photographs with distinct foreground and background scenery * Foreground detection, a concept in computer vision to detect changes in image sequences *Foreground and background in photography and cinematography, a principle important for **Depth of field, the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope detects a faint background glow that is almost isotropic, uniform and is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other astronomical object, object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The accidental Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s. The CMB is landmark evidence of the Big Bang scientific theory, theory for the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang cosmological models, during the earliest periods, the universe was filled with an Opacity (optics), opaque fog of dense, hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Rotation
The Faraday effect or Faraday rotation, sometimes referred to as the magneto-optic Faraday effect (MOFE), is a physical magneto-optical phenomenon. The Faraday effect causes a polarization rotation which is proportional to the projection of the magnetic field along the direction of the light propagation. Formally, it is a special case of gyroelectromagnetism obtained when the dielectric permittivity tensor is diagonal. This effect occurs in most optically transparent dielectric materials (including liquids) under the influence of magnetic fields. Discovered by Michael Faraday in 1845, the Faraday effect was the first experimental evidence that light and electromagnetism are related. The theoretical basis of electromagnetic radiation (which includes visible light) was completed by James Clerk Maxwell in the 1860s. Maxwell's equations were rewritten in their current form in the 1870s by Oliver Heaviside. The Faraday effect is caused by left and right circularly polarized wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization, and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly relativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an Optical telescope, optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an Human eye, eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolution. It is used in optics applied to light waves, in antenna (radio), antenna theory applied to radio waves, and in acoustics applied to sound waves. The colloquial use of the term "resolution" sometimes causes confusion; when an optical system is said to have a high resolution or high angular resolution, it means that the perceived distance, or actual angular distance, between resolved neighboring objects is small. The value that quantifies this property, ''θ,'' which is given by the Rayleigh criterion, is low for a system with a high resolution. The closely related term spatial resolution refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to space, which is directly connected to angular resolution in imaging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |